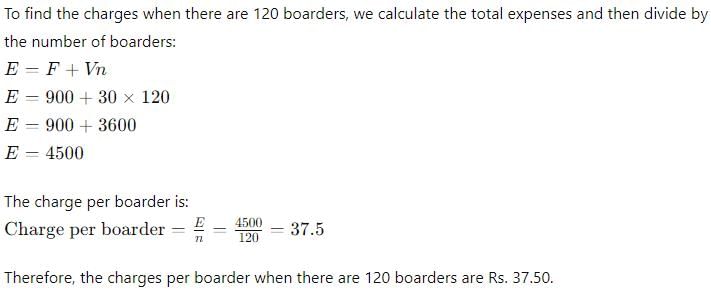Important Questions Test: Ratio & Proportion- 3 - CAT MCQ
14 Questions MCQ Test - Important Questions Test: Ratio & Proportion- 3
Shalaj and Associates, a shoe-manufacturing company, has three machines producing shoes. If machine X produces l/4th as many as machine Y produces in the same time, and machine Y produces twice as many as machine Z produces in the same time, then during a fixed time, what fraction of the total number of shoes is produced by machine Z?
The inhabitants of Hawaii Island are taxed in a peculiar manner. They have to pay a fixed sum irrespective of their income strata. In addition to this they have to pay an amount which is proportional to the excess of their salary over Rs 50,000. Mr Kalyan pays a total tax of Rs 6,200 when his annual salary is Rs 60,000 and his wife Mrs. Kalyan pays a total tax of Rs 7,700 when her annual salary is Rs 75,000. What is the yearly salary of Mr Ajay who pays an annual tax of Rs 8,200?
The speed of man while walking, running and driving are in the ratio of 1:3:9. If he travels equal distance while walking, running and driving, what is the ratio

The time period of oscillation T for a pendulum is given
where l is the length of the pendulum and g is the acceleration due to gravity, ‘k’ is any const. If ‘k’ and ‘g’ remain unchanged under any condition, what should be the percentage change in l such that the time period T increases by 10%?
Price of each article of type P, Q, and R is Rs. 300, Rs. 180 and Rs. 120 respectively. Suresh buys articles of each type in the ratio 3:2:3 in Rs. 6480. How many articles of type Q did he purchase?
Read the passage below and solve the questions based on it.
In a class, every student plays exactly one of the following games—squash, table tennis, hockey, handball, cricket. Exactly 1/ 12th of the girls and 1/8th of the boys play- squash. 1/15th of the girls and 1/6th of the boys play hockey, 1/4th of the girls and 1/12th of the boys play handball. 1/5th of the girls and 3/8th of the boys plays table tennis and the remaining boys and girls play cricket. The total strength of the class is less than 120
Q. How many girls are there in the class?
Read the passage below and solve the questions based on it.
In a class, every student plays exactly one of the following games—squash, table tennis, hockey, handball, cricket. Exactly 1/ 12th of the girls and 1/8th of the boys play- squash. 1/15th of the girls and 1/6th of the boys play hockey, 1/4th of the girls and 1/12th of the boys play handball. 1/5th of the girls and 3/8th of the boys plays table tennis and the remaining boys and girls play cricket. The total strength of the class is less than 120
Q. Which of the following cannot be the ratio of boys and girls in the class?
The expenses of a hostel are partly fixed and partly variable with the number of boarders. When there are 50 boarders the charge is Rs. 48 per head and when there are 30 boarders the charge is Rs. 60 per head. Find the charges when there are 120 boarders?
There are two drums, each containing a mixture of paints A and B. In drum 1, A and B are in the ratio 18 : 7. The mixtures from drums 1 and 2 are mixed in the ratio 3 : 4 and in this final mixture, A and B are in the ratio 13 : 7. In drum 2, then A and B were in the ratio
The scores of Amal and Bimal in an examination are in the ratio 11 : 14. After an appeal, their scores increase by the same amount and their new scores are in the ratio 47 : 56. The ratio of Bimal’s new score to that of his original score is
Raju and Lalitha originally had marbles in the ratio 4:9. Then Lalitha gave some of her marbles to Raju. As a result, the ratio of the number of marbles with Raju to that with Lalitha became 5:6. What fraction of her original number of marbles was given by Lalitha to Raju?
Consider three mixtures - the first having water and liquid A in the ratio 1:2, the second having water and liquid B in the ratio 1:3, and the third having water and liquid C in the ratio 1:4. These three mixtures of A, B, and C, respectively, are further mixed in the proportion 4: 3: 2. Then the resulting mixture has
If a, b, c are three positive integers such that a and b are in the ratio 3 : 4 while b and c are in the ratio 2:1, then which one of the following is a possible value of (a + b + c)?
The marks scored by a student in three subjects are in the ratio of 4 : 5 : 6. If the candidate scored an overall aggregate of 60% of the sum of the maximum marks and the maximum marks in all three subjects is the same, in how many subjects did he score more than 60%?