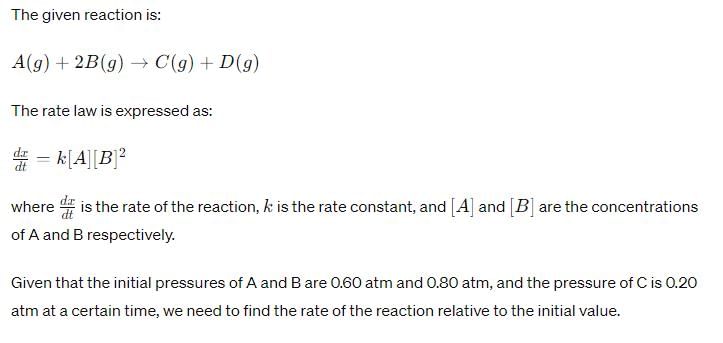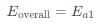Test: Chemical Kinetics - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chemical Kinetics - 1
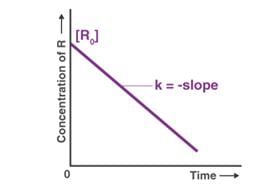
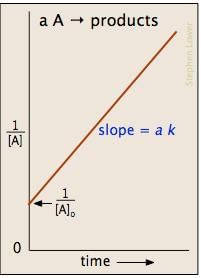
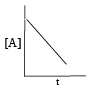
For which of the following remarks the concentration of a reactant decreases linearly with time. What is the order of the reaction?
Consider the unimolecular reaction: A(g) → products, were made:
(I) The reaction is second order at low pressure and become first order at high pressure.
(II) The reaction is first order at low pressure and become second order at high pressure.
(III) The reaction is zero order.Which of the fo llowing is correct?
(II) The reaction is first order at low pressure and become second order at high pressure.
(III) The reaction is zero order.Which of the fo llowing is correct?
Examine the following first order consecutive reactions. The rate constant (in s-1 units) for each step. Is given above the arrow mark:
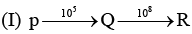
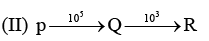
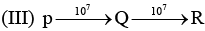
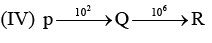
Steady–state approximation can be applied to.
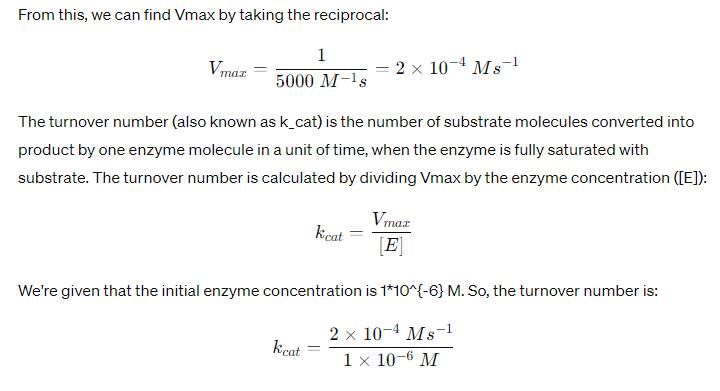
In the Lineweaver–Burk plot of (initial rate)–1 vs. (initial substrate concentration) –1 for an enzyme catalyzed reaction following Michaelis-Menten mechanism, the y–intercept is 5000 M–1 s. If the initial enzyme concentration is 1*10-6M, then turnover number is:
For the first order reactionAfter two average lives, concentration of the reactant is reduced to:
Vmax and Km for an enzyme catalyzed reaction are 2.0 * 10-3 Ms -1 and 1.0 * 10-6 M, respectively. The rate of the reaction when the substrate concentration is 1.0 * 10-6 M is
