Test: Mechanism - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mechanism - 2
The figure below shows a planar mechanism with single degree of freedom. The instant centre 24 for the given configuration is located at a position
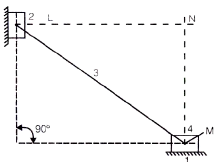
[GATE-2004]
In the figure shown, the relative velocity of link 1 with respect to link 2 is 12 m/sec. Link 2 rotates at a constant speed of 120 rpm. The magnitude of Carioles component of acceleration of link 1 is
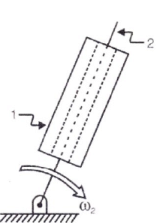
The coupling used to connect two shafts with large angular misalignment is
[GATE-2002]
For the audio cassette mechanism shown in Figure given below where is the instantaneous centre of rotation (point) of the two spools?
[GATE-1999]
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer
[IES-2002]
Consider the following statements:
1. The degree of freedom for lower kinematic pairs is always equal to one.
2. A ball-and-socket joint has 3 degrees of freedom and is a higher kinematic pair
3.Oldham's coupling mechanism has two prismatic pairs and two revolute pairs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[IES-2005]
A round bar A passes through the cylindrical hole in B as shown in the given figure. Which one of the following statements is correct in this regard?
[IES-1995]
Which of the following are examples of forced closed kinematic pairs?
1. Cam and roller mechanism
2. Door closing mechanism
3. Slider-crank mechanism
4. Automotive clutch operating mechanism
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
[IES-2003]
Consider the following statements
1. A round bar in a round hole form a turning pair.
2. A square bar in a square hole forms a sliding pair.
3. A vertical shaft in a footstep bearing forms a successful constraint.
Of these statements
[IES-2000]
Assertion (A): Hydraulic fluid is one form a link.
Reason (R): A link need not necessarily be a rigid body but it must be a resistant body.
[IES-1996]
Assertion (A): The elements of higher pairs must be force closed.
Reason (R): This is required in order to provide completely constrained motion.
[IES-1995]
Assertion (A): When a link has pure translation, the resultant force must pass through the centre of gravity.
Reason (R): The direction of the resultant force would be in the direction of acceleration of the body.
[IES-1994]
Consider the following pairs of parts:
1. Pair of gear in mesh
2. Belt and pulley
3. Cylinder and piston
4. Cam and follower Among these, the higher pairs are
[IES-2000]
Consider the following pairs of parts:
1. Pair of gear in mesh
2. Belt and pulley
3. Cylinder and piston
4. Cam and follower Among these, the higher pairs are
[IES-2000]
In a Kinematic chain, a quaternary joint is equivalent to:
[IES-2005]
Consider the following statements:
1. Lower pairs are more resistant than the higher pairs in a plane mechanism.
2. In a 4-bar mechanism (with 4 turning pairs), when the link opposite to the shortest link is fixed, a double rocker mechanism results.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[IES-2006]
Which of the following are examples of a kinematic chain?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
[IES-1998]
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
The kinematic chain shown in the above figure is a
[IES-2000]
Assertion (A): The elements of higher pairs must be force closed.
Reason (R): This is required in order to provide completely constrained motion.
[IES-1995]
The two-link system, shown in the given figure, is constrained to move with planar motion. It possesses
Assertion (A): When a link has pure translation, the resultant force must pass through the centre of gravity.
Reason (R): The direction of the resultant force would be in the direction of acceleration of the body.
[IES-1994]
A linkage is shown below in the figure in which links ABC and DEF are ternary Jinks whereas AF, BE and CD are binary links.
The degrees of freedom of the linkage when link ABC is fixed are
[IES-2002]
When supported on three points, out of the 12 degrees of freedom the number of degrees of reedom arrested in a body is
[IES-1993]
f = 3 (n - 1) - 2j. In the Grubler's equation for planar mechanisms given, j is the
[IES-2003]
Which one of the following conversions is used by a lawn-sprinkler which is a four bar mechanisms?
[IES-2004]
The centre of gravity of the coupler link in a 4-bar mechanism would experience
[IES-1996]





















