Test: Diabetes Mellitus & Insulinoma- 1 - NEET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Diabetes Mellitus & Insulinoma- 1
A morbidly obese diabetic patient on metformin presents with uncontrolled blood sugar level even after increasing dosage. He has a history of pancreatitis and a family history of bladder cancer. Patient does not want to take injections. What will you prescribe next? (AIIMS Nov 2017)
Which of the following drugs is to be immediately stopped in a patient of diabetes with hypertension, severe septicemia and serum creatinine level of 5.7 mg? (AIHMS Nov 2017)
Which of the following is known as Type 1A diabetes mellitus? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which is best for ascertaining glycemic control in a diabetic woman at the time of conception? (Recent Pattern Questions)
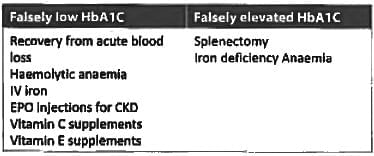
Which is best for ascertaining glycemic control in bronze diabetes? (Recent Pattern Questions)
False positive OGTT is seen in all except? (Recent Pattern Questions)
High Glycemic index is defined as value more than? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which sulfonylurea drug has the highest insulinotropic potency? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which of the following sulfonylureas cannot be used in patients with kidney failure? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which is not a side effect of Thiazolidinediones?
Hemorrhagic pancreatitis is a side effect of? (Recent Pattern Questions)
An 11 year old type 1 diabetes mellitus patient was on CSII. While on holiday with her family she has become disoriented. On admission Na = 126mEq/dl, potassium = 4.3mEq/dl, BUN = 100mg/dl, bicarbonate is 10 mEq/dl and blood sugar is 600 mg%. All are required for management except? (Recent Pattern Questions)
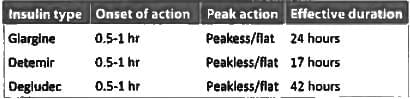
Which of the following is known as peakless insulin? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Weight loss is seen with all except? (Recent Pattern Questions)
All are complications due to use of the medical device shown here except? (Recent Pattern Questions)

Which is the most common cause of death in type I diabetes mellitus? (Recent Pattern Questions)
A type 1 DM patient on insulin is having consistent values of Pre-breakfast hyperglycemia. Hence the physician ordered self-monitoring of blood glucose including at night. The record of blood sugar of patient is given below. Which is the correct description for the recording shown? (Recent Pattern Questions)

Which of the following is the best to reduce incidence of macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetes? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which is the most common complication in type 2 diabetes mellitus? (Recent Pattern Questions)
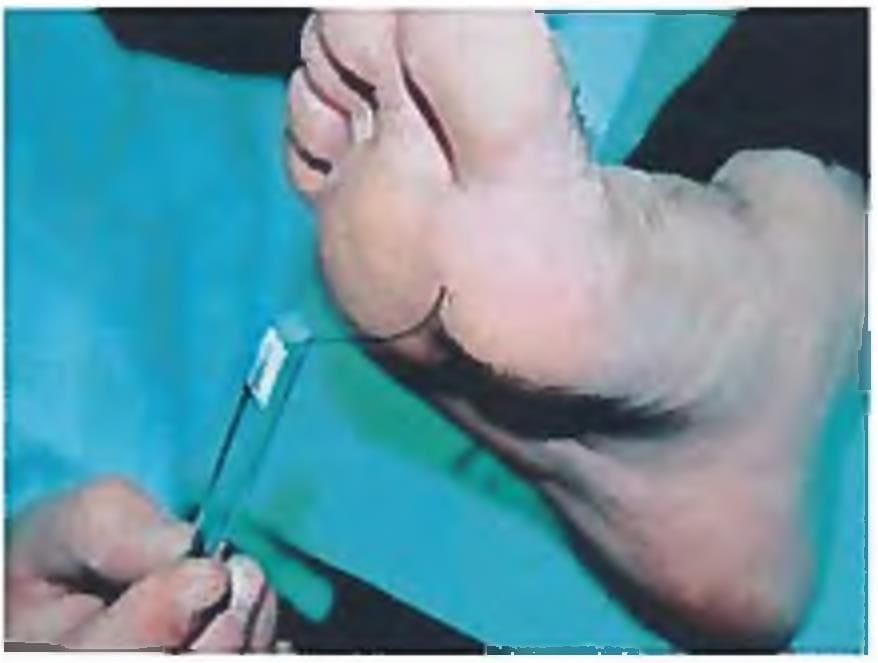
The following test is being performed on a patient of type 2 diabetes mellitus with HbA1c of 10.2%. Name the test. (Recent Pattern Questions)
Which of the following is correct about diabetic nephropathy? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Diabetic Amyotrophy presents with? (Recent Pattern Questions)
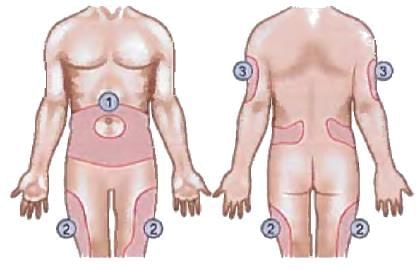
All are sites of insulin administration except? (Recent Pattern Questions)
An unconscious diabetic is brought to the ER. His medical records show he is on warfarin for atrial fibrillation. Which of the following Investigations will not be done in this patient for work up? (AIIMS Nov 2016)
Which of the following anti-diabetic drugs can be used safely in renal failure? (AIIMS Nov 2016)
Gene involved in pathogenesis of Type I Diabetes mellitus is? (Recent Question 2016-17)
Amyloid fibril deposition is seen in which type of diabetes? (Recent Question 2016-17)
All are true about diabetic ketoacidosis except? (JIPMER May 2015)
Match the antidiabetic drug which is NOT to be used in the given situation. (APPG 2016)
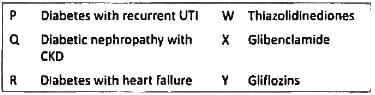
![]()