Test: Mechanism - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mechanism - 1
What are the minimum number of kinematic pairs required in a kinematic chain?
The minimum number of links in a single degree-of-freedom planar mechanism with both higher and lower kinematic pairs is:
A planar mechanism has 8 links and 10 rotary joints. The number of degrees of freedom of the mechanism, using Grubler's criterion, is
The number degrees of freedom of a planar linkage with 8 links and 9 simple revolute joints is
Match the approaches given below to perform stated kinematics/dynamics analysis of machine.
A simple quick return mechanism is shown in the figure. The forward to return ratio of the quick return mechanism is 2: 1. If the radius of the crank O1P is 125 mm, then the distance 'd' (in mm) between the crank centre to lever pivot centre point should be
In a four-bar linkage, S denotes the shortest link length, L is the longest link length, P and Q are the lengths of other two links. At least one of the three moving links will rotate by 360° if
The lengths of the links of a 4-bar linkage with revolute pairs only are p, q, r, and s Given that p < q < r < s. Which of these links should be the fixed one, for obtaining a “double crank” mechanism?
Choose the option which does NOT belong to the category of simple machine:
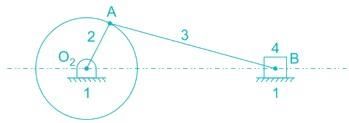
The input link O2P of a four bar linkage is rotated at 2 rad/s in counter clockwise direction as shown below. The angular velocity of the coupler PQ in rad/s, at an instant when ∠O4O2 P = 180°, is
and O2P = O2O4 = a.
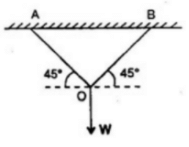
Two wires AO and BO support a vertical load W at O as shown in the figure below. The wires are of equal length and equal cross sectional area. The tension in each wire is equal to
For the planar mechanism shown in figure select the most appropriate choice for the motion of link 2 when link 4 is moved upwards.
Instantaneous center of a body rolling with sliding on a stationary curved surface lies: