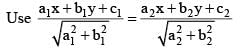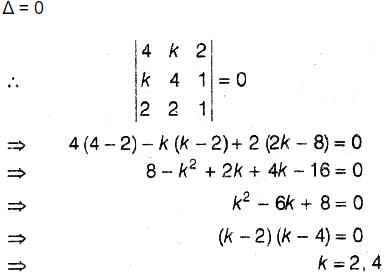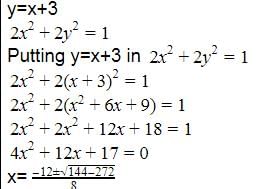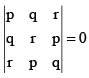JEE Advanced Level Test: Straight Lines- 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced Level Test: Straight Lines- 2
Angles made with the x - axis by two lines drawn through the point (1, 2) and cutting the line x + y = 4 at a distance 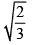 from the point (1,2) are
from the point (1,2) are
Consider a family of straight lines (x + y) + λ(2x - y + 1) = 0. Find the equation of the straight line belonging to this family that is farthest from (1, -3)
One side of an equilateral triangle is 3x+4y=7 and its vertex is (1,2). Then the length of the side of the triangle is
Equation of the line through the point of intersection of the lines 3x+2y+4=0 and 2x+5y-1=0 whose distance from (2,-1) is 2
The acute angle bisector between the lines 3x-4y-5 = 0, 5x+12y-26 = 0 is
Find the equation of the bisector of the angle between the lines x+2y–11 = 0, 3x–6y–5 = 0 which contains the point (1,–3)
A straight line which make equal intercepts on +ve x and y axes and which is at a distance '1' unit from the origin intersects the straight line y = 2x + 3 + √2 at (x0, y0) then 2x0 + y0
If P (1+t/√2, 2+t/√2) be any point on a line, then the range of the values of t for which the point p lies between the parallel lines x+2y = 1 and 2x + 4y = 15 is
Locus of point of intersection of the perpendicular lines one belonging to (x + y – 2) + λ(2x + 3y – 5) = 0 and other to (2x + y – 11) + λ(x + 2y – 13) = 0 is a
A non-trival solution of the system of equations x + λy + 2z = 0 , 2x + λz = 0 , 2λx - 2y + 3z = 0 is given by x : y : z =
The number of values of k for which the linear equations 4x + ky + 2z = 0 , kx + 4y + z = 0 , 2x + 2y + z = 0 posses a non zero solution is
The locus of the image of the point (2, 3) in the line (x - 2y + 3) + λ (2x - 3y + 4) = 0 (λ ∈ R) is
A straight line L with negative slope passes through the point (8, 2) and cuts the positive co-ordinate axes at points P and Q. As L varies, the absolute minimum value of OP + OQ (O being origin) is
When the origin is shifted to a point P, the point (2, 0) is transformed to (0, 4) then the coordinates of P are
If the transformed equation of a curve when the origin is translated to (1, 1) is X2 + Y2 + 2X – Y + 2 = 0 then the original equation of the curve is
In order to make the first degree terms missing in the equation 2x2 + 7y2 + 8x – 14y + 15 = 0, the origin should be shifted to the point
The distance of any point (x, y) from the origin is defined as d = max {| x |, | y |} , then the distance of the common point for the family of lines x(1 + λ) + λy + 2 + λ = 0 (λ being parameter) from origin is
If the point P(α2, α) lies in the region corresponding to the acute angle between the lines x - 3y = 0 and x - 5y = 0 then
Let ax + by + c = 0 be a variable straight line, where a, b and c are 1st, 3rd and 7th terms of some increasing A. P. Then the variable straight line always passes through a fixed point which lies on
Give the family f lines, a(2x + y + 4) + b(x – 2y – 3) = 0.amongteh lines of the family, the number of lines situated at a distance of √10 from the point M(2, -3) is
Angle between the lines x2 + 2xy sec α + y2 = 0 is
If θ is the acute angle between the pair of liens x2 + 3xy – 4y2 = 0 then sin θ =
The product of perpendiculars from (k, k) to the pair of lines x2 + 4xy + 3y2 = 0 is 4/√5 then k is
The value k such that 3x2 + 11xy + 10y2 + 7x + 13y + k = 0 represents a pair of straight lines is
Angle between the pair of lines 2x2 – 7xy + 3y2 + 3x + y – 2 = 0
If the angle between the pair of lines 2x2 + λxy + 3y2 + 8x + 14y + 8 = 0 is (π/4), then the value of λ is
If the distance between the pair of parallel lines x2 + 2xy + y2 – 8ax – 8ay – 9a2 = 0 is 25√2units. What is 'a'?
The equation to the pair of lines joining the origin to the points of intersection of y = x + 3 and 2x2 + 2y2 = 1 is
If the lines ax + by + c = 0, bx + cy + a = 0 and cx + ay + b = 0 are concurrent then the point of concurrency is
If the lines 3x + 2y – 5 = 0, 2x – 5y + 3 = 0, 5x + by + c = 0 are concurrent then b + c =