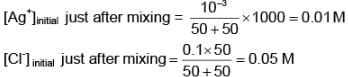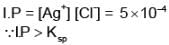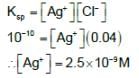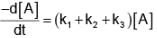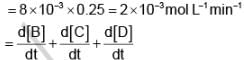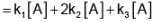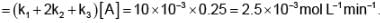JEE Advanced Practice Test- 3 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced Practice Test- 3
An engine whistling at a constant frequency n0 and moving with a constant velocity goes past a stationary observer. As the engine crosses him, the frequency of the sound heard by him changes by a factor f. The actual difference in the frequency of the sound heard by him before and after the engine across him is
A ball of density ρ0 falls from rest from point P onto the surface of a liquid of density ρ in time T. It enters the liquid stops moves up and returns to P in a total time 3T. Neglect viscosity, surface tension and splashing. The ratio p/p0 is equal to
When an object is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length f, a virtual image is produced with a magnification of 2. To obtain a real image with a magnification of 2. The object has to be moved by a distance equal to
A solid cube is placed on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between them is μ, where μ < 1/2 . A variable horizontal force is applied on the cube’s upper face, perpendicular to one edge and passing through the mid-point of that edge. The maximum acceleration with which it can move without toppling is
A spherical body of mass m, radius r and moment of inertia I about its centre moves along the x-axis. Its centre of mass moves with velocity = v0 and it rotates about its centre of mass with angular velocity ω0.LO = lω0 + mvor . The angular momentum of the body about the origin O is
DIRECTION ;- This section contains 2 multiple choice questions from 8 to 9. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for its answer, out which ONE OR MORE is/are correct
The temperature of a solid object is observed to be constant during a period. In this period
The electric potential decreases uniformly from 120 V to 80 V as one moves on the axis from x = –1 cm to x = 1 cm. The electric field at the origin
This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon the first paragraph 2 multiple choice questions and based upon the second paragraph 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions has four choices A), B), C) and D) out of WHICH ONLY ONE IS CORRECT.
paragraph for question no.12 and 13
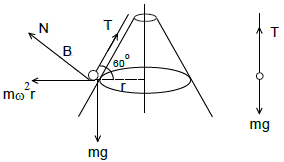
The base of a hollow right cone of semi vertical angle 30o is fixed to a horizontal plane. Two particle each of mass m are connected by a light inextensible string which passes through a small hole in the vertex of the cone. One particle A hangs at rest inside the cone. The other particle B moves on the outer smooth surface of the cone at a distance ℓ from vertex in a horizontal circle with centre at A. Neglecting friction, now answer the following.
The tention in the string is
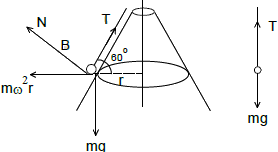
The base of a hollow right cone of semi vertical angle 30o is fixed to a horizontal plane. Two particle each of mass m are connected by a light inextensible string which passes through a small hole in the vertex of the cone. One particle A hangs at rest inside the cone. The other particle B moves on the outer smooth surface of the cone at a distance ℓ from vertex in a horizontal circle with centre at A. Neglecting friction, now answer the following.
The angular velocity of B is
Paragraph For Question No.14 and 16
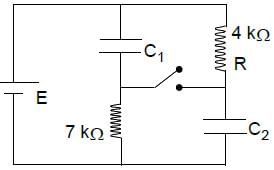
The switch S has been closed for long time and the electric circuit shown carries a steady current. Let C1 = 3μF, C2 = 6μF, R1 = 4 kΩ and R2 = 7.0 kΩ. The power dissipated in R2 is 2.8 W.
The power dissipated to the resistor R1 is
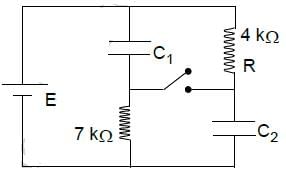
The switch S has been closed for long time and the electric circuit shown carries a steady current. Let C1 = 3μF, C2 = 6μF, R1 = 4 kΩ and R2 = 7.0 kΩ. The power dissipated in R2 is 2.8 W.
The power dissipated to the resistor R1 is
The charge on capacitance C1 and C2 are respectively
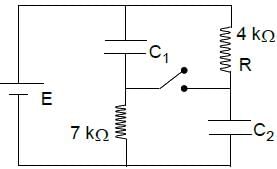
The switch S has been closed for long time and the electric circuit shown carries a steady current. Let C1 = 3μF, C2 = 6μF, R1 = 4 kΩ and R2 = 7.0 kΩ. The power dissipated in R2 is 2.8 W.
