Test: Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
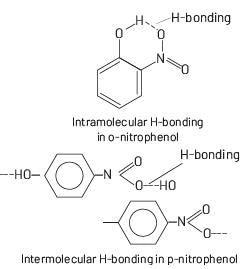
The most suitable method of separation of 1:1 mixture of ortho and para-nitrophenols is
Which of the statements is not true?
The best method for the separation of naphthalene and benzoic acid from their mixture is
Camphor is often used in molecular mass determination because
In steam distillation of toluene, the pressure of toluene in vapour is
Which of the following techniques is most suitable for purification of cyclohexanone from a mixture containing benzoic acid, isoamyl alcohol, cyclohexane and cyclohexanone?
A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of
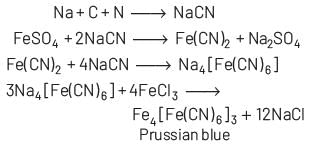
Prussian blue is formed when
The Lassaigne’s extract is boiled with conc. HNO3 while testing for halogens. By doing so it
Lassaigne’s test for the detection of nitrogen fails in