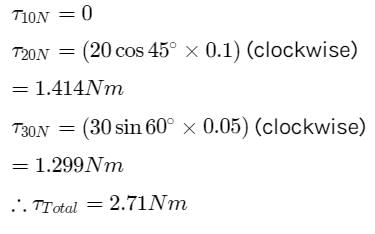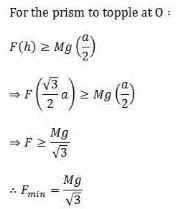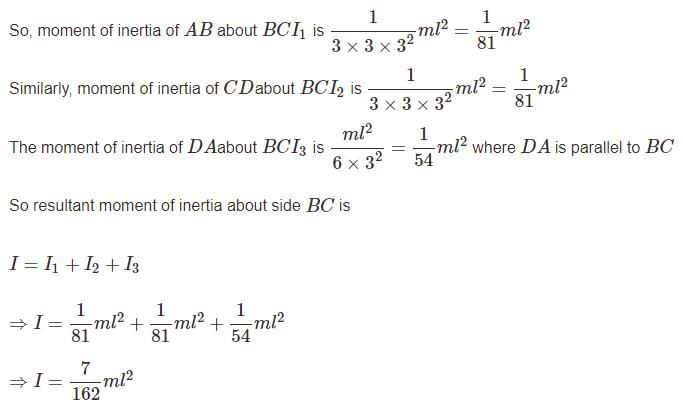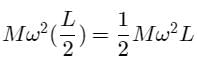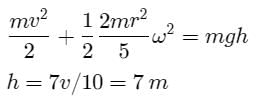Test: Rotational Motion - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Rotational Motion - 2
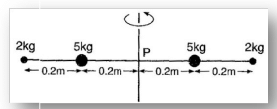
Four masses are fixed on a massless rod as shown fig. The moment of inertia about the axis P is about :
An inclined plane makes an angle of 30o with the horizontal. A ring rolling down this inclinedplane from rest without slipping has a linear acceleration equal to :
A disc of radius b and mass m rolls down an inclined plane of vertical height h. the translational speed when it reaches the bottom of the plane will be
The kinetic energy T of a particle of mass m moving in a circle of radius r varies with the distance traced, S as T = KS2. The tangential acceleration of the particle is
Two rings of radius R and nR made up of same material have the ratio of moment of inertia about an axis passing through centre is 1 : 8. The value of n is
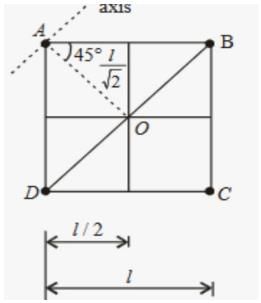
Four point masses, each of value m, are placed at the corners of a square ABCD of side l. The moment of inertia of this system about an axis passing through A and parallel to BD is
A solid sphere of radius R has moment of inertia I about its diameter. It is melted into a disc of radius r and thickness t. If its moment of inertia about the tangential axis (which is perpendicular to plane of the disc), is also equal to I, then the value of r and t are (respectively)
Point C is the centre of the rigid body shown in fig. Find the total torque acting on the body
about point C.(CW - clockwise ACW - anticlockwise)
A thin rod of length 4 l , mass 4 m is bent at the points as shown in the fig. What is the moment of inertia of the rod about the axis passing through point O and perpendicular to the plane of the paper :
In the pulley system shown, if radii of the bigger and smaller pulley are 2 m and 1 m respectively and the acceleration of block ‘A’ is 5 m/s2 in the downward direction , then the acceleration of block B will be :
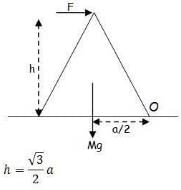
An equilateral prism of mass m rests on a rough horizontal surface with coefficient of friction m . A horizontal force F is applied on the prism as shown in the fig. If the coefficient of friction is sufficiently high so that the prism does not slide before toppling, then the minimum force required to topple the prism is :
A uniform rod of mass m and length L lies radially on a disc rotating with angular speed ω in a horizontal plane about its axis. The rod does not slip on the disc and the centre of the rod is at a distance R from the centre of the disc,. Then the kinetic energy of the rod is
A uniform rod of length L and mass M is bent to make a reactangle PQRS such that QR/PQ = 1/2 Moment of inertia of the rectangle about the side QR can be expressed as :
A uniform disc of radius 20 cm and mass 2 kg is fixed at its centre and can rotate about an axis through the centre and perpendicular to its plane. A massless cord is round along the rim of the disc. If a uniform force 2 newton is applied on the cord, tangential acceleration of a point on the rim of the disc will be
Fig shows a hemisphere of radius 4R A ball of radius R is released from position P. It rolls . A ball of without slipping along the inner surface of the hemisphere. Linear speed of its centre of mass when the ball is at position Q is
Three point masses, each m, are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side ‘α" Moment of inertia of the system about the axis COD which passes through the mass at O and lies in the plane of triangle and perpendicular to OA is
An object of mass m is projected with a velocity u at an angle 45° with the horizontal. When the object is at maximum height, its angular momentum about the point of projection is
A spherical ball of mass 2 kg is rolling without slipping with a speed 4 m/s on a rough floor. Its rotational kinetic energy is :
Fig shows a flywheel of radius 10 cm. Its moment of inertia about the rotation axis is 0.4 kg m2. A massless string passes over the flywheel and a mass 2 kg is attached at its lower end. Angular acceleration of the mass in rad/s2 is nearly.
Fig. shows a uniform rod of length l and mass M which is pivoted at end A such that it can rotate in a vertical plane. The free end of the rod B is initially vertically above the pivot and then released. As the rod rotates about A, its angular acceleration when it is inclined to horizontal at angel q is :
A thin wire of length L and uniform linear mass density r is bent into a circular loop with centre O as shown. The moment of inertia of the loop about the axis XX is
A metal wire of mass m and length l is rotated in a circle by holding it at one end. The breaking stress of wire is F and its area of cross-section is a. calculate the maximum frequency of rotation at which it breaks
A cylinder of mass m radius R is spinned in a clockwise direction with angular velocity ωo and then gently placed on an inclined plane for which coefficient of friction μ = tanθ, θ is the angle of inclined plane with the horizontal. The cylinder continues to spin without failing for time
A solid sphere of mass M, radius R and having moment of inertia about an axis passing through the centre of mass as I, is recast into a disc of thickness t, whose moment of inertia about an axis passing through its edge and perpendicular to its plane remains I. then, radius of the disc will be :
A cylinder is placed on a rough inclined surface of inclination q. Minimum value of coefficient of static friction between the cylinder and the surface so that the cylinder rolls without slipping is :
A tube of length L is filled completely with an incompressible liquid of mass M and is closed at both ends. The tube is then rotated in a horizontal plane about one of its ends with a uniform angular velocity w. Force exerted by the liquid at the other end is :
A small object of uniform density rolls up a curved surface with an initial velocity v. it reaches up to a maximum height of with respect to the initial position. The object is
A solid sphere of mass 2 kg rolls on a smooth horizontal surface at 10 m/s. it then rolls up a smooth inclined plane of inclination 30° with the horizontal. The height attained by the sphere before it stops is
A solid sphere is rolling without slipping on a horizontal surface. The ratio of its rotational kinetic energy to its translational kinetic energy is
A body of mass 1.5 kg rotating about an axis with angular velocity of 0.3 rad s-1 has an angular momentum of 1.8 kg m2s-1. The radius of gyration of the body about an axis is :