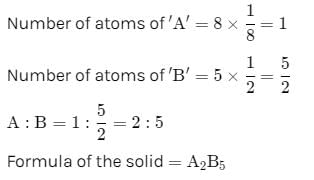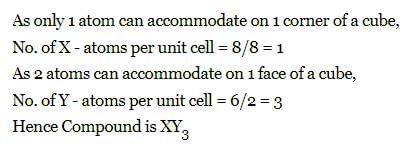Test: Solid State - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Solid State - 2
A solid has a structure in which W-atoms are located at the corners of a cubic lattice, O-atoms at the centre of edges and Na atom at the centre of the cube. The formula for the compound is
The density of CaF2 (fluorite structure) is 3.18 g/cm3. The length of the side of the unit cell is:
If the anions (A) form hexagonal closest packing and cations (C) occupy only 2/3 octahedral voids in it, then the general formula of the compound is
A solid is formed and it has three types of atoms X, Y, Z. X forms a FCC lattice with Y atoms occupying all the tetrahedral voids and Z atoms occupying half the octahedral voids. The formula of the solid is:
In FCC unit cell, what fraction of edge is not covered by atoms:
If edge length of the unit cell is 356 pm, then radius of carbon atom in diamond:
In a cubic unit cell, the angle between normal to the planes (111) and (121) is:
How many unit cells are present in a cube-shaped ideal crystal of NaCl of mass 1.0 g?
Co-ordination no. of ‘c’ in Be2C3 whose structure is co-related with CaF2 is:
The value of d111 in a cubic crystal is 325.6 pm. The value of d333 is (d = interplaner spacing):
X-rays of wKa (wavelength 154 pm) are diffracted by a set of atomic planes in a crystals in the following manner. The separation of the la yers in the crystals in 404 Pm. Find the angle a along which the first order reflection will occur:
In a fcc lattice, atom A occupies the corner position and atom B occupies the face centre position. If one atom of B is missing from one of the face centred points, the formula of the compound is:
The angle between the two planes represented by the Miller indices (110) and (111) in a simple cubic:
The coordinate number for an atom in a primitive cubic unit cell is
The three dimensional graph of lattice points which sets the pattern for the whole lattice is called
When Frenkel defects are created in an otherwise perfect ionic crystal, the density of the ionic crystal:
The compound formed by elements X and Y crystallizes in cubic structure in which X atoms are at the corners of the cube and Y atoms are at the face centre . The formula of the compound is
The angle at which the first order Bragg reflection is observed from (110) plane in a simple cubic unit cell of side 3.238 Å when chromium Ka radiation of wavelength 2.29 Å is used, is:
Number of rotational symmetry axes for triclinic crystal system is:
The lattice parameter of an element stabilized in a fcc structure is 4.04 Å. The atomic radius of the element is:
A metal crystallizes in fcc structure with a unit cell side of 500 pm. If the density of the crystal is 1.33 g/cc, the molar mass of the metal is closed to:
Percentage of free space in a body centred cubic unit cell is
An element exists in two crystallographic modifications with FCC and BCC structures. The ratio of the densities of the FCC and BCC modifications in terms of the volumes of their unit cells (VFCC and VBCC) is:
Metallic gold crystallizes in fcc structure with unit cell dimension of 4.00 Å The atomic radius.
Both NaCl and KCl crystallize with Fcc structure. However, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern corresponds to the fcc structure whereas, that, of KCl corresponds to sample cubic structure. This is because:
In a simple cubic, body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic structure, the ratio of the number of atoms present is respectively
The interplanar spacing of (110) planes in a cubic unit cell with lattice parameter a = 4.242 Å is:
The edge length of a face centred cubic cell of an ionic substance is 508 pm. If the radius of the cation is 110 pm, the radius of the anion is