CUET PG Economics Mock Test - 3 - CUET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - CUET PG Economics Mock Test - 3
Sequence the following in increasing order of integration of member economies.
(A) Free Trade Area
(B) Economic Union
(C) Custom Union
(D) Preferential Trade Agreements
(E) Common Market
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) Free Trade Area
(B) Economic Union
(C) Custom Union
(D) Preferential Trade Agreements
(E) Common Market
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match List-I with List-II:
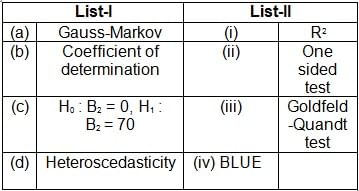
Choose the correct option from those given below:

For a moderately skewed distribution, the value of mode is 10 and value of median is 20. Then the mean is
Measurement of income inequality is done by :
A. Gini coefficient
B. Lorenz curve
C. Palma Ratio
D. Deprivation ratio
E. Phillips Curve
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
With reference to the Demand-Pull Inflation, consider the following statements:
1. Demand-pull inflation exists when aggregate demand for a good or service outstrips aggregate supply.
2. If aggregate demand rises faster than productive capacity, then firms will respond by putting up prices, creating inflation.
3. Demand-Pull inflation is also when overall prices increase (inflation) due to increases in the cost of wages and raw materials.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Which of the following can cause Demand-Pull Inflation?
1. Population Pressure
2. Increase in Net Exports
3. Monetary Stimulus
4. Policy Decisions
5. Increase in indirect taxes
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Given below are two statements
Statement I: Dualism refer to economic and social divisions in an economy, such as difference in the level of technology between sectors or regions, differences in the degree of geographic development and differences in social customs and attitudes.
Statement II: The developing countries in the early stage of development experience dualism, which have implications for future pattern and pace of development.
In the light of the above statements. choose the most correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements about price elasticity of demand is correct?
(a) Price elasticity of demand is a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good.
(b) Price elasticity of demand is computed as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
(c) Price elasticity of demand in the long run would be different from that of the short run.
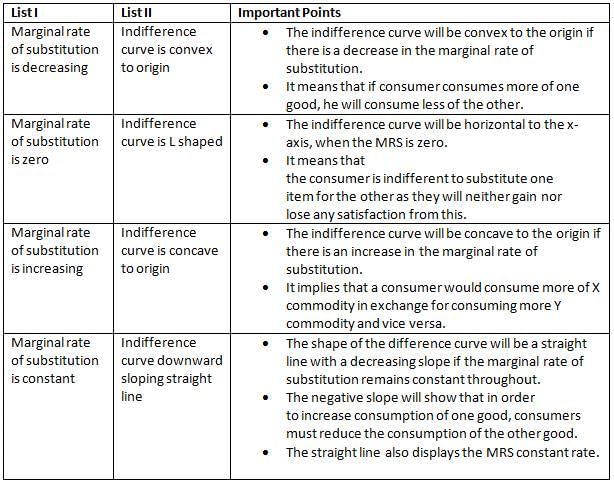
Match the items of List I with the items of List II and choose the correct answer from the code given below.
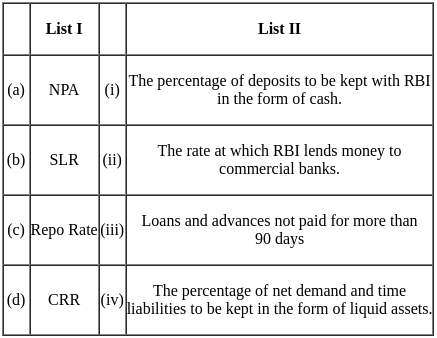
Match List-I and List-II
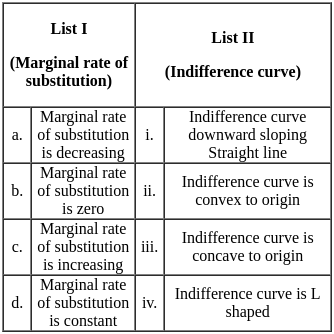
Choose the correct code:
Dusenberry was of the opinion that less developed countries will have serious and adverse effect on their balance of payments due to :
Which of the following is/are the possible impacts of the devaluation of a currency in a country?
1. It may help in combating inflation.
2. It may lead to an increase in aggregate demand for domestically produced goods.
3. It may lead to an improvement in the current account balance.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
The negative network externality in which a consumer wishes to own an exclusive or unique good such as specially designed sports car is:
Which distribution is characterized by a symmetric bell-shaped curve?
Which of the following are correct?
(A) Current account includes merchandise export
(B) Current account do not include merchandise export
(C) Current account includes invisible export
(D) Current account do not includes invisible export
(E) Current account includes both merchandise exports and imports and invisible exports and imports
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
For oil-importing countries, the increase in oil prices in 1970's and mid-2000 contributed to which of the following:
(a) Improving terms of trade
(b) Balance of trade deficits
(c) Price Inflation
(d) Constrained economic growth
Choose the correct answer from the codes given below :
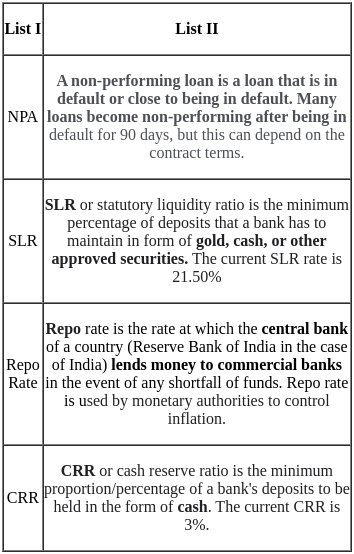
Which of the following statement regarding Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) is/are correct?
1. It is used while helping banks in resolving cash shortages.
2. It is performed by lowering the repo rate.
3. RBI can use it to control inflation.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
If the consumer wants to buy x1 units of item 1 and x2 units of item 2 and the prices of the two items are p1and p2 respectively, and M is the income of the consumer, then p1x1 + p2x2 ≤ M is called the consumer's _______ .
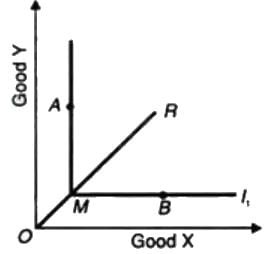
Which of the followingis the usual shape of the indifference curve of two complementary goods, such as pencil and eraser?



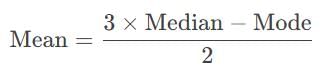
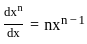
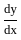 = 2x
= 2x