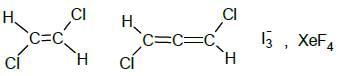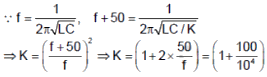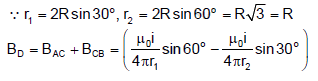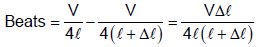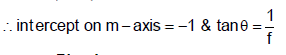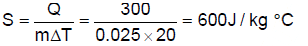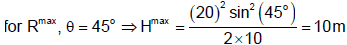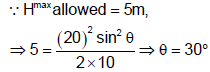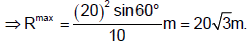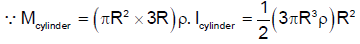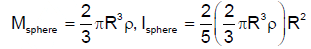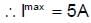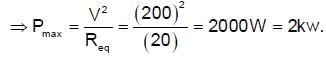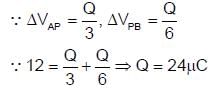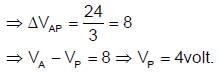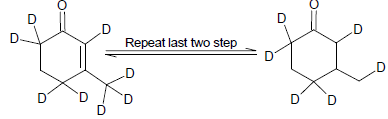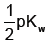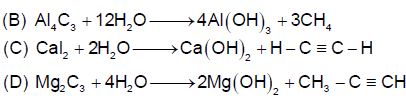JEE Advanced Practice Test- 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced Practice Test- 2
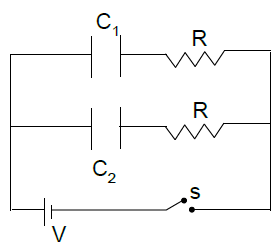
In the circuit shown C1 = 2C2. Switch S is closed at time t = 0. Let i1 & i2 be the current flowing through C1 and C2 at any time t, then the ratio I1/I2
The capacitor of an oscillatory circuit of frequency 104Hz is enclosed in a container. When the container is evacuated, the frequency changes by 50 Hz, the dielectric constant of the gas is
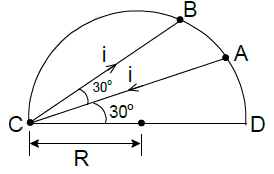
A current carrying wire is placed in the grooves of an insulating semicircular disc of radius ‘R’ as shown. The current enters atpoint A and leaves point B. Determine the magnetic field at point D.
The organ pipes, both closed at one end, have lengths ℓ and ( ℓ + Δ ℓ) vibrates in fundamental mode. Neglect end correction. If the velocity of sound in air is v, then the number of beats/sec is (assume Δ ℓ << ℓ)
Light is incident normally on face AB of a prism as shown. Aliquid of refractive index μ is placed on face AC of the prism.The prism is made of glass of refractive index 3/2. The limit of μ for which total internal reflection takes place on face AC is
Figure shows variation of magnification m(produced by a thin convexlens) and distance v of image from pole of the lens. Which of the following statements are correct?
A certain substance has a mass of 50g/mol. When 300J of heat is added to 25 gm of sample of this material, its temperature rises from 25 to 45oC.
Q. The specific heat capacity of the substance is
A certain substance has a mass of 50g/mol. When 300J of heat is added to 25 gm of sample of thismaterial, its temperature rises from 25 to 45oC.
Q. The molar heat capacity of the substance is
Matrix – Match Type
This section contains 2 questions. Each question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column II are labelled p, q, r, s and t. Any given statement in Column I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as illustrated in the following example:
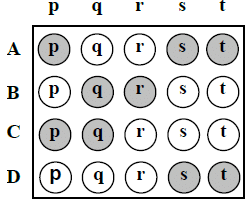
If the correct matches are A – p, s and t; B – q and r; C – p and q; and D – s
and t; then the correct darkening of bubbles will look like the following:
1. Match the following
A projectile is projected with a speed 20 m/s from the floor of a 5 m high room as shown. The maximum horizontal range of the projectile is found to be m. Find n [Take g = 10 ms-2].
