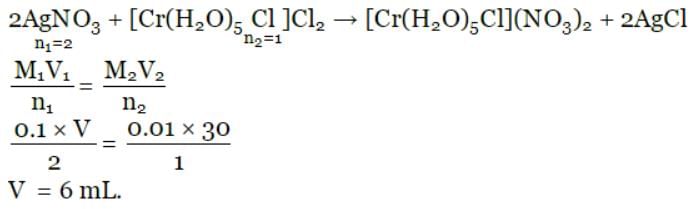Test: Coordination Chemistry- 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Coordination Chemistry- 1
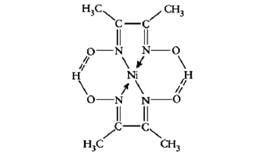
Which of the following represents a chelating ligand
The complex compounds which result from the coordination of carbon monoxide are known as
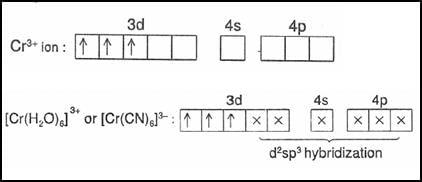
In the complexes [Fe(CN)6]3– and [Co(en)3]3+, the coordination number of iron and cobalt are respectively (en = ethylenediamine):
The oxidation number, coordination number and magnetic moment in the following complex, [Cr(C2O4)2 (NH3)2]- is:
Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series: Ti4+,V2+,Mn3+,Cr3+
(Atomic numbers: Ti=22,V=23,Mn=25,Cr=24)
Which ion is most stable?
Which of the following is a spin paired complex ion?
Compound ‘X’ has the molecular formula CrCl2Br.6H2O. It can show which type of isomerism:
(I) Hydrate isomerism
(II) Ionization isomerism
(III) Geometrical isomerism
(IV) Optical isomerism
What is the change in the oxidation state of cobalt in the following reaction?
[Co(NH3)4 Cl2]+ + H2O → [Co(NH3)4 (H2O)Cl]2+ + Cl–
The first-row transition metal complexes having tetrahedral geometry are high–spin due to:
The zero magnetic moment of octahedral K2NiF6 is due to:
What is the spin only magnetic moment value in (Bohr Magneton units) of Cr(CO)6?
The volume (in mL) of 0.1 M AgNO3 required for complex precipitation of chloride ions present in 30 mL of 0.01 M solution of [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2, as silver chloride is close to:
Which of the following elements do not form a complex with EDTA?
When EDTA solution is added to Mg2+ ion solution, then which of the following statements is not true?
The total number of geometrical isomers for the complex [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)(NH3)] is:
Which one the following octahedral complexes will be distorted:
The compound which exhibits Jahn-Teller distortion is: