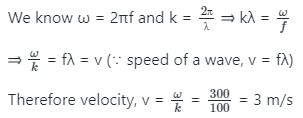Test: Waves - Transverse ,longitudinal & Displacement relation in a progressive(15 Oct) - PAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Waves - Transverse ,longitudinal & Displacement relation in a progressive(15 Oct)
Waves associated with moving protons, electrons, neutrons, atoms are known as
Maximum destructive inference between two waves occurs when the waves are out of the phase by
In what types of waves can we find capillary waves and gravity waves?
To the nearest order of magnitude, how many times greater than the speed of sound is the speed of light?
The angular frequency 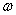 is related to the time period T by
is related to the time period T by
Linear density of a string is 1.3 x 10−4 kg/m and wave equation is y = 0.021 sin (x + 30t). Find the tension in the string when x is in meter and t is in second.
The equation of a simple harmonic wave is given by y = 5 sin (50πt – πx/2); where x and y are in meter and time is in second. The period of the wave in second will be:
The equation of SHM is y = a sin (3πnt + α) Then its phase at time t is:
A transverse wave passing through a string with equation y = 3 sin (4t - π/6) . Here ‘y’ is in meter and ‘t’ is in seconds. Calculate the maximum velocity of the particle in a wave motion.
Equation of a wave is y = 15 x 10-2 sin (300t – 100x) where x is in meter and t is in seconds. The wave velocity is :



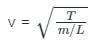
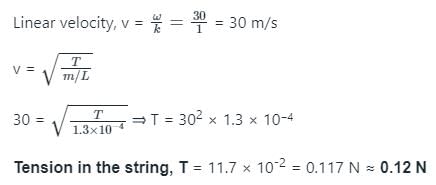
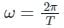
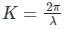

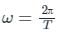
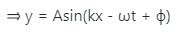
 is the angular frequency (ω = 2πf).
is the angular frequency (ω = 2πf).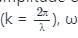 is the angular frequency (ω = 2πf).
is the angular frequency (ω = 2πf).