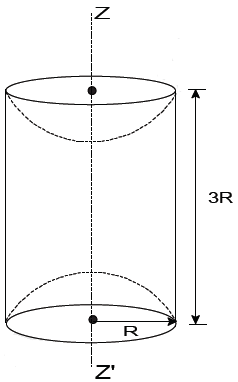
A solid cylinder is made of radius R and height 3R having mass density ρ. Now two half spheres of radius R are removed from both ends. The moment of intertia of remaining portion about axis ZZ’ can be calculated as Find K.
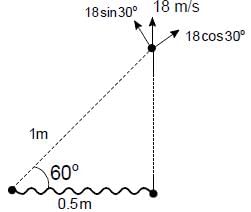
Two particles each of mass m are connected by a string of length 1m. The particles are kept on a smooth horizontal plane. The initial separation between the particles is 0.5 m. One of the particles is given a velocity 18 m/s as shown. Find the magnitude of angular velocity of one particle with respect to the other particle just after the string becomes taut (in m/s)
A 10 m long nichrome wire having 80Ω resistance has current carrying capacity of 5 A. This wire can be cut into equal parts and equal parts can be connected in series or parallel. What is the maximum power which can be obtained as heat by the wire from a 200 V mains supply (in KW).
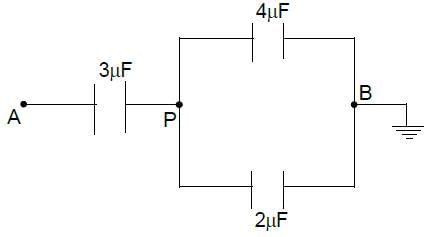
In the given figure, a potential of +12 volt is given to point A, and point B is earthed. What is the potential at point P in volt?
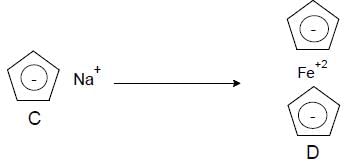
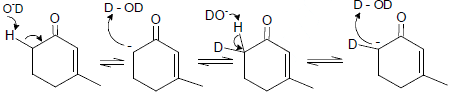
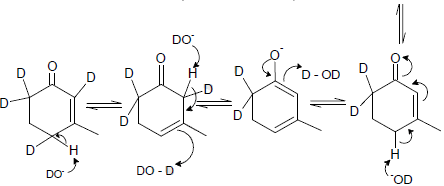
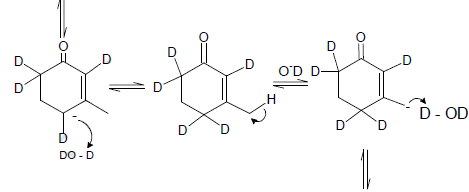
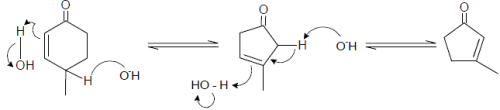
Cyclopentadiene
Which one of the following in not true about D.
Which one of the following reaction is not possible:-
(I) Co(CO)6
(II) Co(CO)5NH3
(III) Co(CO)4(NH3)2
(IV) Co(CO)3(NH3)3
(V) Co(CO)2(NH3)4
(VI) Co(CO)(NH3)5
Which statement is correct for these compounds?
Which among the following statements is/are correct?
4.5 g of Al (atomic mass = 27) is deposited at cathode from Al+3 solution by certain quantity of charge. The correct statement/s is/are:
On the basis of aromaticity, there are three types of compounds i.e. aromatic, non-aromatic and antiaromatic. The increasing order of stability of these compounds are is under: Anti-aromatic compound < non-aromatic compound < aromatic compounds. Compounds to be aromatic follow the following conditions (according to valence bond theory)
(i) The compounds must be be cyclic in structure having (4n + 2)π e–, where n = Hückel’s number = 0, 1, 2, 3 et.c
(ii) The each atoms of the cyclic structure must have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. the atoms of the compounds have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. usually have sp2 hybrid or planar.
