Test: Structural Analysis & Steel Structures- 1 - GATE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Structural Analysis & Steel Structures- 1
A cantilever beam AB, fixed at the end A and carrying a load W at the force end B, is found to deflect by δ at the midpoint of AB. The deflection of B due to load W/2 at the midpoint will be
Due to some point load anywhere one fixed beam, the maximum free bending moment is M. The sum of fixed end moments is?
The bending moment diagram for an overhanging beam is shown in the below figure
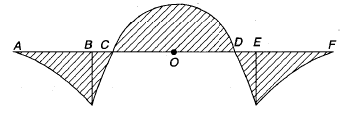
The points of contra-flexure for the above beam are
A fixed beam of uniform section is carrying a point load at its midspan. When the moment of inertia of the middle half length is reduced to half its original value, then the fixed and moments
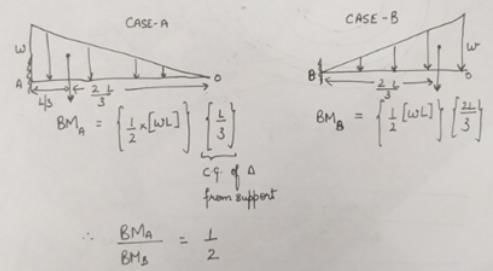
In case of a cantilever beam carrying uniformly varying load, the ratio of the maximum bending moment at free end for conditions, that is, when the load increase from zero at free end to w at fixed end and to that when the load increase from zero at fixed end is
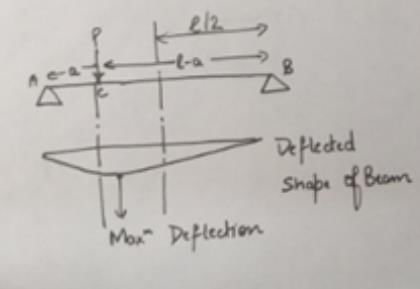
A simply supported beam is subjected to an eccentric concentrated load. Where does the maximum deflection of the beam due to the applied load occur?
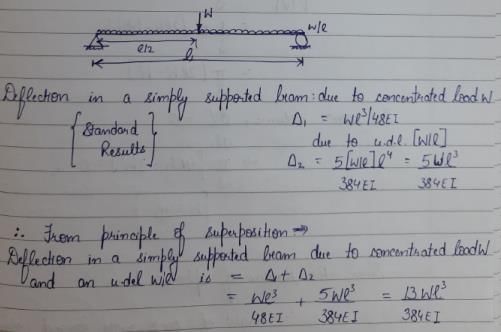
A simply supported beam AB of span 1 has a uniform cross section throughout. It carries a central concentrated load W and another load that is uniformly distributed over the entire span, its total magnitude being W. The minimum deflection in the beam is
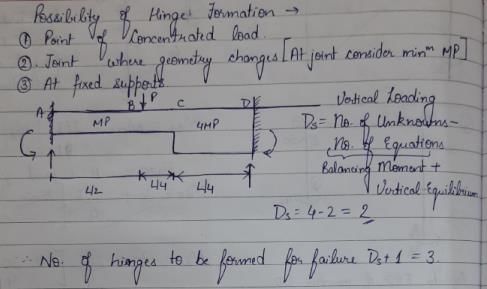
For the beam shown below, the collapse load P is given by
The shear force diagram for the portal frame loaded as shown below is
The influence line diagram for the force in members of the truss shown below is
What is the carry-over factor from A to B while using moment distribution for analyzing the given beam?
The influence line for force in member BC is
What is the value of flexibility coefficient f12 for the continuous beam shown below?
What is the ordinate of influence line at B for reaction RD in the figure below?
What is the value of vertical reaction at A for the frame shown below?