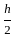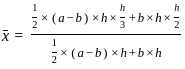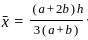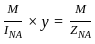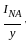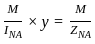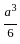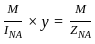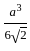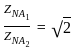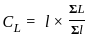HPCL Civil Engineer Mock Test - 2 - HPSC (Haryana) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HPCL Civil Engineer Mock Test - 2
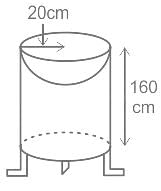
Payal made a bathing vessel for birds by placing a hemisphere on the upper end of a cylinder. The radius of the top of the circular shape is 20 CM and the height of the cylinder is 160 CM. Find the total curved area of the bird bath bowl.
A man lends out an amount of Rs. 25,000 into two parts. The first part of the money is lent out at 8% simple interest and the second part of the money is lent out at 8.5% simple interest. If total annual income of the man is Rs. 2031.25, then find how much money is lent out at the rate of 8.5%?
A bag contains 4 green, 5 blue, 2 red and 3 yellow balls. If eight balls are drawn at random, what is the probability that there are equal number of balls of each colour?
 and xy =
and xy = 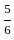 then the value of 8x3 + 27y3 is?
then the value of 8x3 + 27y3 is?
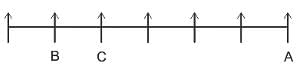
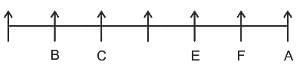
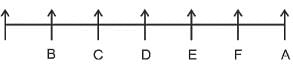
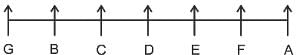
A, B, C, D, E, F, and G are 7 friends sitting in a single row facing North.
1. D is to the immediate right of C.
2. E and A are neighbors of F.
3. B is to the immediate left of C and in second place from the leftmost end.
4. A is at the rightmost end.
What is the position of E?
Select the most appropriate option that can substitute the underlined words in the given sentence.
The new restaurant is more better than the old one.
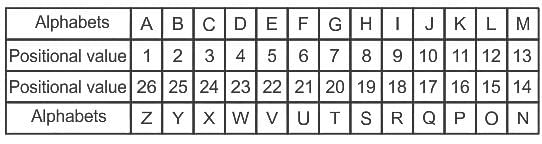
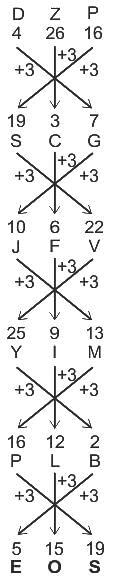
Select the number that will replace the question mark (?) in the following series.
DZP, SCG, JFV, YIM, PLB, ?
The following question consists of a statement followed by two arguments I and II. You have to decide which of the arguments is a STRONG argument:
Statement: Should new big industries be started in Mumbai?
Arguments:
I. Yes. It will create job opportunities.
II. No. it will further add to the pollution of the city.
The average weight of 6 members of a family is 25 kg, If one family member whose weight is 40 kg leave the group, then find the new average weight of remaining family members.
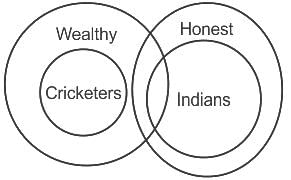
In this question, three statements are given, followed by two conclusions numbered I and II. Assuming the statements to be true, even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts, decide which of the conclusion(s) logically follows/follow from the statements.
Statements:
All cricketers are wealthy.
Some wealthy are Indians.
All Indians are honest.
Conclusions:
I. All Indians are cricketers.
II. Some cricketers are honest.
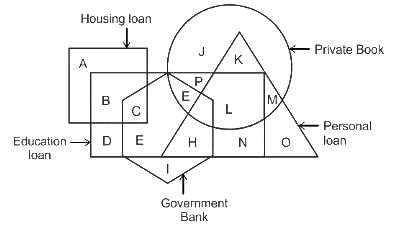
In the following figure, triangle represents personal loan, circle represents private bank, hexagon represents government bank, rectangle represents education loan and square represents housing loan.
What does letter ‘L’ represents?
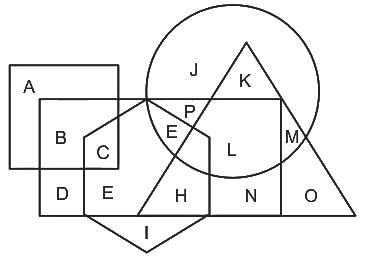
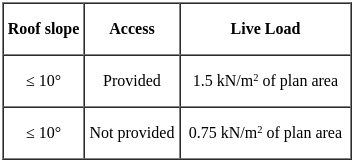
What will be the value of maximum shear force for the given beam in figure below?
Arrange the stages of construction of highway projects in the correct sequence:
1. Cleaning site of work or construction
2. Construction of drainage work such as culverts etc.
3. Earthwork
4. Construction of road and its shoulders
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
In survey work, the Total Station has to be handled properly. From the following options, mark the improper way of handling the total station:
The observed value of N from a standard penetration test conducted on a saturated sandy soil stratum is 33. The corrected value of N for dilatancy can be estimated as:
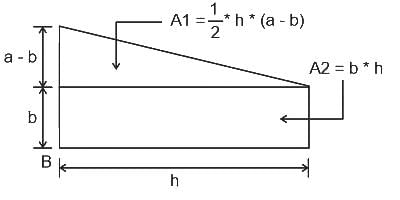
What is the value of x - coordinate from the left base point 'B' of the center of mass of the given figure below?

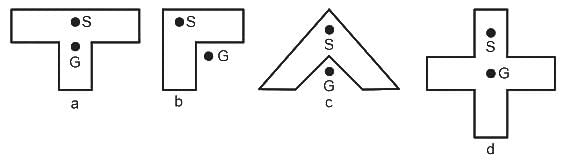
Identify the WRONG diagram. (G-Centroid, s-shear center)
A 4-hours rainfall in a catchment of 250 km2 produces rainfall depths of 6.2 cm and 5.0 cm in successive 2-hour unit periods. Assuming the φ index of the soil to be 1.2 cm/hour, the runoff volume in ha-m will be
The bending moment diagram of a simply supported beam AC is shown in figure. The load acting on the beam is:
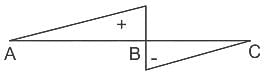
The ratio of the flexural strengths of two beams of square cross section, the first beam being placed with its top and bottom sides horizontal and second beam being placed with one diagonal horizontally, is:



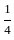 = Rs. 6250
= Rs. 6250
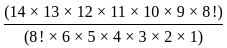 = 3003
= 3003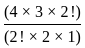 ×
× 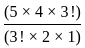
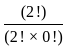

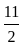 and xy =
and xy = 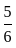
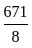
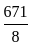

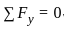
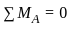
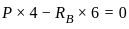
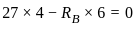
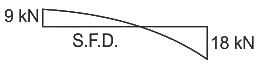
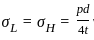
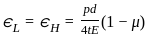
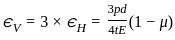
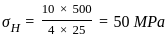
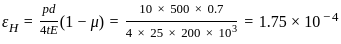
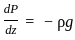
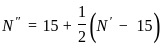
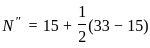
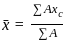
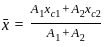
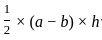 ,
,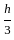 ,
, ,
,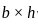 ,
,