Test: Introduction to Power Plant & Steam Cycle - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Introduction to Power Plant & Steam Cycle - 2
In thermal power plants, coal is transferred from bunker to the other place by
The correct sequence of factors in order of deceasing importance for location of a thermal power plant is
Consider a steam power plant using a reheat cycle as shown. Steam leaves the boiler and enters the turbine at 4 MPa, 350°C (h3 = 3095 kJ/kg). After expansion in the turbine to 400 kPa (h4 = 2609 kJ/kg), the steam is reheated to 350°C (h5 = 3170 kJ / kg), and then expanded in a low pressure turbine to 10 kPa (h6= 2165 kJ/kg). The specific volume of liquid handled by the pump can be assumed to be .
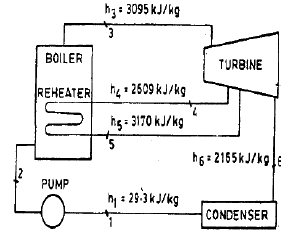
The thermal efficiency of the plant neglecting pump work is
Consider a steam power plant using a reheat cycle as shown. Steam leaves the boiler and enters the turbine at 4 MPa, 350°C (h3 = 3095 kJ/kg). After expansion in the turbine to 400 kPa (h4 = 2609 kJ/kg), the steam is reheated to 350°C (h5 = 3170 kJ / kg), and then expanded in a low pressure turbine to 10 kPa (h6= 2165 kJ/kg). The specific volume of liquid handled by the pump can be assumed to be .
The enthalpy at the pump discharge (h2) is
12. A steam plant has the boiler efficiency of 92%, turbine efficiency (mechanical) of 94%, generator efficiency of 95% and cycle efficiency of44%. If 6% of the generated power is used to run the auxiliaries, the overallplant efficiency is
In steam and other vapour cycles, the process of removing noncondensableis called
Which one of the following statements is correct?
During which of following process does heat rejection take place in Carnotvapour cycle?
The main advantage of a reheat Rankine cycle is
Assertion (A): The performance of a simple Rankine cycle is not sensitive to the
efficiency of the feed pump.
Reason (R): The net work ratio is practically unity for a Rankine cycle
The reheat cycle in steam power plant is mainly adopted to
Assertion (A): The purpose of employing reheat in a steam power plant is mainlyto improve its thermal efficiency.Reason (R): The use of regeneration in a steam power plant improves theefficiency.
Consider the following statements:If steam is reheated during the expansion through turbine stages
1. Erosion of blade will decrease
2. The overall pressure ratio will increase.
3. The total heat drop will increase.Of these statements
Assertion (A): An ideal regenerative Ranking cycle power plant with saturated steam at the inlet to the turbine has same thermal efficiency as Carnot cycleworking between the same temperature limits . Reason (R): The change in entropy of steam during expansion in the turbine is equal to the change in entropy of the feed water during sensible heating at steam generator pressure.
(A): The thermal efficiency of a regenerative Rankine cycle is always higher than that of a cycle without regeneration.Reason (R): In regeneration cycle the work output is more
In a steam power plant, the ratio of the isentropic heat drop in the primemover to the amount of heat supplied per unit mass of steam is known as
Assertion (A): Rankine efficiency would approach Carnot cycle efficiency byproviding a series of regenerative feed heating.Reason (R): With regenerative feed heating, expansion through the turbine approaches an isentropic process.
A regenerative steam cycle renders
When is the greatest economy obtained in a regenerative feed heatingcycle?
In a regenerative feed heating cycle, the economic number of the stages of regeneration
Which one of the following statements is not correct for a regenerative steam cycle?
In which one of the following steam turbines, steam is taken from various points along the turbine, solely for feed water heating?
The temperature-entropy diagram for a steam turbine power plant, operating on the Rankine cycle with reheat and regenerative feed heating is shown in the given figure. If m denotes the fraction of steam bled for feed heating, the work developed in the turbine per kg steam entering the turbine at state 5 is
In thermal power plants, the deaerator is used mainly to
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer:
Consider the following statements:The efficiency of the vapour power Rankine cycle can be increased by
1. Increasing the temperature of the working fluid at which heat is added.
2. Increasing the pressure of the working fluid at which heat is added.
3. Decreasing the temperature of the working fluid at which heat isrejected.
Which of these statements is/are correct?
Assertion (A): Rankine cycle is preferred for waste heat recovery.Reason (R): Rankine cycle gives high thermal efficiency even at low temperature scompared to other dynamic energy conversion systems
The efficiency of Rankine cycle is lower than that corresponding Carnotcycle because [IES-1992]
In the bottoming cycle of cogeneration, low grade waste heat is used for
A power plant, which uses a gas turbine followed by steam turbine for power generation, is called:














