Test: Probability & Statistics- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Probability & Statistics- 2
A probability density function is of the form
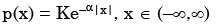
The value of K is
If E denotes expectation, the variance of a random variable X is given by
Px(x) = M exp(–2|x|) – N exp(–3 |x|) is the probability density function for the real random variable X, over the entire x axis. M and N are both positive real numbers. The equation relating M and N is
A fair coin is tossed independently four times. The probability of the event “the number of time heads shown up is more than the number of times tails shown up” is
The standard deviation of a uniformly distributed random variable between 0 and 1 is
The probability of a defective piece being produced in a manufacturing process is 0.01. The probability that out of 5 successive pieces, only one is defective, is
An unbiased coin is tossed three times. The probability that the head turns up in exactly two cases is
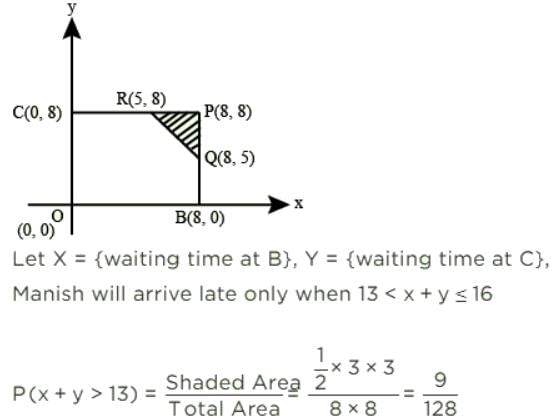
Manish has to travel from A to D changing buses at stops B and C enroute. The maximum waiting time at either stop can be 8 minutes each, but any time of waiting up to 8 minutes is equally likely at both places. He can afford up to 13 minutes of total waiting time if he is to arrive at D on time. What is the probability that Manish will arrive late at D?
From a pack of regular from a playing cards, two cards are drawn at random. What is the probability that both cards will be Kings, if first card in NOT replaced
A single die is thrown twice. What is the probability that the sum is neither 8 nor 9?
A coin is tossed 4 times. What is the probability of getting heads exactly 3 times?
A box contains 2 washers, 3 nuts and 4 bolts. Items are drawn from the box at random one at a time without replacement. The probability of drawing 2 washers first followed by 3 nuts and subsequently the 4 bolts is
A regression model is used to express a variable Y as a function of another variable X. This implies that
A class of first year B. Tech. Students is composed of four batches A, B, C and D, each consisting of 30 students. It is found that the sessional marks of students in Engineering Drawing in batch C have a mean of 6.6 and standard deviation of 2.3. The mean and standard deviation of the marks for the entire class are 5.5 and 4.2, respectively. It is decided by the course instructor to normalize the marks of the students of all batches to have the same mean and standard deviation as that of the entire class. Due to this, the marks of a student in batch C are changed from 8.5 to
A hydraulic structure has four gates which operate independently. The probability of failure off each gate is 0.2. Given that gate 1 has failed, the probability that both gates 2 and 3 will fail is
There are 25 calculators in a box. Two of them are defective. Suppose 5 calculators are randomly picked for inspection (i.e., each has the same chance of being selected), what is the probability that only one of the defective calculators will be included in the inspection?
If probability density functions of a random variable X is
Then, the percentage probability
Two coins are simultaneously tossed. The probability of two heads simultaneously appearing is
A fair coin is tossed three times in succession. If the first toss produces a head, then the probability of getting exactly two heads in three tosses is
A box contains 4 white balls and 3 red balls. In succession, two balls are randomly selected and removed from the box. Given that the first removed ball is white, the probability that the second removed ball is red is
Consider a Gaussian distributed radom variable with zero mean and standard deviation σ. The value of its cumulative distribution function at the origin will be
The probability that there are 53 Sundays in a randomly chosen leap year is
Two dices are rolled simultaneously. The probability that the sum of digits on the top surface of the two dices is even, is
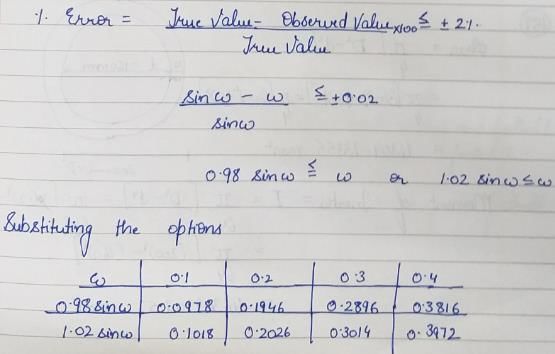
The function y = sin φ, (φ > 0) is approximated as y = φ, where φ is in radian. The maximum value of φ for which the error due to the approximation is with in ±2% is
Aishwarya studies either computer science or mathematics everyday. if the studies computer science on a day, then the probability that she studies mathematics the next day is 0.6. If she studies mathematics on a day, then the probability that she studies computer science the next day is 0.4. Given that Aishwarya studies computer science on Monday, what is the probability that she studies computer science on Wednesday?
An examination paper has 150 multiple-choice questions of one mark each, with each question having four choices. Each incorrect answer fetches – 0.25 mark. Suppose 1000 students choose all their answers randomly with uniform probability. The sum total of the expected marks obtained all these students is
Let f(x) be the continuous probability density function of a random variable X. The probability that a < X ≤ b, is
Let P(E) denote the probability of the even E. Given the values of
respectively are
For each element is a set of size 2n, an unbiased coin is tossed. The 2n coin tossed are independent. An element is chosen if the corresponding coin toss were head. The probability that exactly n elements are chosen is