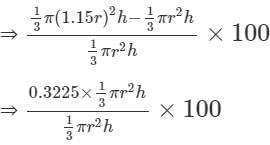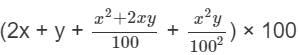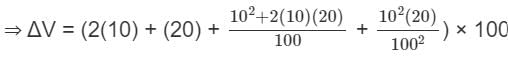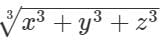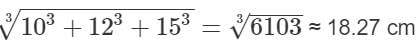MPTET Varg 2 Math Mock Test - 5 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 2 Math Mock Test - 5
The total surface area of a solid hemisphere is 1848 cm2. What is the length of the diameter of the flat surface of the hemisphere. [Use π = 22/7]
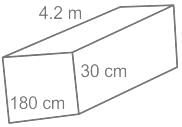
Find the surface area (in dm2) of a cuboid whose length is 4.2 m, breadth is 30 dm and height is 180 cm.
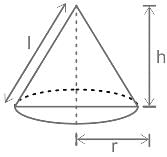
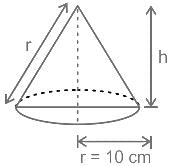
The total surface area of right circular cone is 360π m2. If the radius is 10 m, then find the height of the right circular cone. (in m)
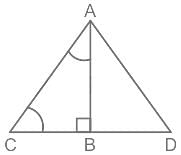
In Fig, ABC is a right triangle and right angled at B such that ∠BCA = 2 ∠BAC then
Find the Total surface area of the hemisphere (in cm2) whose radius is 51cm and π = 3.14.
The difference between the compound and the simple interests for 3 years at the rate of 20% per annum is ₹432. What is the principal lent?
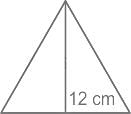
The altitude of an equilateral triangle is 12 cm. What is the perimeter of the triangle?
The radius of the base of a right circular cone is increased by 15% keeping the height fixed. The volume of the cone will be increased by:
If the radius of the cone is increased by 10% and the height of the cone is increased by 20%, find the percentage increase in the volume of the cone.
A teacher uses the exploratory approach, use manipulatives and involvement of students in discussion while giving the concepts of mathematics. She uses this strategy to
The cubes of side length 10 cm, 12 cm and 15 cm all three melted as casted into a single cube. Find the side length of the casted cube. (in cm)
Find the radius of the semi-circle whose perimeter is 72 cm. (Take π = 22/7)
What will be the difference between mean and median of the given data?
21, 11, 27, 8, 5, 12, 7, 23, 3, 14, 9, 19


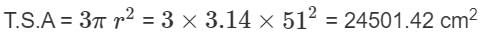
 432 = P[(3.64 - 3)/5]
432 = P[(3.64 - 3)/5]