Experimentally determined rate law for the chemical reaction,
The rate determining step consistent with the rate law is:
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by about
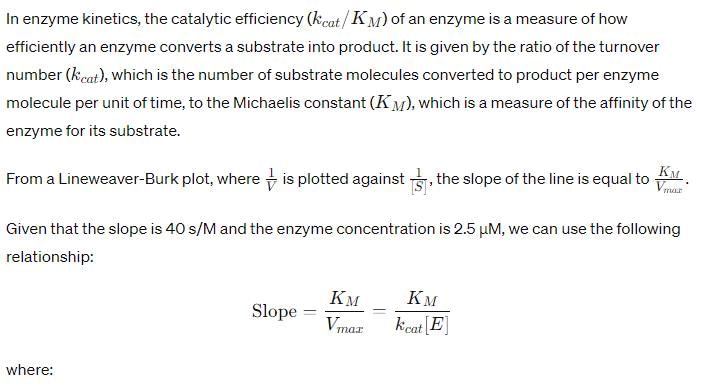
For an enzyme-substrate reaction, a plot between yields a slope of 40 s. If the enzyme concentration is 2.5 μM , then the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme is:
Acid hydrolysis of ester in first order reaction and rate constant is given by,
Where, V0, Vt and V∞ , are the volume of standard NaOH required to neutralize acid present as a given time, if ester is 50% neutralized then
For the reaction, A (g) + 2B(g) → C(g ) + D (g) ,
Initial pressure of A and B are respectively 0.60 atm and 0.80 atm. At a time when pressure of C is 0.20 atm, rate of the reaction, relative to the initial value is:
If 60% of a first order reaction was completed in 60 minutes, 50% of the same reaction would be completed in approximately
The decomposition of ozone to oxygen,
Where, M is the catalyst molecule.
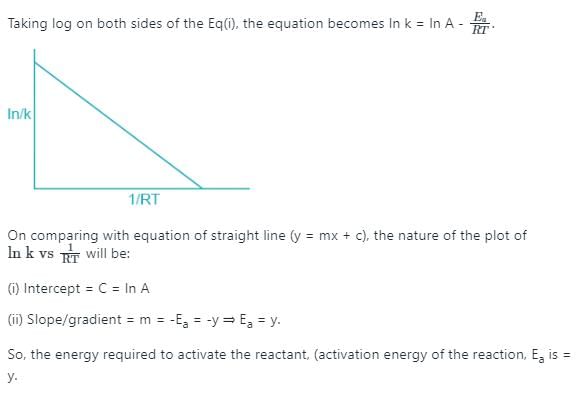
K’ are rate constants and Ea1 is the act ivat ion energy for the elementary step.
Q.
Assuming k3[O3]>>k2[O2][M], the activation energy of the overall reaction is:
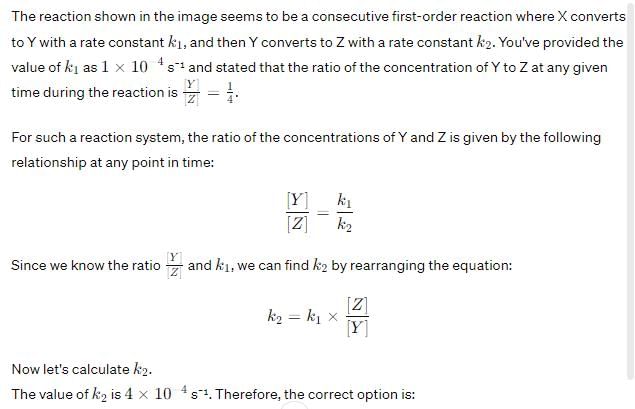
For the reaction shown below,
The value of k1 is . If the reaction starts from X, the ratio of the concentration of Y and Z at any given time during the course of the reaction is found to be
The value of k2 is
At T = 300K, the thermal energy [kbT] in cm–1 is approximately:
In a homogenous catalytic reaction, 1.0 mM of a substrate band 1.0 μM of a catalyst yields 1.0 mM of a product in 10 s. The turnover frequency (TOF) of the reaction (s-1) is.
The value of the rate constant for the gas phase reaction, 2NO2 +F2 →2NO2F is 38 dm3 mol–1s–1 at 300K. The order of the reaction is: