Test: Boiling, Condensation & Heat Exchangers - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Boiling, Condensation & Heat Exchangers - 1
Consider the following phenomena:
1. Boiling
2. Free convection in air
3. Forced convection
4. Conduction in air
Their correct sequence in increasing order of heat transfer coefficientis:
1. Boiling
2. Free convection in air
3. Forced convection
4. Conduction in air
Their correct sequence in increasing order of heat transfer coefficientis:
The given figure shows a pool-boiling curve. Consider the followingstatements in this regard:
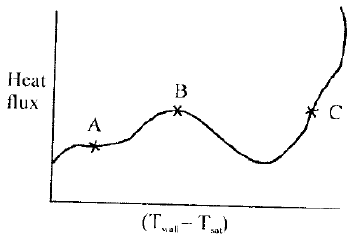
1. Onset of nucleation causes amarked change in slope.
2. At the point B, heat transfercoefficient is the maximum.
3. In an electrically heated wiresubmerged in the liquid, filmheating is difficult to achieve.
4. Beyond the point C, radiationbecomes significantOf these statements:
1. Onset of nucleation causes amarked change in slope.
2. At the point B, heat transfercoefficient is the maximum.
3. In an electrically heated wiresubmerged in the liquid, filmheating is difficult to achieve.
4. Beyond the point C, radiationbecomes significantOf these statements:
Drop wise condensation usually occurs on
Consider the following statements regarding condensation heattransfer
1. For a single tube, horizontal position is preferred over vertical position for better heat transfer.
2. Heat transfer coefficient decreases if the vapour stream moves athigh velocity.
3. Condensation of steam on an oily surface is dropwise.
4. Condensation of pure benzene vapour is always dropwise.Of these statements
The burnout heat flux in the nucleate boiling regime is a function ofwhich of the following properties?
1. Heat of evaporation
2. Temperature difference
3. Density of vapour
4. Density of liquid
5. Vapour-liquid surface tension
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Codes:
The given figure shows a pool-boiling curve. Consider the following statements in this regard:
1. Onset of nucleation causes amarked change in slope.
2. At the point B, heat transfer coefficient is the maximum.
3. In an electrically heated wiresubmerged in the liquid, film heating is difficult to achieve.
4. Beyond the point C, radiation becomes significant Of these statements:
Assertion (A): If the heat fluxes in pool boiling over a horizontal surfaceis increased above the critical heat flux, the temperature difference between the surface and liquid decreases sharply.
Reason (R): With increasing heat flux beyond the value corresponding to the critical heat flux, a stage is reached when the rate of formation of bubbles is so high that they start to coalesce and blanket the surface with a vapour film.
When a liquid flows through a tube with sub-cooled or saturated boiling, what is the process known?
Assertion (A): Even though dropwise condensation is more efficient,surface condensers are designed on the assumption of film wise condensation as a matter of practice.
Reason (R): Dropwise condensation can be maintained with the use of promoters like oleic acid.
Assertion (A): Even though dropwise condensation is more efficient,surface condensers are designed on the assumption of film wisecondensation as a matter of practice.
Reason (R): Dropwise condensation can be maintained with the use ofpromoters like oleic acid.
Assertion (A): The rate of condensation over a rusty surface is less than that over a polished surface.
Reason (R): The polished surface promotes drop wise condensation which does not wet the surface.
In a counter flow heat exchanger, for the hot fluid the heat capacity = 2kJ/kg K, mass flow rate = 5 kg/s, inlet temperature = 150°C, outlet temperature = 100°C. For the cold fluid, heat capacity = 4 kJ/kg K, massflow rate = 10 kg/s, inlet temperature = 20°C. Neglecting heat transfer tothe surroundings, the outlet temperature of the cold fluid in °C is:
The logarithmic mean temperature difference (LMTD) of a counter flow heat exchanger is 20°C. The cold fluid enters at 20°C and the hot fluidenters at 100°C. Mass flow rate of the cold fluid is twice that of the hotfluid. Specific heat at constant pressure of the hot fluid is twice that ofthe cold fluid. The exit temperature of the cold fluid
For the same inlet and outlet temperatures of hot and cold fluids, theLog Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD) is:
In a counter flow heat exchanger, hot fluid enters at 60°C and cold fluidleaves at 30°C. Mass flow rate of the hot fluid is 1 kg/s and that of thecold fluid is 2 kg/s. Specific heat of the hot fluid is 10 kJ/kgK and that ofthe cold fluid is 5 kJ/kgK. The Log Mean Temperature Difference(LMTD) for the heat exchanger in °C is:
Air enters a counter flow heat exchanger at 70°C and leaves at 40°C.Water enters at 30°C and leaves at 50°C. The LMTD in degree C is
Hot oil is cooled from 80 to 50°C in an oil cooler which uses air as the coolant. The air temperature rises from 30 to 40°C. The designer uses aLMTD value of 26°C. The type of heat exchanger is:
In a parallel flow heat exchanger operating under steady state, theheat capacity rates (product of specific heat at constant pressure and mass flow rate) of the hot and cold fluid are equal. The hot fluid,flowing at 1 kg/s with Cp = 4 kJ/kgK, enters the heat exchanger at 102°Cwhile the cold fluid has an inlet temperature of 15°C. The overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger is estimated to be 1 kW/m2K and the corresponding heat transfer surface area is 5 m2. Neglect heat transfer between the heat exchanger and the ambient. The heat exchanger is characterized by the following relation: 2ε = 1 – exp(–2NTU). The exit temperature (in °C) for - the cold fluid is:
Which one of the following heat exchangers gives parallel straight line pattern of temperature distribution for both cold and hot fluid?
Consider the following statements:
The flow configuration in a heat exchanger, whether counter flow or otherwise, will NOT matter if:
1. A liquid is evaporating
2. A vapour is condensing
3. Mass flow rate of one of the fluids is far greater
Of these statements:














