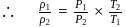Test: Kinetic theory-Pressure and Energy of gas (28 Sep) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Kinetic theory-Pressure and Energy of gas (28 Sep)
The expansion of unit mass of a perfect gas at constant pressure is shown in Fig. Here
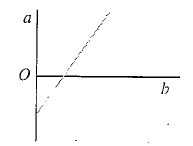
A gas is heated at a constant pressure. The fraction of heat supplied used for external work is
Energy of all molecules of a monatomic gas having a volume 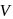 and pressure
and pressure 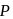 is
is 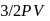 . The total translational kinetic energy of all molecules of a diatomic gas at the same volume and pressure is
. The total translational kinetic energy of all molecules of a diatomic gas at the same volume and pressure is
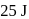 of work when it expands at constant pressure. The heat absorbed by gas is
of work when it expands at constant pressure. The heat absorbed by gas is
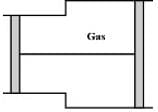
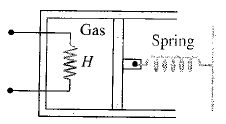
A gas is filled in the cylinder shown in the figure. The two pistons are joined by a string. If the gas is heated, the pistons will
An ideal monatomic gas is confined in a cylinder by a spring-loaded piston of cross-section 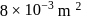 . Initially the gas is at
. Initially the gas is at 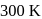 and occupies a volume of
and occupies a volume of 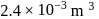 and the spring is in a relaxed state. The gas is heated by a small heater coil
and the spring is in a relaxed state. The gas is heated by a small heater coil 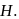 The force constant of the spring is
The force constant of the spring is 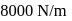 and the atmospheric pressure is
and the atmospheric pressure is 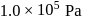 . The cylinder and piston are thermally insulated The piston and the spring are massless and there is no friction between the piston and cylinder. There is no heat loss through heater coil wire leads and thermal capacity of the heater coil is negligible. With all the above assumptions, if the gas is heated by the heater until the piston moves out slowly by
. The cylinder and piston are thermally insulated The piston and the spring are massless and there is no friction between the piston and cylinder. There is no heat loss through heater coil wire leads and thermal capacity of the heater coil is negligible. With all the above assumptions, if the gas is heated by the heater until the piston moves out slowly by 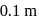 , then the final temperature is
, then the final temperature is
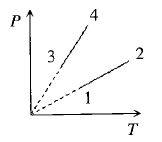
Pressure versus temperature graph of an ideal gas of equal number of moles of different volumes is plotted as shown in Fig. Choose the correct alternative.
Molar specific heat at constant pressure 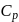 is related to internal energy
is related to internal energy 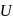 and absolute temperature
and absolute temperature 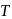 as
as 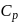 is equal to
is equal to
Forty calories of heat is needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of an ideal monatomic gas from 20∘C to 30∘C at a constant pressure. The amount of heat required to raise its temperature over the same interval at a constant volume (R = 2calmol−1 K−1) is
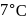 and a barometer reads
and a barometer reads 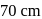 of
of 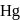 . At the bottom of the mountain these read
. At the bottom of the mountain these read 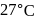 and
and 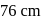 of
of 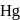 , respectively. Ratio of density of air at the top with that of bottom is
, respectively. Ratio of density of air at the top with that of bottom is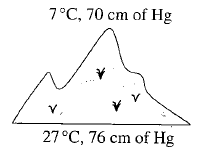


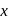 -axis and negative intercept on the
-axis and negative intercept on the 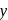 -axis.
-axis.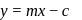 ...(i)
...(i)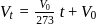
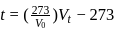 ...(ii)
...(ii)
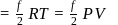
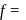 degree of freedom
degree of freedom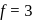
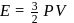
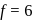 (given), therefore
(given), therefore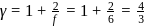
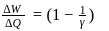
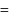 Pressure
Pressure 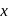 Area). So the piston will move towards the right.
Area). So the piston will move towards the right.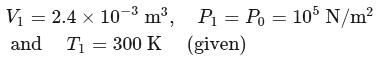
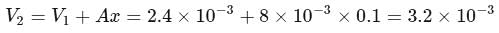
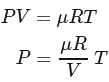
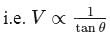

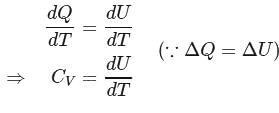
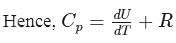
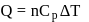
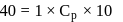
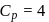
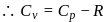

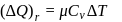
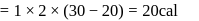
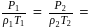 constant
constant