Test: Random Process - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Random Process
Consider a low-pass random process with a white-noise power spectral density 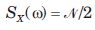 as shown in fig.
as shown in fig.
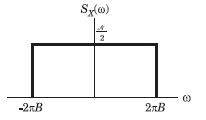
Que: The auto correlation function Rx(τ) is
Consider a low-pass random process with a white-noise power spectral density 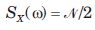 as shown in fig.
as shown in fig.

Que: The power PX is
If X(t) is a stationary process having a mean value E[X(t)] = 3 and autocorrelation function 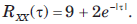
The variance of random variable Y = 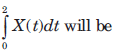
A random process is defined by X(t) = Acos(πt) where A is a gaussian random variable with zero mean and variance σπ2. The density function of X(0)
The two-level semi-random binary process is defined by X(t) = A or -A
where (n-1)T < t < nt and the levels A and -A occur with equal probability. T is a positive constant and
Que: The mean value E[X(t)] is
The two-level semi-random binary process is defined by X(t) = A or -A
where (n-1)T < t < nt and the levels A and -A occur with equal probability. T is a positive constant and
Que: The auto correlation Rxx = (t1 = 0.5T, t2 = 0.7 T) will be
A random process consists of three samples function X(t, s1 ) = 2, X(t, s2 ) = 2cos t1 and X(t, s3 ) = 3sint - each occurring with equal probability. The process is
The auto correlation function of a stationary ergodic random process is shown in fig.
Que: The mean value E[X(t)] is
The auto correlation function of a stationary ergodic random process is shown in fig.
Que: The E[X2(t)] is
The auto correlation function of a stationary ergodic random process is shown in fig.
Que: The variance σx2 is
A stationary zero mean random process X(t) is ergodic has average power of 24 W and has no periodic component. The valid auto correlation function is
A stationary random process X(t) is applied to the input of a system for which If E[X(t)] = 2, the mean value of the system's response Y(t) is
A random process X(t) is applied to a network with impulse response where a > 0 is a constant. The cross correlation of X(t) with the output Y(t) is known to have the same form
Que: The auto correlation of Y(t) is
A random process X(t) is applied to a network with impulse response where a > 0 is a constant. The cross correlation of X(t) with the output Y(t) is known to have the same form
Que: The average power in Y(t) is
A random noise X(t) having a power spectrum is applied to a differentiator that has a transfer function H(ω) = j(ω). The output is applied to a network for which
Que : The average power in X(t) is
A random noise X(t) having a power spectrum is applied to a differentiator that has a transfer function H(ω) = j(ω). The output is applied to a network for which
Que : The power spectrum of Y(t) is
White noise with power density N0 /2 is applied to a low pass network for which |H(0)| = 2. It has a noise bandwidth of 2 MHz. If the average output noise power is 0.1 W in a 1 - Ω( resistor, the value of N0 is
An ideal filter with a mid-band power gain of 8 and bandwidth of 4 rad/s has noise X(t) at its input with power spectrum The noise power at the network's output is (F(2) = 0.9773)
White noise with power density N0 /2 = 6 μW/Hz is applied to an ideal filter of gain 1 and bandwidth W rad/s. If the output's average noise power is 15 watts, the bandwidth W is
A system have the transfer function where W is a real positive constant. The noise bandwidth of the system is



















