HTET PGT Political Science Test - 2 - HTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HTET PGT Political Science Test - 2
Observational learning is also called
I. Vicarious learning
II. Social learning
III. Modelling
The process of habituating the child to repeat and modify elicited and emitted behaviour is called __________.
_______ is defined as any student-centred school-community interaction that directly or indirectly supports the physical, social, emotional and intellectual needs of students.
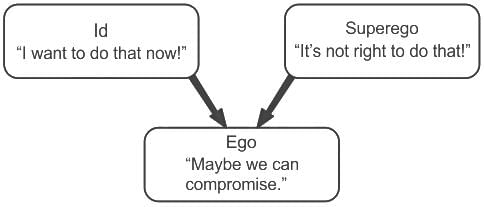
Sunita always do whatever she wants to do without thinking about the consequences. So as per Sigmund Frued, the dominance is of _________.
Children's intrinsic motivation to learn is increased when-
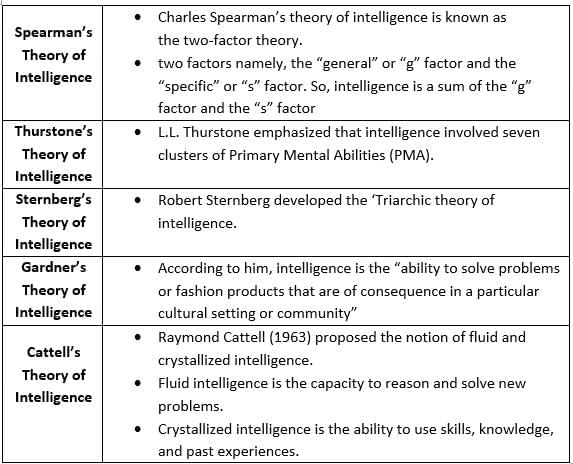
As per contemporary theories of intelligence, Intelligence is -
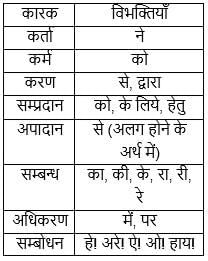
'तुम्हारा घर बहुत सुंदर है।' वाक्य के रेखांकित पद में किस कारक का प्रत्यय है?
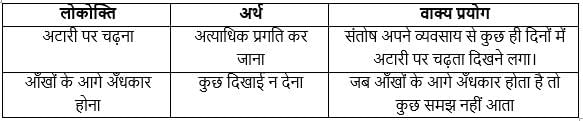
दिए गए वाक्य के लिए सही लोकोक्ति का चयन कीजिए |
बहुत ज्यादा उत्तेजित होना।
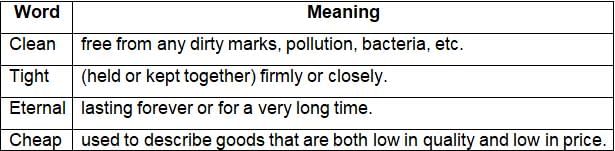
Select the most appropriate antonym of the below word.
Evanescent
In the following question, out of the four alternatives, select the alternative which best expresses the meaning of the Idiom/ Phrase.
Fish out of water
Select the most appropriate ANTONYM of the given word.
Compassionate
A picture is 40 cm wide and 1.6 m long. The ratio of its width to its perimeter is:
Haryana's Lala Lajpat Rai University of Animal Science Center is located in which district?
With regard to the following statements, choose the appropriate answer.
Statement 1: Terrorism is a phenomenon restricted to specific regions and countries.
Statement 2: Globalization has facilitated the spread of terrorist ideologies and activities.
Which one of the following statements about the Judiciary is false?
Which of the following statements are true about the Authoritarianism and Totalitarianism?
(A) In authoritarian regime, government is not constitutionally responsible to the public
(B) Authoritarian regimes may be institutionalised and legitimate
(C) Totalitarian regimes seek to control and transform all aspects of the state, society and economy
(D) Totalitarian regimes do not have strong ideological goal and do not use violence as a tool for remaking institutions
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct option based on the given multiple statements.
I: J.L. Nehru served as the President of the Indian National Congress only 1 time.
II: Jaya Prakash Narayan was a prominent leader in the Indian independence movement.
III: Deendayal Upadhyaya was a key ideologue of the socialist movement in India.
IV: Periyar E. V. Ramasamy actively participated in the Non-Cooperation Movement led by Gandhi.