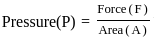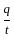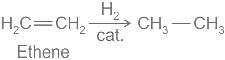MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 2 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 2
What is the velocity of light in a diamond if the refractive index of diamond with respect to vacuum is 2.5?
Compound A used as strong oxidizing agent is amphoteric in nature. It is the part of lead storage batteries. Compound A is:
A bus is moving with a speed of 72 km/h, convert its speed into m/s:
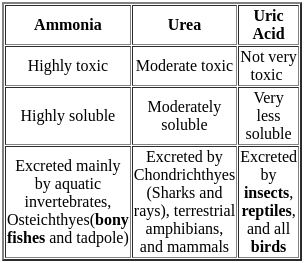
A colourless gas with choking smell is evolved when Cu turnings are heated with conc. H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>. The gas is ______.
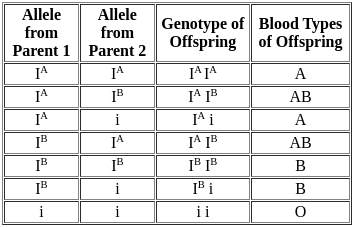
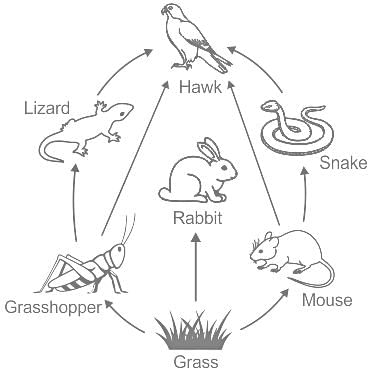
Mendel's work of genetics was based upon which of the following?
Fig. shows a container filled with water. Which of the following statements is correct about pressure of water?

Consider the following statements about Light year:
1. Light year is a unit for measurement of very large distances.
2. Light year is a unit for measurement of very large time intervals.
3. Light year is a unit for measurement of intensity of light.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
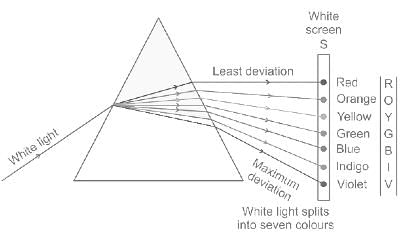
Write the given four colors in the ascending order of their wavelength.
Yellow, Red, Green, And Violet
Which of the following can be the best way to teach the concept of "physical and chemical change" to class Vth students?
When two bodies are in thermal contact, heat flow will occur between them if they differ in ______.
What is the amount of charge (in Coulomb) present in between the two points of a conductor, when electric current of 5A flow in 10s?
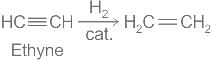
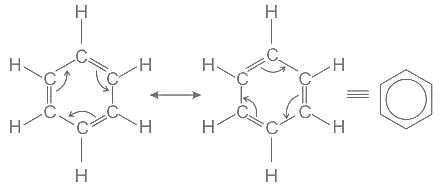
Reason for less reactivity of benzene than ethene and ethyne towards addition reaction is -


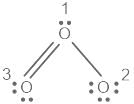

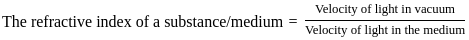
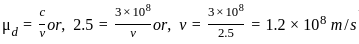
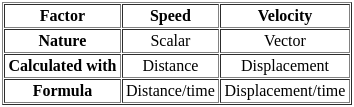

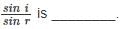 .
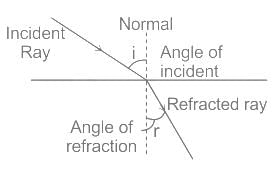
.

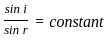 . Therefore option 2 is correct.
. Therefore option 2 is correct.