(iii) There must be a ring current of π electrons in the ring or cyclic structure i.e. cyclic structure must undergo resonance .
Compounds to be anti-aromatic, it must have 4nπe– where n = 1, 2… and it must be planar and undergo resonance. Non-aromatic compounds the name itself spells that compounds must be non-planar irrespective of number of π electrons. Either it has 4nπe– or (4n + 2) π electrons it does not matter. The rate of reaction of any aromatic compounds depends upon the following factors:
(i) Electron density
(ii) stability of carbocation produced
Higher the amount of electron density of the ring, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic substitution and vice-versa. Similarly, higher will be the stability of the produced carbocation after the attack of electrophile, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic substitution. There is a great effect of kinetic labelling on the rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution. As we known that higher the atomic weight or, molecualr weight, higher will be the van der Waal’s force of attraction or, bond energy. Since there will be effect of kienetic labelling if the 2nd step of the reaction will be the slow step, (r.d.s.) otherwise there will be no effect of kinetic labelling.
Q. Which of the following is correct order of the rate of reaction of C6H6, C6D6 and C6T6 towards
sulphonation?
On the basis of aromaticity, there are three types of compounds i.e. aromatic, non-aromatic and antiaromatic. The increasing order of stability of these compounds are is under:
Anti-aromatic compound < non-aromatic compound < aromatic compounds. Compounds to be aromatic follow the following conditions (according to valence bond theory)
(i) The compounds must be be cyclic in structure having (4n + 2)π e–, where n = Hückel’s number = 0, 1,2, 3 et.c
(ii) The each atoms of the cyclic structure must have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. the atoms of the compounds have unhybridised p-orbital i.e. usually have sp2 hybrid or planar.
(iii) There must be a ring current of π electrons in the ring or cyclic structure i.e. cyclic structure must undergo resonance .
Compounds to be anti-aromatic, it must have 4nπe– where n = 1, 2… and it must be planar and undergo resonance. Non-aromatic compounds the name itself spells that compounds must be non-planar irrespective of number of π electrons. Either it has 4nπe– or (4n + 2) π electrons it does not matter.
The rate of reaction of any aromatic compounds depends upon the following factors:
(i) Electron density
(ii) stability of carbocation produced
Higher the amount of electron density of the ring, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic substitution and vice-versa. Similarly, higher will be the stability of the produced carbocation after the attack of electrophile, higher will be its rate towards aromatic electrophilic substitution. There is a great effect of kinetic labelling on the rate of aromatic electrophilic substitution. As we known that higher the atomic weight or, molecualr weight, higher will be the van der Waal’s force of attraction or, bond energy. Since there will be effect of kienetic labelling if the 2nd step of the reaction will be the slow step, (r.d.s.) otherwise there will be no effect of kinetic labelling.
Q. Which of the following is correct order of the rate of reaction of C6H6, C6D6 and C6T6 towards
nitrations?
The Bertholet’s equation of state for 1 mole real gas is given as under:
Where a and b are van der Waal’s constants. van der Waal’s constant “a” signifies, the force of attraction among the gas molecules. van der Waal’s constant “b” signifies incompressible volume i.e. volume having no effect of compression and expansion. It is also known as co-volume. Thereby the volume having effect of compression and expansion i.e. compressible volume = V – b (for 1 mole real gas). One of the form of van der Waal’s equation of state is virial equation. The virial equation for 1 mole real gas is as under:
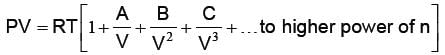
where A, B, C are known as 2nd, 3rd and 4th virial coefficients respectively. The temperature at which real gases obey ideal gas equation (PV = RT), is known as Boyles temperature i.e. TB.
Q. If where Ti is the inversion temperature, then which of the following is the correct relation of the Boyle’s temperature TB obtained by the Bertholet’s equation
The Bertholet’s equation of state for 1 mole real gas is given as under:
Where a and b are van der Waal’s constants. van der Waal’s constant “a” signifies, the force of attraction among the gas molecules. van der Waal’s constant “b” signifies incompressible volume i.e. volume having no effect of compression and expansion. It is also known as co-volume. Thereby the volume having effect of compression and expansion i.e. compressible volume = V – b (for 1 mole real gas). One of the form of van der Waal’s equation of state is virial equation. The virial equation for 1 mole real gas is as under:
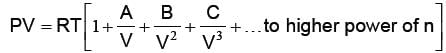
where A, B, C are known as 2nd, 3rd and 4th virial coefficients respectively. The temperature at which real gases obey ideal gas equation (PV = RT), is known as Boyles temperature i.e. TB.
Q. If the value of a and b increases by 8 times and 2 times respecively, then new Boyle’s temperature will increases by how many times and what will be effect on the ease of liquification ?
The Bertholet’s equation of state for 1 mole real gas is given as under:
Where a and b are van der Waal’s constants. van der Waal’s constant “a” signifies, the force of attraction among the gas molecules. van der Waal’s constant “b” signifies incompressible volume i.e. volume having no effect of compression and expansion. It is also known as co-volume. Thereby the volume having effect of compression and expansion i.e. compressible volume = V – b (for 1 mole real gas). One of the form of van der Waal’s equation of state is virial equation. The virial equation for 1 mole real gas is as under:
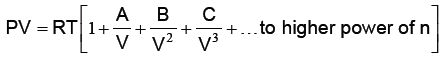
where A, B, C are known as 2nd, 3rd and 4th virial coefficients respectively. The temperature at which real gases obey ideal gas equation (PV = RT), is known as Boyles temperature i.e. TB.
Q. If the third virial coefficient of 4 moles of mono-atomic as is 0.04 (lit/mol)2 at NTP, then what will be the real gas at NTP?
(Matrix-Match Type)
This section contains 2 questions. Each question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column II are labelled p, q, r, s and t. Any given statement in Column I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as
illustrated in the following example:
If the correct matches are A – p, s and t; B – q and r; C – p and q; and D – s and t; then the correct darkening of bubbles will look like the following:
1. Match the following.
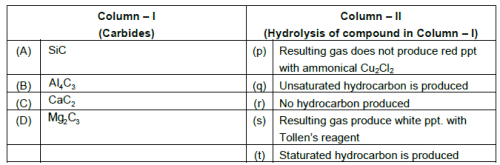
(Matrix-Match Type)
This section contains 2 questions. Each question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column II are labelled p, q, r, s and t. Any given statement in Column I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as
illustrated in the following example:
If the correct matches are A – p, s and t; B – q and r; C – p and q; and D – s and t; then the correct darkening of bubbles will look like the following:
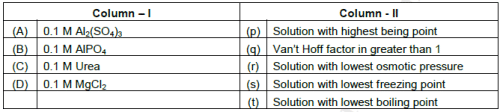
2. Match the solution given in column I with the properties given in column II.
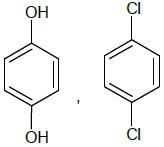
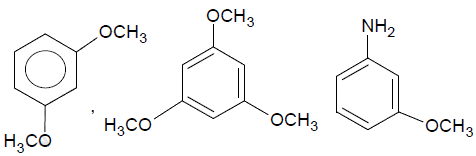
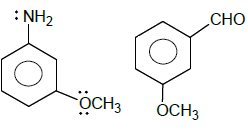
Examine the structural fromuals shown below and identify how many compounds will show coupling reaction with diazonium salt faster than anisole
For the first order reaction The value of x will be
Total no of molecules/ions which have non zero dipole moment is