Test: Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors - 2
For the matrix 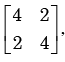 the eigen value corresponding to the eigenvector
the eigen value corresponding to the eigenvector 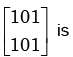
For which value of x will the matrix given below become singular?
If a square matrix A is real and symmetric, then the eigenvaluesn
For a matrix the transpose of the matrix is equal to the inverse of the matrix,
The value of x is given by
In the matrix equation Px = q which of the following is a necessary condition for the existence of at least one solution for the unknown vector x:
Cayley - Hamiltion Theorem states that square matrix satisfies its own characteristic equation, Consider a matrix
A satisfies the relation
The characteristic equation of a (3×3) matrix P is defined as If I denote identity matrix, then the inverse of matrix P will be
Let P be a 2×2 real orthogonal matrix and s a real vector
with length
Then which one of the following statements is correct?
Let A be an n × n real matrix such that A2 = I and y = be an n – dimensional vector. Then the linear system of equations Ax = y has
The following system of equations
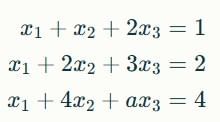
has a unique solution. The only possible value(s) for a is/are
The number of different n × n symmetric matrices with each element being either 0 or 1 is: (Note : power (2, x) is same as 2x)
In an M × N matrix such that all non-zero entries are covered in a rows and b column. Then the maximum number of non-zero entries, such that no two are on the same row or column, is
Consider the following system of equation in three real variables x1, x2 and x3
This system of equations has
How many of the following matrics have an eigenvalue 1?
The condition for which eigenvalues of the matrix A are positive, is
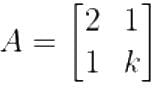
What are the eigen values of the following 2 × 2 matrix?
Consider a 3 × 3 real symmetric matrix S such that two of its eigen values are a ≠ 0 , b ≠ 0 with respective eigenvectors X and Y. If a ≠ b then x1y1 + x2y2 + x3y3 equals
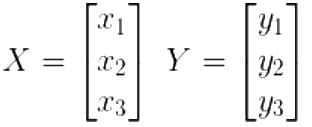




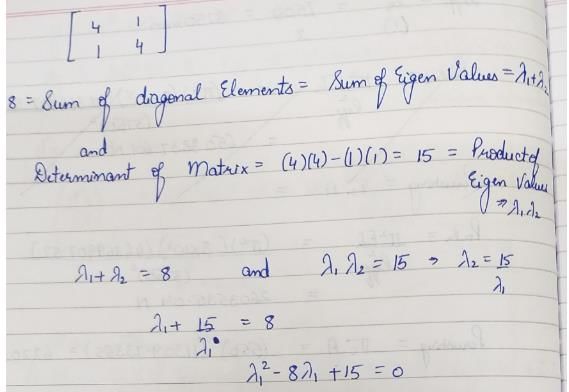

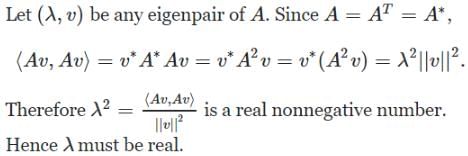




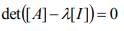
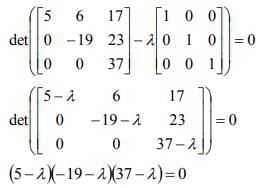
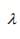 = 5,-19,37 are the roots of the equation; and hence, the eigenvalues of [A].
= 5,-19,37 are the roots of the equation; and hence, the eigenvalues of [A].
















