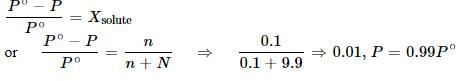Test: Colligative Properties - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Colligative Properties - 1
The vapour pressure of a given liquid will decreases if:
The normal boiling point of water is 373 K. Vapour pressure of water at temperature T is 23 mm Hg. If the enthalpy of vaporization is 40.67 kJ/mol, then temperature T would be:
A sample of liquid H2O of mass 18.0 g is injected into an evacuated 7.6 L flask maintained at 27.0°C. If vapour pressure of H2O at 27°C is 24.63 mm Hg. What weight percentage of the water will be vaporized when the system comes to equilibrium? Assume water vapours behaves as an ideal gas. The volume occupied by the liquid water is negligible compared to the volume of the container:
Raoult’s law is obeyed by each constituent of a binary liquid solution when:
For a binary ideal liquid solution, the total pressure of the solution is given as:
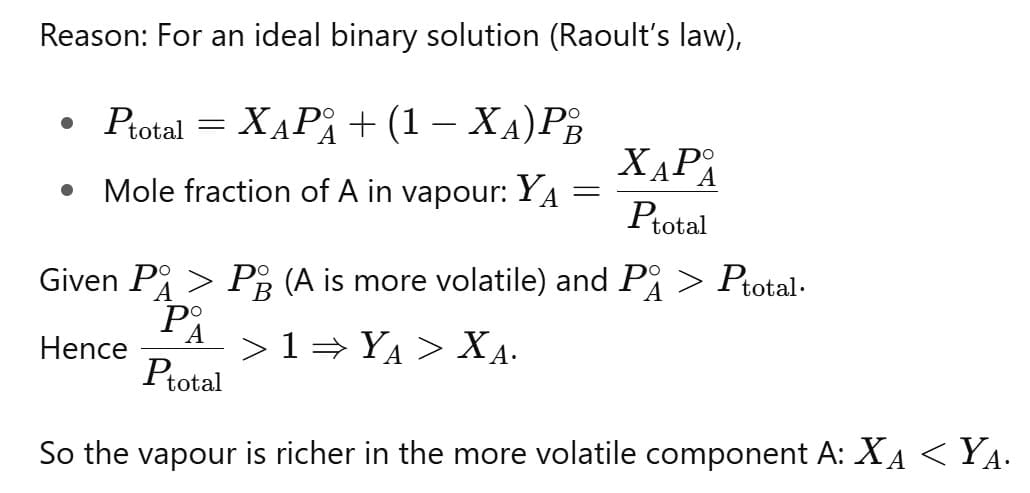
For an ideal binary liquid solution with , which relation between XA (mole fraction of A in liquid phase) and YA (mole fraction of A in vapour phase) is correct?
An ideal solution is formed by mixing two volatile liquids A and B, XA and XB are the mole fractions of A and B respectively in the solution and YA and YB are the mole fractions of A and B respectively in the vapour phase. A plot of along y–axis against
along x–axis gives a straight line. What is the slope of the straight line?
For a dilute solut ion, Raoult’s law states that:
The solubility of a specific non–volatile salt is 4 g in 100 g of water at 25°C. If 2.0 g, 4.0 g and 6.0 g of the salt added of 100 g of water at 25°C, in system X, Y, and Z. The vapour pressure would be in the order:
The boiling point of C6H6, CH3OH, C6H5NH2 and C6H5NO2 are 80°C, 65ºC, 184°C and 212°C respectively. Which will show highest vapour pressure at room temperature:
6.0 g of urea was dissolved in 9.9 moles of water. If the vapour pressure of pure water is P°, the vapour pressure of solution is:
An ideal solution was found to have a vapour pressure of 80 torr when the mole fraction of a non– volatile solute was 0.2. What would be the vapour pressure of the pure solvent at the same temperature?
The vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of sucrose at 373 K is found to be 750 mm Hg. The molality of the solution at the same temperature will be:
Estimate the lowering of vapour pressure due to the solute (glucose) in a 1.0 M aqueous solution at 100°C:
Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molar mass 40 g mol-1) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
Equal weight of a solute are dissolved in equal weight of two solvents A and B formed very dilute solution. The relative lowering of vapour pressure for the solution B has twice the relative lowering of vapour pressure for the solut ion A. If MA and MB are the mo lecular weights of so lvents A and B respectively, then:
An ideal solution has two components A and B. A is more volatile than B, i. e., and also
If XA and YA are mole fractions of components A in liquid and vapour phases, then
At 25°C, the vapour pressure of pure liquid A (mol. wt. = 40) is 100 torr, while that of pure liquid B is 40 torr, (mol. wt. = 80). The vapour pressure at 25°C of a solution containing 20 g of each A and B is:
Two liquids A and B from ideal solutions. At 300 K, the vapour pressure of solution containing 1 mole of A and 3 mole of B is 550 mm Hg. At the same temperature, if one more mole of B is added this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm Hg. Determine the vapour pressure of A and B in their pure states (in mm Hg):
Two liquids A and B have vapour pressure in the ratio at a certain temperature. Assume A and B form an ideal solution and the ratio of mole fractions A and B in the vapour phase is 4:3. Then the mole fraction of B in the solution at the same temperature is: