Test: Prokaryotic Cells - ACT MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Prokaryotic Cells
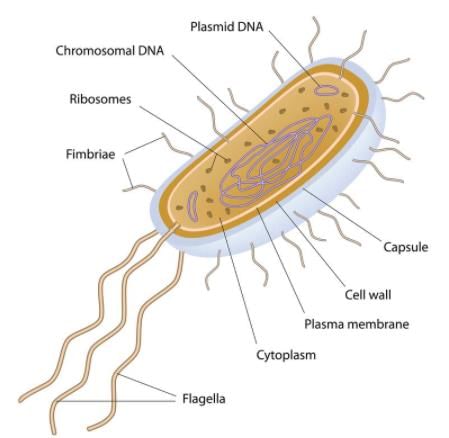
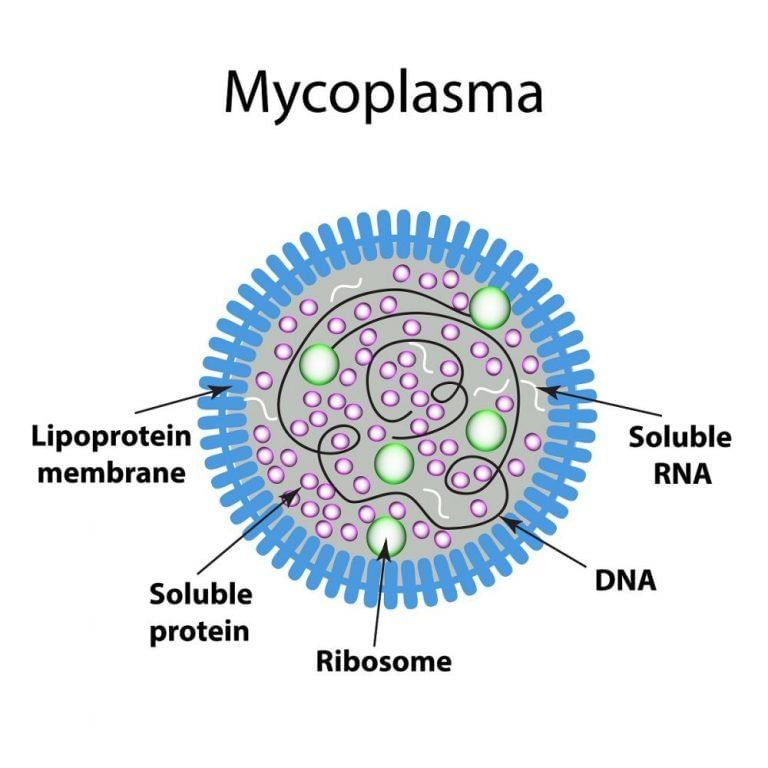
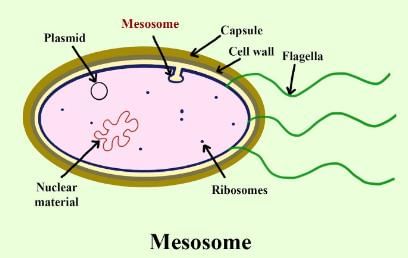
Which cell organelle is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells are different from prokaryotic cells in having:
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
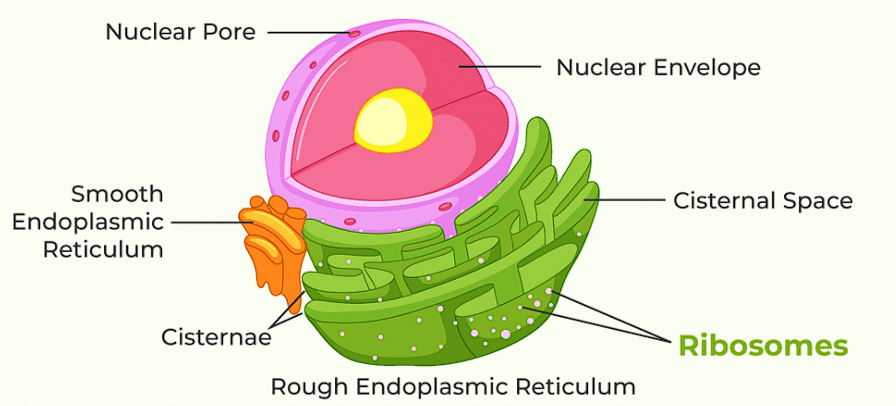
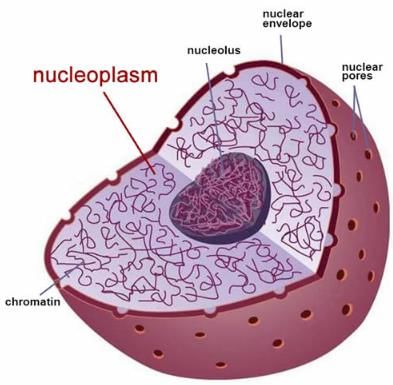
Assertion: Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles.
Reason: Prokaryotic cells lack membrane bound organelles.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion: Ribosomes are non-membrane bound organelles found in the prokaryotic cells only.
Reason: Ribosomes are present only in the cytoplasm.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion: Eukaryotic cells have more DNA than prokaryotic cells.
Reason: Eukaryotes are genetically more complex than prokaryotes.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
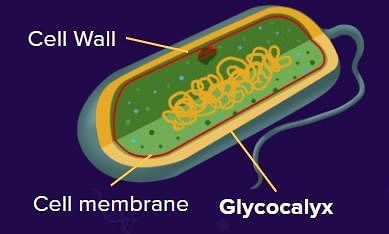
What is the primary function of the cell envelope in prokaryotic cells, particularly bacterial cells?
How does the composition of the glycocalyx vary among different bacteria?
What are the three parts that compose a bacterial flagellum?