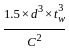BPSC AE Civil Paper 5 (Civil) Mock Test - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 5 (Civil) Mock Test - 2
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. A steel structure designer can guarantee the safety of the structure.
2. Working stress method of design of steel structures offers a safer and economical structure.
3. Strength and serviceability of a structure cannot be predicted on account of several unforeseen factors.
A thin-walled spherical shell is subjected to an internal pressure of 10 MPa. The shell has a uniform wall thickness of 25 mm and a diameter of 500 mm. Take E = 20 GPa and μ = 0.3.
Assertion (A): Trusses comprise triangular figures.
Reason (R): A pin-jointed stable figure is a triangle.
Choose the correct combination for the given Table:
Which of the following failure is not a type of failure in tension members in steel structures?
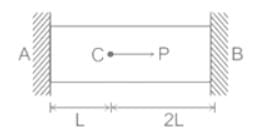
A straight bar which is fixed at the ends A and B and having elastic modulus (E) and cross-sectional area (A), is subjected to a load P = 120 N at C as shown in the figure. The reactions at the ends are:
As per IS 875 part-2, imposed loads on balconies in dwelling houses shall be ________ Consider type of occupancy as residential building.
In the moment distribution method, the sum of distribution factors for all the members meeting at a joint is always:
The Muller Breslar principal in structural analysis is used for
In which of the following sections will the position of actual neutral axis (n) shift above the critical neutral axis (nc )i.e. n < nc and steel is fully stressed and concrete is under stressed?
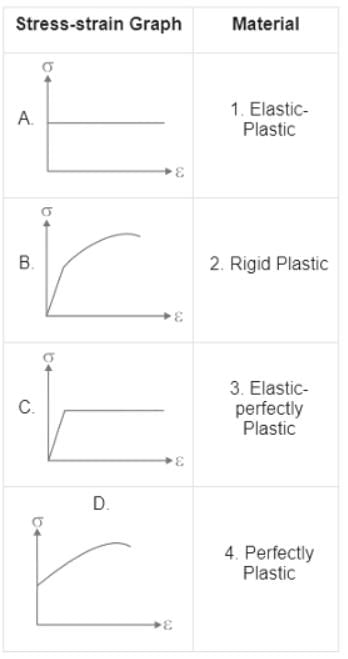
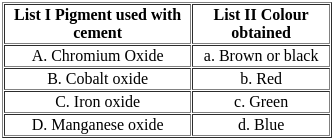
Match List - I with List - II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
When the air permeability method is used to determine the fineness of cement, the fineness is expressed as
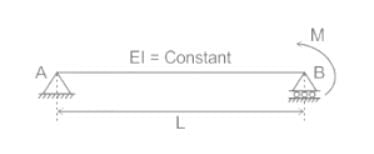
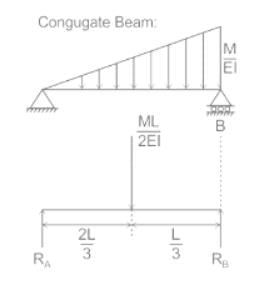
The ratio of θA and θB for beam as shown will be:-
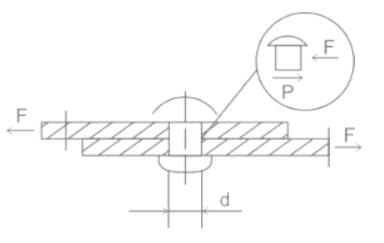
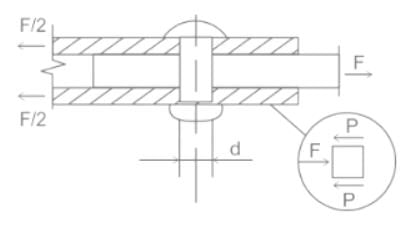
Determine the single shear stress induced in a circular pin which has an area of 115 mm2 undergoing a tension force of 12 kN.
If σcbc is permissible compressive stress of centre in bending, then modular ratio is given by -
The utilization of concrete in tension zone of prestressed concrete member saves concrete ranging between
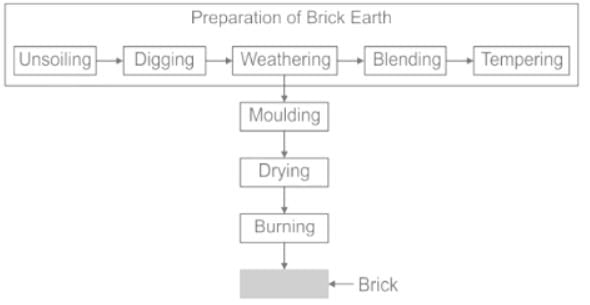
Which of the following is not one of the four distinct operations involved in bricks manufacturing?
The type of bond provided in brick masonry for carrying heavy loads is:
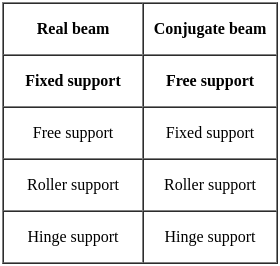
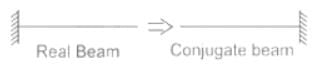
The imaginary beam of same span as the original beam loaded with M/EI diagram of the original beam, such that the shear force and bending moment at a section will represent the rotation and deflection at that section in the original beam ________.
Horizontal stiffness coefficient ( K11) of a bar ‘AB’ is given by –
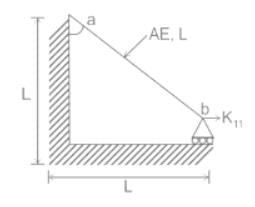
(Where A is cross section area and E is Young’s Modulus)
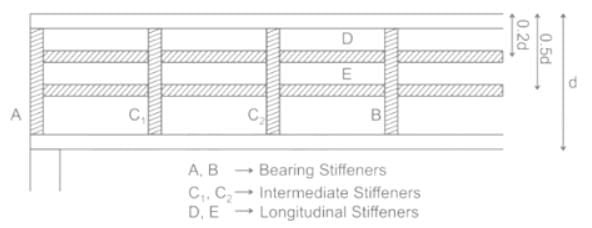
Where the horizontal stiffeners are provided 'd' in mm shall be taken as a clear distance between the horizontal stiffeners and tension flange. These vertical stiffeners shall be designed so that I is not less than
When Timber is subjected to dry rot, ________ is an excellent prevention


