Test: Transcription, Genetic Code & Types of RNA - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Transcription, Genetic Code & Types of RNA
Removal of the introns and joining of the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called _________.
Select the incorrectly matched pair.
Which out of the following statements is incorrect?
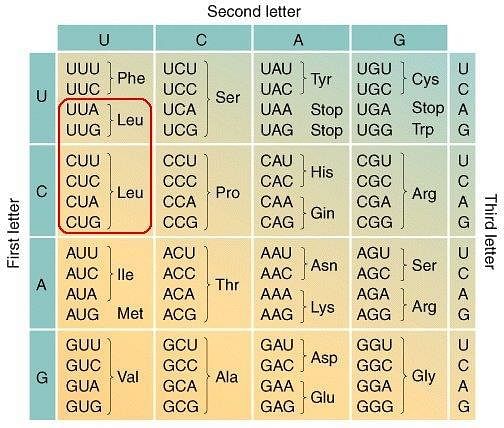
Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the genetic code is
The mutations that involve addition, deletion or substitution of a single base pair in a gene are referred to as
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given:
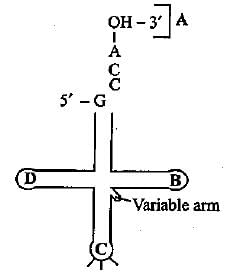
Identify the labels A, B, C and Din the given structure of tRNA and select the correct option.
During expression of an operon, RNA polymerase binds to
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given :
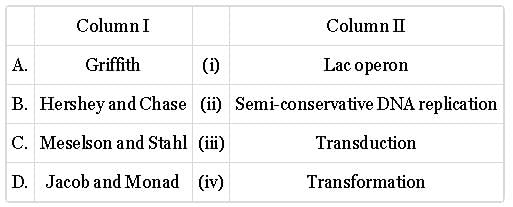
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
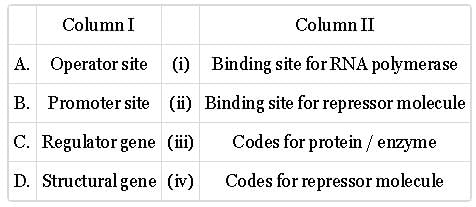
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given:
The given figure shows lac operon and its functioning. Select the option which correctly labels A, B, X, Y and Z.
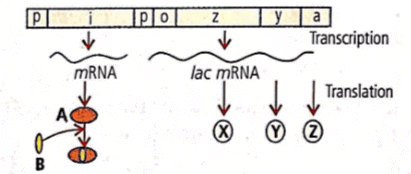
Regulation of gene expression occurs at the level of
During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called _________.
The coding segment of DNA is called _________.
Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon hence, the code is:
Out of 64 codons, the number of codons with GGG is:
Control of gene expression takes place at the level of _________.
The amino acid attaches to the tRNA at its:
The portion of DNA which contains information for an entire polypeptide is called:
The following code codes for which of the amino acids respectively?
AUG and GUG
What is the role of the anticodon loop in tRNA?



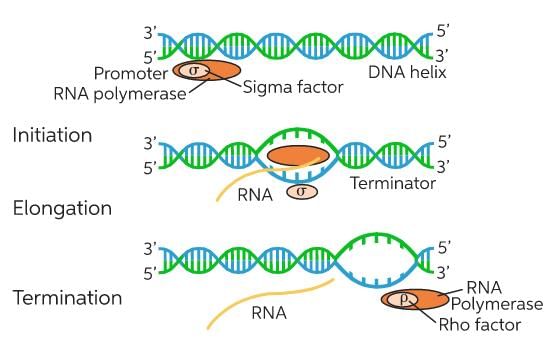
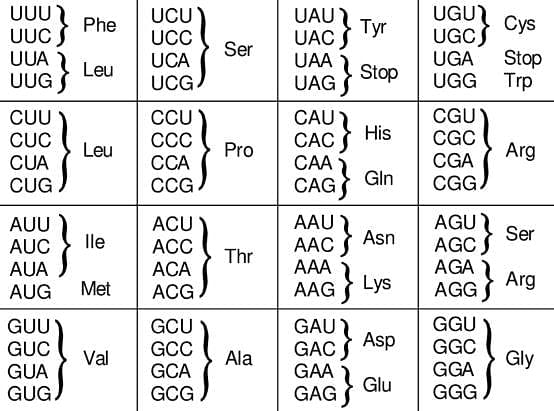
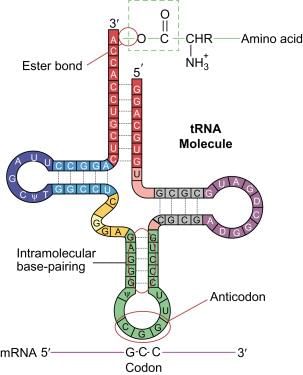
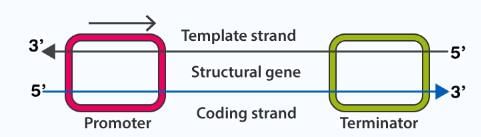 Fig: DNA transcription unit
Fig: DNA transcription unit