Test: Fabrication Processes (Welding) - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Fabrication Processes (Welding) - 2
Fabrication weldability test is used to determine
Match List I (Welding problems) with List II (Causes) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:

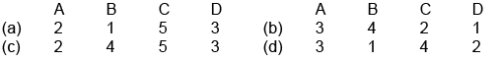
[IES - 2004]
By which one of the following methods gray iron is usually welded?
In a gas welding of mild steel using an oxy-acetylene flame, the total amount of acetylene consumed is 10 litre. The oxygen consumption from the cylinder is
In arc welding, d.c. reverse polarity is used to hear greater advantage in
In an arc welding process, the voltage and current are 25 V and 300 A respectively. The arc heat transfer efficiency is 0.85 and welding speed is 8 mm/see. The net heat input (in J/mm) is
An arc welded joint is shown in the above figure. The part labelled 'B' in the figure is known as
In which of the following welding processes, flux is used in the form of granules?
In resistance welding, heat is generated due to the resistance between
Assertion (A): Spot welding is adopted to weld two overlapped metal pieces between two electrode points. Reason (R): In this process when current is switched on, the lapped pieces of metal are heated in a restricted area.
Two 1 mm thick steel sheets are to be spot welded at a current of 5000 A. Assuming effective resistance to be 200 micro-ohms and current flow time of 0.2 second, heat generated during the process will be
Assertion (A): In electron beam welding process, vacuum is an essential process parameter
Reason (R): Vacuum provides a highly efficient shield on weld zone
Match List I (Welding processes) with List II (Features) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
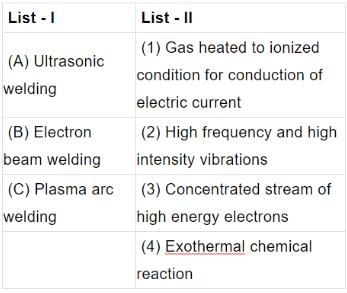
Codes:
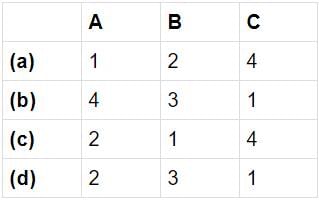
Which one of the following is a solid state joining process?
Consider the following statements: The magnitude of residual stresses in welding depends upon
1. design of weldment
2. support and clamping of components
3. welding process used
4. amount of metal melted / deposited
Which of the statements given above are correct?
The ratio of acetylene to oxygen is approximately………. for a neutral flames used in gas welding.
In Oxyacetylene gas welding, temperature at the inner cone of the flame is around
In oxy-acetylene gas welding, for complete combustion, the volume of oxygen required per unit of acetylene is
Oxyacetylene reducing flame is used while carrying out the welding on
Assertion (A): The electrodes of ac arc welding are coated with sodium silicate, whereas electrodes used for dc arc welding are coated with potassium silicate binders.
Reason (R): Potassium has a lower ionization potential than sodium.
In d.c. welding, the straight polarity (electrode negative) results in
Which one of the following statements is correct?
In MIG welding, the metal is transferred into the form of which one of the following?
For butt -welding 40 mm thick steel plates, when the expected quantity of such jobs is 5000 per month over a period of 10 year, choose the best suitable welding process out of the following available alternatives.
Resistance spot welding is performed on two plates of 1.5 mm thickness with 6 mm diameter electrode, using 15000 A current for a time duration of 0.25 seconds. Assuming the interface resistance to be 0.0001 Ω , the heat generated to form the weld is
Which one of the following is not an electric resistance method of welding?
In which one of the following welding techniques is vacuum environment required?



