The power dissipated to the resistor R1 is
Long time after switch is opened the charge on C1 is
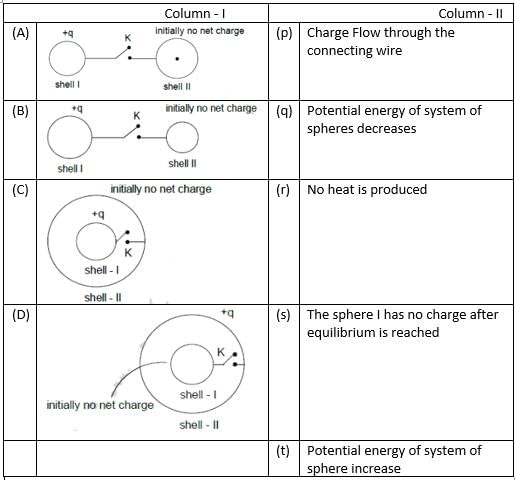
Column – I gives certain situation involving two thin conducting shells connected by a conducting wire via a key K. In all situation one sphere has net charge +q and other sphere has no net charge. After the key K is pressed
column – II gives some resulting effect. Match the figures in column with the statements in column – II.
A particle of mass 2 kg is moving on straight line under the action of force F = (8 – 2x)N. The
particle is released at rest from x = 6m. For the sub-sequent motion match the following (All the
values in the right column are in there SI units).

This section contains 6 questions. Each question, when worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
In the arrangement shown in figure, pulley are light and frictionless, threads are inextensible and mass of blocks A, B and C are m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 4 kg and m3 = 2.5 kg respectively and co-efficient of friction for both the planes is μ = 0.50. Calculate the acceleration of block A (in m/sec), when the system is released from rest. (g = 10 m/sec)
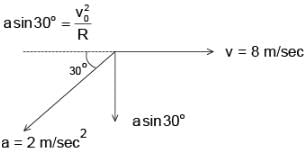
The figure shows the velocity and acceleration of a point like body at the initial moment of its motion. The acceleration vector of the body remains constant. The minimum radius of curvature of trajectory of the body is
A disc ‘A’ of mass M is placed at rest on the smooth inclined surface of inclination θ. A ball B of mass m is suspended vertically from the centre of the disc A by a light inextensible string of light ℓ as shown in the figure. If the acceleration of the disc B immediately after the system is released from rest
A uniform rod AB of mass M and length R √2 is moving in a vertical plane inside a hollow sphere of radius R. The sphere is rolling on a fixed horizontal surface without slipping with velocity of its centre of mass 2v, when the end B is at the lowest position, its speed is found to be v as shown in the figure. If the kinetic energy of rod at this instant is 4/k mv2. Find k.
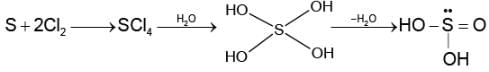
Sulphur reacts with chlorine in 1 : 2 ratio and forms X. Hydrolysis of X gives a sulphur compoundY. What is the hybridization state of central atom in the compound Y?
Find out the correct representation of trans - decaline
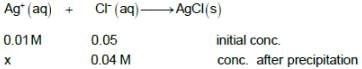
50 ml of a solution containing 10-3 mol of Ag+ is mixed with 50 ml of a 0.1 M HCl solution. Howmuch [Ag+] remains in solution? Given: Ksp of AgCl = 10-10
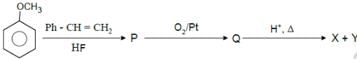
Where X is a compound that forms azodye with benzene diazonium chloride in faintly basic medium.
Hence the products P, X and Y are respectively.
Which of the following solutions show lowering of vopour pressure on mixing?
Which of the following will produce aromatic compound as a product?
This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon the first paragraph 2 multiple choice questions and based upon the second paragraph 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions has four choices A), B), C) and D) out of WHICH ONLY ONE IS CORRECT.
Paragraph For Question No.12 and 13
A white compound (A) on strong heating decomposes to produce two products (B) and (C). (B) on reaction with white phosphorus produces (D), which is a strong dehydrating agent. (D) on reaction with perchloric acid converts it to its anhydride.
The compound (A) is
Paragraph For Question No.12 and 13
A white compound (A) on strong heating decomposes to produce two products (B) and (C). (B) on reaction with white phosphorus produces (D), which is a strong dehydrating agent. (D) on reaction with perchloric acid converts it to its anhydride.
The product/s obtained on hydrolysis of (D) is
A’ is a substance that converts into B, C and D by three first order parallel paths simultaneously according to the following stoichiometry
The partial t1/2 of A along path I and path II are 173.25 min and 346.5 min respectively. The energies of activation of the reaction along path I, path II and path III are 40, 60 and 80 kJ/mol respectively.
The percent distribution of C in the product mixture B, C and D at any time is equal to
A’ is a substance that converts into B, C and D by three first order parallel paths simultaneously according to the following stoichiometry
The partial t1/2 of A along path I and path II are 173.25 min and 346.5 min respectively. The energies of activation of the reaction along path I, path II and path III are 40, 60 and 80 kJ/mol respectively.
The initial rate of consumption of A and the sum of the initial rate of formation of B, C and D arerespectively, taking [A] = 0.25 M, equal to
A’ is a substance that converts into B, C and D by three first order parallel paths simultaneously according to the following stoichiometry
The partial t1/2 of A along path I and path II are 173.25 min and 346.5 min respectively. The energies of activation of the reaction along path I, path II and path III are 40, 60 and 80 kJ/mol respectively.
The overall energy of activation of A along all the three parallel path is equal to