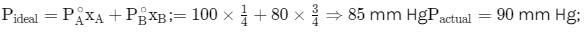Test: Colligative Properties - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Colligative Properties - 2
Two liquids A and B have 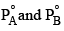 in the ratio of 1:3 and the ratio of number of moles of A and B in liquid phase are 1:3 then mole fraction of ‘A’ in vapour phase in equilibrium with the solution is equal to:
in the ratio of 1:3 and the ratio of number of moles of A and B in liquid phase are 1:3 then mole fraction of ‘A’ in vapour phase in equilibrium with the solution is equal to:
The boiling point of an azeotropics mixture of water–ethanol is less than that of both water and ethanol. Then:
Formation of a solut ion from two components can be considered as:
(i) Pure solvent → separated solvent molecules, ΔH1
(ii) Pure solute → separated solute mo lecules, ΔH2
(iii) Separated solvent and solute molecules → solution, ΔH3
Solution so formed will be ideal if:
Total vapour pressure of mixture of 1 mol X is 240 torr. In this case:
In mixture of A and B, components show positive deviation when:
Total vapour pressure of mixture of 1 mole of volatile component and 3 mole of volatile component B
is 90 mm Hg. For such case:
The azeotropics mixture of water (B.P. = 100°C) and HCl (B.P. = 86°C) boils at about 120°C. During fractional distillation of this mixture it is possible to obtain:
An azeotropic mixture of two liquids has a boiling point higher than either of them when it:
If two liquids A and B
are completely immiscible wit h each other (each one will behave independently of the other) are present in a closed vessel. The total vapour pressure of the system will be:
When a liquid that is immiscible with water was steam distilled at 95.2°C at a total pressure of 748 torr, the distillate contained 1.25 g of the liquid per gram of water. The vapour pressure of water is 648 torr at 95.2°C, what is the molar mass of liquid?
Water and Chlorobenzene are immiscible liquids. Their mixture boils at 89°C under a reduced pressure of 7.7×104 Pa. The vapour pressure of pure water at 89°C is 7×104 Pa. Weight per cent of Chlorobenzene in the distillate is:
Which of the following is not a Colligative property?
The degree of dissociation of an electrolyte is a α and its van’t Hoff factor is i. The number of ions obtained by complete dissociation of 1 molecule of the electrolyte is:
The van’t Hoff factor I for an electrolyte which undergoes dissociation and association in solvent are respectively:
An aqueous solution is 1.00 molal in KI. Which change will cause the vapour pressure of the solution to increase:
Four solutions of K2SO4 with the concentrations 0.1 m, 0.01 m, 0.001 m and 0.0001 m are available. The maximum value of Colligative property corresponds to:
Moles of Na2SO4 to be dissolved in 12 mole water to lower its vapour pressure by 10 mm Hg at a temperature at which vapour pressure of pure water is 50 mm is:
A very diluted saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt X3Y4 has a vapour pressure of 20 mm Hg at temperature T, while pure water exerts a pressure of 20.0126 mm Hg at the same temperature. Calculate molality (m) at temperature T:
When 1 mole of a solute is dissolved in 1 kg of H2O, boiling point of solution was found to be 100.5°C. Kb for H2O is:
Chloro form, CHCl3, boils at 61.7°C. If the Kb for chloroform is 3.63°C/molal, what is the boiling point of a solution of 15.0 kg of CHCl3 and 0.616 kg of acenaphthalene, C12H10?
A compound has the empirical formula C10H8Fe. A solution of 0.26 g of the compound in 11.2 g of benzene (C6H6) boils at 80.26°C. The boiling point of benzene is 80.10°C; the Kb is 2.53°C/molal. What is the molecular formula of the compound?
A solution of 0.640 g of azulene in 100.0 g of benzene bo ils at 80.23°C. The boiling point of benzene is 80.10°C; the Kb is 2.53°C/molal. What is the molecular weight of azulene?
One molal solution of a carboxylic acid in benzene shows the elevation of boiling point of 1.518 K. The degree of association for dimerization of the acid in benzene is (Kb for benzene = 2.53 K kg mol–1):
The boiling point elevation constant for toluene is 3.32 K kg mol–1. The normal boiling point of toluene is 110.7°C. The enthalpy of vaporization of toluene would be nearly:
Which one of the following aqueous solutions will exhibit highest boiling point:
When a solution containing non–volatile solute freezes, which equilibrium would exist ?