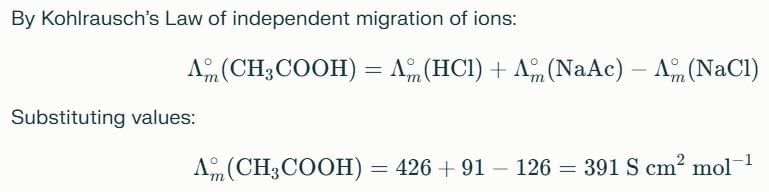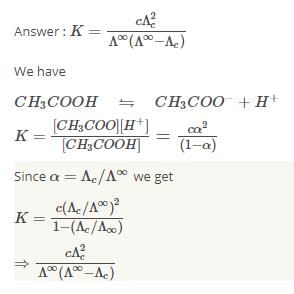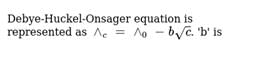Test: Conductance - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Conductance - 1
The cell constant of a conductivity cell is defined as:
Where l = distance between electrodes and A = area of cross-section of each of the electrodes
Molar conductivity is defined as:
Where k = conductivity, G = conductance, l = distance between two electrodes and Vm = volume of solution containing 1 mol of electrolyte
For a dilute solution of a strong electrolyte, the variation of molar conductivity with concentration is given by:
Which of the following ion is expected to have least value of molar conductivity at infinite dilution in an aqueous solution:
The degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte is given by:
Which of the following ion has highest molar conductivity at infinite dilution in an aqueous solution:
The equilibrium constant of acetic acid in an aqueous solution of concentration C is given by
Equivalent conductivity of Fe2(SO4)3 is related to molar conductivity by the expression:
If x is the specific resistance of the electrolyte solution and y is he molarity of the solution, then is given by:
When a conductance cell was filled with a 0.0025 M solution of K2SO4, its resistance was 326 Ω. The specific conductance of the solution, if cell constant is 4.
Equivalent conductance of 0.1 M HA (weak acid) solution is 10 cm2 equivalent–1. The pH of HA solution is(molar conductivity at infinite dilution is 200).
For HCl solution at 25ºC, the equivalent conductivity at infinite dilution is 425 Ω-1 cm2 eq-1. The specific conductance of a solution of HCl is 3.825 Ω-1 cm-1. If the apparent degree of dissociat ion is 90%, the normality of solution is
The correct relation which depicts the Debye-Huckel Onsager Theory for strong electrolytes is:
The unit of A in Debye-Huckel-Onsager equation for strong electrolytes is:
Which of the following solutions will show the minimum value of transference number of Cl–1 ions: