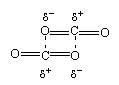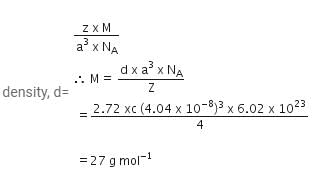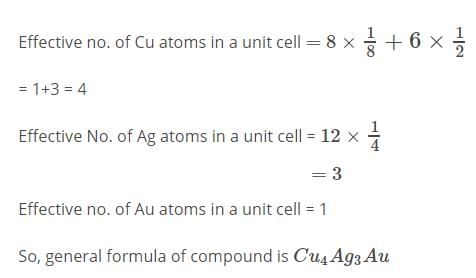Test: Solid State - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Solid State - 1
Which of the units given can be used to build the structure of covalent crystal, diamond:
Which of the following expressions is true in case of a sodium chloride unit cell?
Name of the crystal class for which all the four types of unit cells are possible:
A metal crystallizes with a face-centered cubic lattice. The edge of the unit cell is 408 pm. The diameter of the metal atom is
An element exists as hexagonal close packed structure as well as cubic closed packed structure. In which case the element would have higher density:
The molar volume of KCl and NaCl are 37.46 ml and 27.94 ml. The ratio of unit cell edges of the two crystals is:
A metal has a fcc lattice. The edge length of the unit cell is 404 pm. The density of the metal is 2.72 g cm-3. The molar mass of the metal is (NA Avogadro's constant= 6.02 x 1023 mol-1)
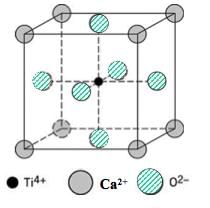
In a crystalline solid, anions B are arranged in CCP lattice and cations A occupy 50% of the octahedral voids and 50% of the tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the solid:
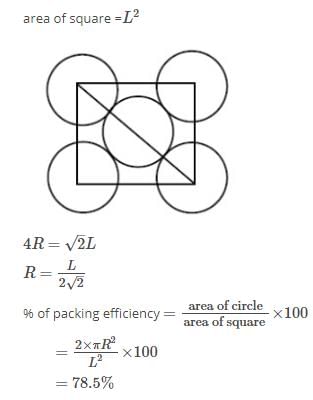
If ‘a’ stand for the edge length of the cubic system: scc, bcc and fcc, then the ratio of the radii of the sphere in the system will be:
In which of the crystal lattice, alternate tetrahedral voids are occupied:
Na crystallizes in fcc lattice having edge length 500 pm. Mass of the Na particle is 4.151 × 10– 23g. The density of the lattice is:
The melting point of RbBr is 682°C, while that of NaF is 988°C. The principal reason that melting point of NaF is much higher than that of RbBr is that:
An alloy of Copper , Silver and Gold is found to have Copper constituting the C.C.P lattice. If Silver atoms occupy the edge centres and Gold is present at body centre , the alloy will have the formula: