UGC NET Paper 1 Mock Test - 3 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 1 Mock Test - 3
A teacher designing a lesson on cultural diversity for a college class in anthropology plans to:
All the parts of this car are made of metal. Therefore, the whole car is made of metal. Which of the following fallacies is committed in this argument?
Pesticides can disrupt ecosystems and harm biodiversity. Which of the following impacts is MOST likely to have a negative long-term effect on people in rural communities?
Identify the fallacy committed in the argument.
All men who understand women are potentially perfect husbands.
All potentially perfect husbands are men of infinite patience.
Therefore, some men of infinite patience are men who understand women.
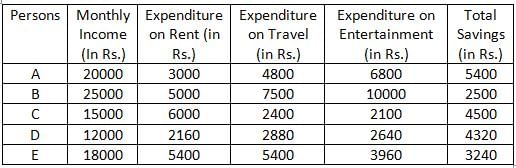
If the yearly savings of C increases by 20%, then yearly savings of C is how much more/less than the yearly expenditure of B on Rent?
What is the difference between the yearly savings of A and B together and C, D, and E together?
What is the sum of yearly expenditure on Entertainment of B, yearly expenditure on Travel of D and yearly savings of E?
A. Delayed means of Communication
B. Heterogeneous Audience
C. Instant Feedback
D. Intermediary Channels
E. Wide and Vast Area.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In Indian logic, an argument is traditionally articulated in a five-part form known as:
According to NEP 2020, a critical objective of education would be to enhance among learners key 21st-century skills namely ________,________, _________, and _________.
A. critical thinking
B. vocational skills
C. creativity
D. cyber security awareness
E. multi-disciplinary awareness
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The correct sequence of the following steps in the communication process is:
A. Decoding
B. Feedback
C. Encoding
D. Transmission
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The material and the efficient cause, according to Samkhya philosophy, are related as
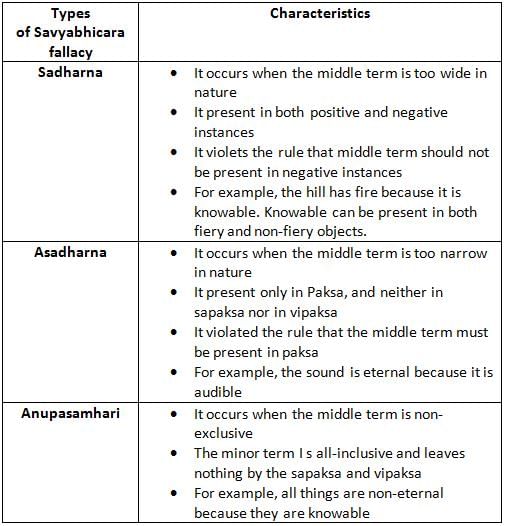
From the following identify those which illustrate the fallacy of the irregular middle ?
A. Ashrayasidha
B. Asadharna
C. Vyapyatvasidha
D. Sadharna
E. Anupasamhari
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: Computer based trainings (CBTs) are learning activities that a trainee can study at his own pace.
Statements II: CBTs typically present content in a linear structure.
In the light of the above statements, Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
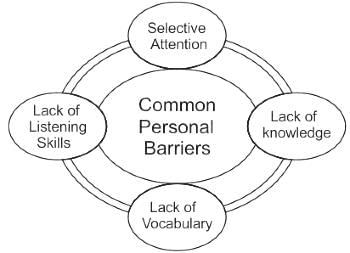
Which of the following is a physical/environmental barrier to communication?
An entity that has the power to express some meaning is termed as ________ in Indian logic.
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : The example (udahāran) is a special feature of the Nyāya syllogism and it illustrates the truth that the universal major premise is the result of a real induction.
Statement II : Induction in Nyāya conception of inference is based on the law of causation and induction and deduction cannot really be separated.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
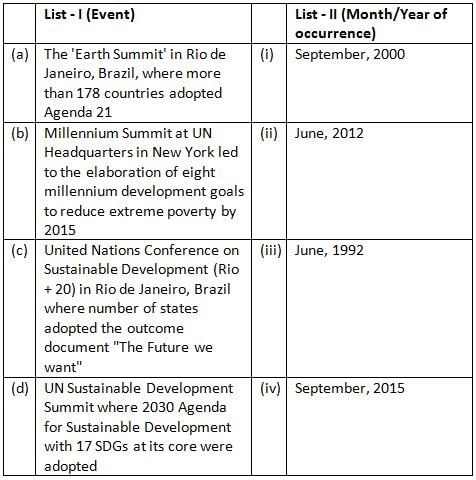
Match items of List-I with the items of List-II and indicate your answer by selecting the correct code.
Assertion (A): Mass communication is more effective in reaching a large audience than interpersonal communication.
Reason (R): Mass communication utilizes mass media channels to disseminate information to a broad range of people, while interpersonal communication is limited to face-to-face interactions between two individuals.
Read the given statement and the arguments carefully and select the appropriate answer from the given options.
Statement:
“If waste management capabilities of Hospital X are dealt with, we will definitely win the ‘excellence in service’ award for year 22-23.” One of the board of directors from Hospital X.
Arguments:
I. In four separate incidents in the year 22-23, 15 patients lost their lives and 46 were injured due to various incidents such as fire breakout in ICU, lack of oxygen etc.
Il. Hospital A located in the nearby city has won ‘excellence in service’ award for a record five times.