Test: Design of Joint - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Design of Joint - 2
A circular rod of diameter d is welded to a flat plate along its circumference by fillet weld of thickness t. Assuming τw as the allowable shear stress for the weld material, what is the value of the safe torque that can be transmitted?
A circular solid rod of diameter d welded to a rigid flat plate by a circular fillet weld of throat thickness t is subjected to a twisting moment T. The maximum shear stress induced in the weld is
The permissible stress in a filled weld is 100 N/mm2. The fillet weld has equal leg lengths of 15 mm each. The allowable shearing load on weldment per cm length of the weld is
Consider the case of a squarethreaded screw loaded by a nut as shown in the given figure. The value of the average shearing stress of the screw is given by (symbols have the usual meaning)
Assertion (A): Uniform-strength bolts are used for resisting impact loads.
Reason (R): The area of cross-section of the threaded and unthreaded parts is made equal.
How can shock absorbing capacity of a bolt be increased?
A key connecting a flange coupling to a shaft is likely to fail in
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
codes A B C D
Match List I (Items in joints) with List II (Type of failure) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
Codes A B C D
The spigot of a cotter joint has a diameter D and carries a slot for cotter. The permissible crushing stress is x times the permissible tensile stress for the material of spigot where x > 1. The joint carries an axial load P. Which one of the following equations will give the diameter of the spigot?
The piston rod and the crosshead in a steam engine are usually connected by means of
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List I (Type of joint)
A.Cotter joint
B.Knuckle joint
C.Turn buckle
D.Riveted joint
List II (Mode of jointing members)
1.Connects two rods or bars permitting small amount of flexibility
2.Rigidly connects two members
3.Connects two rods having threaded ends
4.Permanent fluid-tight joint between two flat pieces
5.Connects two shafts and transmits torque
Match List-I (Type of keys) with List-II (Characteristic) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
Assertion (A): The effect of keyways on a shaft is to reduce its load carrying capacity and to increase its torsional rigidity.
Reason (R): Highly localized stresses occur at or near the corners of keyways.
What is sunk key made in the form of a segment of a circular disc of uniform thickness, known as?
What are the key functions of a master schedule?
1. To generate material and capacity requirements
2. To maintain valid priorities
3. An effective capacity utilization
4. Planning the quantity and timing of output over the intermediate time horizons
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which one of the following statements is correct?
While designing a parallel sunk key it is assumed that the distribution of force along the length of the key
Match List-I (Device) with List-II (Component/Accessory) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
[IES 2003]
Assertion (A): A Woodruff key is an easily adjustable key.
Reason (R): The Woodruff key accommodates itself to any taper in the hub or boss of the mating piece.
Match List I (Keys) with List II (Characteristics) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
Codes: A B C D
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
Codes: A B C D
Consider the following statements:
A splined shaft is used for
1. Transmitting power
2. Holding a flywheel rigidly in position
3. Moving axially the gear wheels mounted on it
4. Mounting V-belt pulleys on it.
Of these statements
A single parallel fillet weld of total length L and weld size h subjected to a tensile load P, will have what design stress?
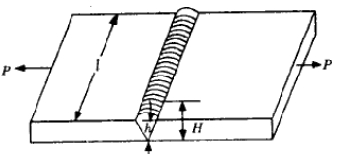
A butt welded joint, subjected to tensile force P is shown in the given figure, l = length of the weld (in mm) h = throat of the butt weld (in mm) and H is the total height of weld including reinforcement. The average tensile stress σt, in the weld is given by
A double fillet welded joint with parallel fillet weld of length L and leg B is subjected to a tensile force P. Assuming uniform stress distribution, the shear stress in the weld is given by
Assertion (A): In design of double fillet welding of un symmetrical sections with plates subjected to axial loads lengths of parallel welds are made unequal.
Reason (R): The lengths of parallel welds in fillet welding of an un symmetrical section with a plate are so proportioned that the sum of the resisting moments of welds about the centre of gravity axis is zero.]



















