Test: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics - 2
A system comprising a single phase is called a
A frictionless piston-cylinder device contains a gas initially at 0.8 MPa and 0.015 m3. It expands quasi-statically at constant temperature to a final volume of 0.030 m3. The work output (in kJ/kg) during this process will be:
Air is compressed adiabatically in a steady flow process with negligible change in potential and kinetic energy. The Work done in the process is given by:
A gas expands in a frictionless piston-cylinder arrangement. The expansion process is very slow, and is resisted by an ambient pressure of 100 kPa. During the expansion process, the pressure of the system (gas) remains constant at 300 kPa. The change in volume of the gas is 0.01 m3. The maximum amount of work that could be utilized from the above process is:
Which of the following variables controls the physical properties of a perfect gas
Which of the following is the extensive property of a thermodynamic system?
Consider the following:
1. Temperature 2. Viscosity 3. Internal energy 4. Entropy
Which of these are extensive properties?
A system comprising a single phase is called a
Assertion (A): A thermodynamic system may be considered as a quantity of working substance with which interactions of heat and work are studied.
Reason (R): Energy in the form of work and heat are mutually convertible.
Which of the following is/are reversible process(es)?
1. Isentropic expansion
2. Slow heating of water from a hot source
3. Constant pressure heating of an ideal gas from a constant temperature source
4. Evaporation of a liquid at constant temperature
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which one of the following represents open thermodynamic system?
Hot coffee stored in a well insulated thermos flask is an example of
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
Consider the following statements:
1. Zeroth law of thermodynamics is related to temperature
2. Entropy is related to first law of thermodynamics
3. Internal energy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature and pressure
4. Van der Waals' equation is related to an ideal gas
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which one of the following correctly defines 1 K, as per the internationally accepted definition of temperature scale?
In a new temperature scale say °ρ, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100°ρ and 300°ρ respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of 0°ρ on the Centigrade scale is:
Match List-I (Type of Thermometer) with List-II (Thermometric Property) and select the correct answer using the code given below the
The time constant of a thermocouple is the time taken to attain:
Work transfer between the system and the surroundings
There is no work transfer involved in this process
The heat transfer, Q, the work done W and the change in internal energy U are all zero in the case of
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of the three processes A, B and C in the increasing order of the amount of work done by a gas following idealgas expansions by these processes?
A piston cylinder contains air at 600 kPa, 290 K and a volume of 0.01m^3. A constant pressure process gives 54 kJ of work out. Find the final volume of the air.
Which one of the following expresses the reversible work done by the system (steady flow) between states 1 and 2?
The following are examples of some intensive and extensive properties:

Which one of the following sets gives the correct combination of intensive and extensive properties?
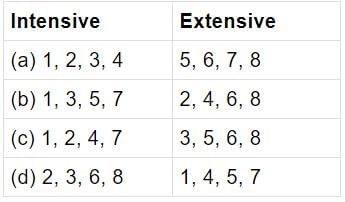
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer:
In free expansion of a gas between two equilibrium states, the work transfer involved
In the temperature-entropy diagram of a vapour shown in the given figure, the thermodynamic process shown by the dotted line AB represents
The door of a running refrigerator inside a room was left open. Which of the following statements is correct?














