Test: Design of Joint - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Design of Joint - 1
Square key of side "d/4" each and length l is used to transmit torque "T" from the shaft of diameter "d" to the hub of a pulley. Assuming the length of the key to be equal to the thickness of the pulley, the average shear stress developed in the key is given by
A 60 mm long and 6 mm thick fillet weld carries a steady load of 15 kNalong the weld. The shear strength of the weld material is equal to 200MPa. The factor of safety is
Assertion (A): A cotter joint is used to rigidly connect two coaxial rods carrying tensile load.
Reason (R): Taper in the cotter is provided to facilitate its removal when it fails due to shear.
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
In a gib and cotter joint, the gib and cotter are subjected to
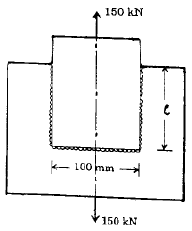
In a cotter joint, the width of the cotter at the centre is 50 mm and its thickness is 12 mm. The load acting on the cotter is 60 kN. What is the shearing stress developed in the cotter?
Match List-l (Machine element) with List-II (Cause of failure) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
A cotter joint is used when no relative motion is permitted between the rods joined by the cotter. It is capable of transmitting
Assertion (A): When the coupler of a turn buckle is turned in one direction both the connecting rods either move closer or move away from each other depending upon the direction of rotation of the coupler.
Reason (R): A turn buckle is used to connect two round rods subjected to tensile loading and requiring subsequent adjustment for tightening or loosening.
A spur gear transmitting power is connected to the shaft with a key of rectangular section. The type (s) of stresses developed in the key is fare.
Which key is preferred for the condition where a large amount of impact torque is to be transmitted in both direction of rotation?
A square key of side d/4 is to be fitted on a shaft of diameter d and in the hub of a pulley. If the material of the key and shaft is same and the two are to be equally strong in shear, what is the length of the key?
A pulley is connected to a power transmission shaft of diameter d by means of a rectangular sunk key of width wand length ‘l’. The width of the key is taken as d/4. For full power transmission, the shearing strength of the key is equal to the torsional shearing strength of the shaft. The ratio of the length of the key to the diameter of the shaft (l/d) is
The shearing area of a key of length 'L', breadth 'b' and depth 'h' is equal to
In a fillet welded joint, the weakest area of the weld is
Two metal plates of thickness ’t’ and width 'w' are joined by a fillet weld of 45° as shown in given figure.
When subjected to a pulling force 'F', the stress induced in the weld will be
In the welded joint shown in the given figure, if the weld at B has thicker fillets than that at A, then the load carrying capacity P, of the joint will
The following two figures show welded joints (x x x x x indicates welds), for the same load and same dimensions of plate and weld.
The joint shown in
Two plates are joined together by means of single transverse and double parallel fillet welds as shown in figure given above. If the size of fillet is 5 mm and allowable shear load per mm is 300 N, what is the approximate length of each parallel fillet?