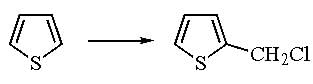Test: Heterocyclic Level - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Heterocyclic Level - 1
The heterocyclic diene employed in cyclo – addition reactions is:
Furan on prolonged heating with dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate yields:
The structures of the products A and B formed in the above reaction scheme respectively are:
The decreasing order of the reactivity of the following compounds towards electrophiles is:
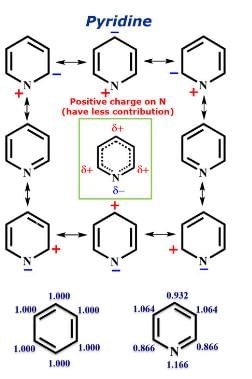
Pyridine undergoes electrophilic nitration at elevated temperature to given the following as a major product:
A pyridine derivative (P) reacts with (Y). (Y) can be a free radical, cation or anion. The structure of intermediate (Q) formed in the reacts is given below. (P) and (Y) respectively are:
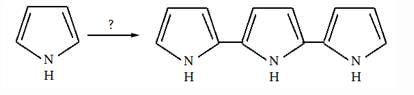
Pyrrole + PhMgBr → E + F
E + MeCl → G + H
F + MeCl → no reaction without a catalyst.
The structure of products E–H, respectively are:
Chose the correct answer from the following four choices.
Statement: Pyridine is more basic than pyrrole.
Reason: The nitrogen in pyrrole carries a proton while the nitrogen in pyridine does not.
Assertion: Nitrogen in trigonal geometry are generally more basic than nitrogens in a tetrahedral geometry.
In the following sequence of reactions, the major product Q is:
What will be the reagent used for the completion of the following reaction?
The correct order of the basicity of the following compound is:
Identify the major Product P in the following two–step reaction:
Match the structures in List–I with their correct names in List–II.
Thiophene reacts with HCHO in presence of aqueous HCl to give:
The reaction of 2-methylfuran with DMF-POCl3 would give:
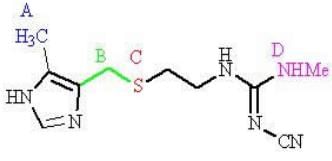
Two regions of cimetidine are susceptible to metabolism. Which regions?