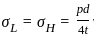
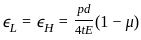
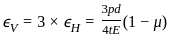
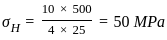
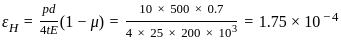

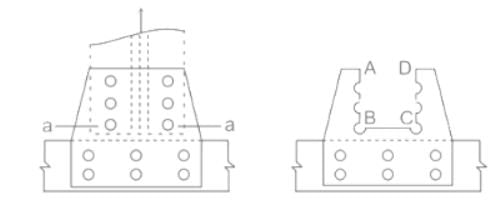
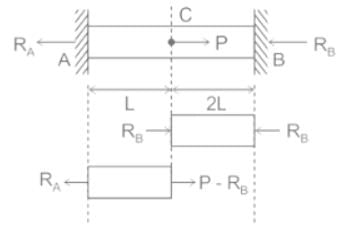
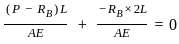
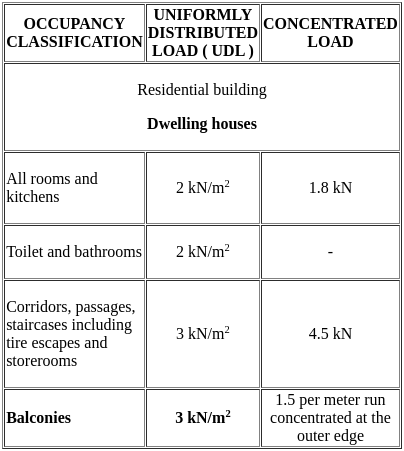
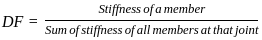

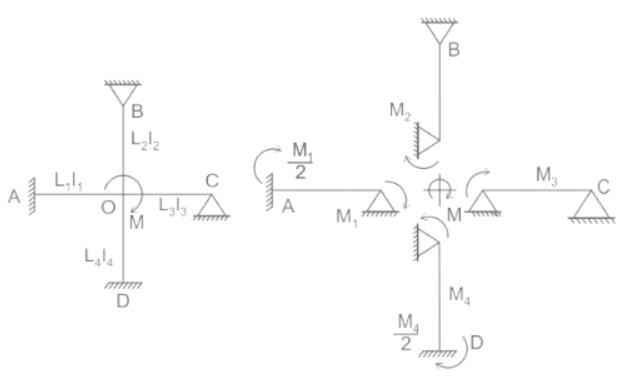

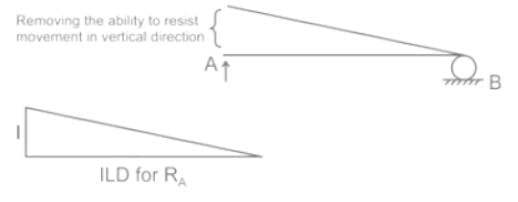
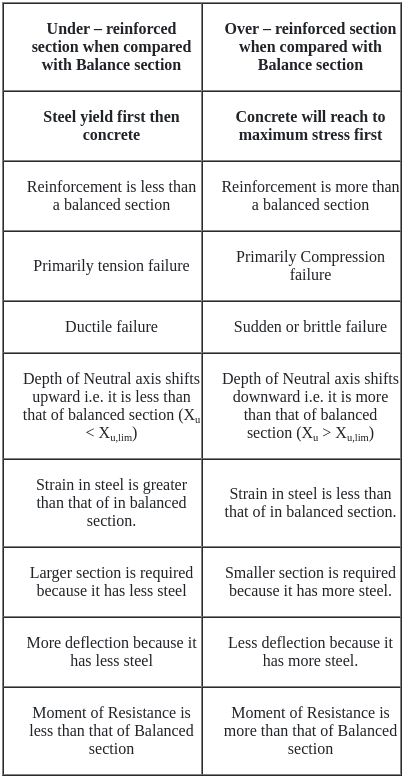
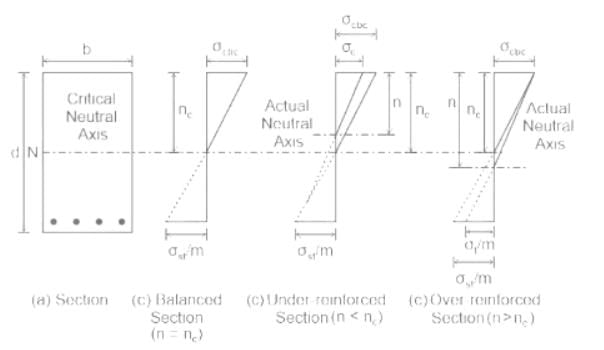
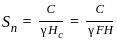
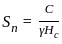
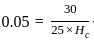
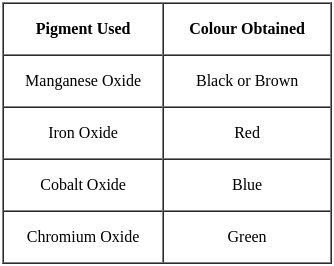
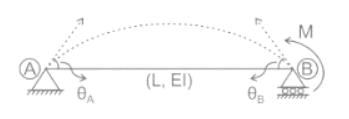
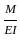 diagram of real beam.
diagram of real beam.
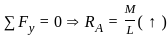

 (clockwise)
(clockwise)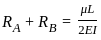

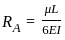
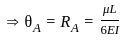
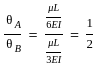

 .
.
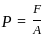 , the average shearing stress is
, the average shearing stress is 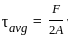
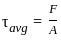
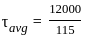
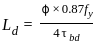
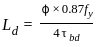
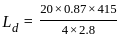 = 645
= 645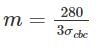
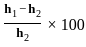
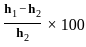
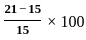
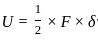
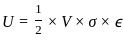 ; V is the volume of material.
; V is the volume of material. 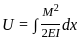
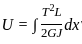
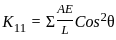

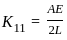
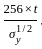 , where t is the thickness of the section )
, where t is the thickness of the section )