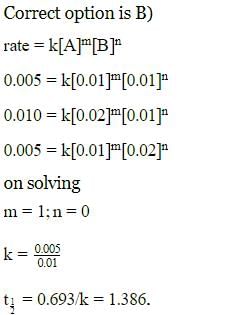Test: Chemical Kinetics - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chemical Kinetics - 2
In a consecutive first order reaction,
(where k1 and k2 are the respective rate constants) species B has transient existence. Therefore,
The specific rate constant of decomposition of a compound is represented by:
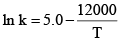
The activation energy of decomposition for this compound at 300 K is
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become
The fluorescence life time of a molecule in solution is 10 ns. If the fluorescence quantum yield is 0.1, the rate constant of fluorescence decay is
Rate of a reaction; A+B → Products; is given below as a function of different initial concentrations of A and B.
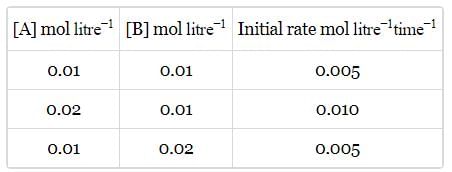
The half life of A in the reaction is :
Sucrose is converted to a mixture of glucose and fructose in a pseudo first order process under alkaline conditions. The reaction has a half˜life of 28.4 min. The time required for the reduction of a 8.0 mM sample of sucrose to 1.0 mM is:
The reaction, 2NO(g) + O2(g) →2NO2(g) proceeds via the following steps:
The rate of this reaction is equal to
1 g of 90Sr gas converted to 0.953 g after 2 yr. The half-line of 90Sr, and the amount of 90Sr remaining after 5 yr are:
How many times will the rate of the elementary reaction 3X + Y → X2Y change if the concentration of the substance X is doubled and that of Y is halved?
A reaction proceeds through the formation of an intermediate B in a unimolecular reaction :The integrated rate law for this reaction is
In radical chain polymerization, the quantity given by the rate of monomer depletion, divided by the rate of propagating radical formation is called:
H2 and Br2 react to give HBr by the following steps:
The probable rate law for the above sequence is
The half–line of a order reaction varies with temperature according to:
The half–life time for a reaction at initial concentrations of 0.1 and 0.4 mol–1 are 200 s and 50 s respectively. The order of the reaction is:
N2O2(g) and NO(g) react to form NO2 according to the stoichiometric equation
N2O2(g) + NO (g) →3NO2(g) (R1)
At a given temperature and pressure. A possible mechanism for this overall reaction is:
Where NO3 is an unstable intermediate. What would be the rate expression of the disappearance of N2O5 in terms of the concentrations of the stable species and the rate constants given above:
Formation of Z and X is theoretically expected to obey the following kinetic scheme.
An experimentalist wants to verify the above scheme, but can observed and measure the concentration of only X and Z. Is it possible that under certain, the measurements of [X] and [Z] as function of time would lead the experimenter to conclude that the kinetic scheme is as given below, and that the species Y is absent:
Following is the graph between (a – x)–1 and time t for a second order reaction,
Hence, rate at the start of the reaction is
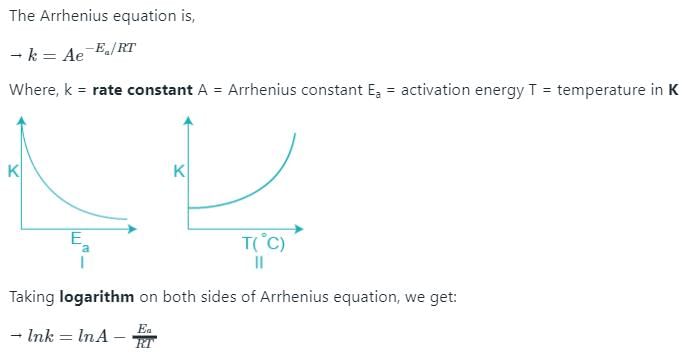
Which of the following plots represent(s) the Arrhenius rate equation, k=Ae–Ea/RT with and
The fraction of group condensed at time t in any stepwise condensation polymerization (overall second order) reaction is
According to Arrhenius equation (K= rate constant and T= Temperature):
The reaction of nitric oxide with ozone takes place according to the following stoichiometry.
The observed rate law for the reaction is found to be
Where α and β are constant. To explain the above rate low, the following reaction scheme has been proposed:
Determine an expression for β .
If the concept of half-life is generalized to quarter–life of a first order chemical reaction, it will e equal to:
The activation energy for the bimolecular reaction A+BC→AB+C is E0 in the gas phase. If the reaction is carried out in a confined volume of λ3 , the activation energy is expected to:
In a reaction, A+B→Product, rate is doubled when the concentration of B is doubled and the rate increases by a factor of 8 when the concentrations of both the reactants (A and B) are doubled, rate law for the reaction can be written as:
The expression for the equilibrium constant (Keq) for the enzyme catalyzed reaction given below is:
For a reaction involving two steps given below:
Assume that the first step attains equilibrium rapidly. The rate of formation of P is proportional to
Consider the reaction H2 + C2 H2 → C2 H6 the molecular diameters of H2 and C2H4
The pre-exponential factor in the rate constant calculated using collision theory in m3 (mol) –1 s–1 is approximately (For this reaction at 300K,
where the symbols have their usual meanings):
A reaction A → D , involves following mechanism:
The rate law of the reaction may be given as: