Test: Conjugate-Beam Method - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
14 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Conjugate-Beam Method - 2
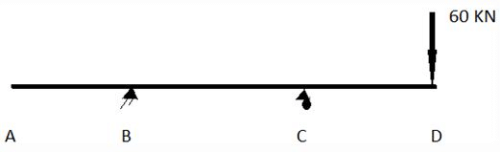
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. What will be the reaction force at support C?
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.

Q. What will be the shape of SFD in this case?
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.

Q. What is the shape of BMD for this diagram?
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. What will be the peak value of SFD?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. Where would peak value of BMD lie?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. Which type of joint would replace point A in its conjugate beam?
How many fixed joint will be there in conjugate beam?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. What will be the shear developed at hinge B in conjugate beam?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. What will be the shear developed at hinge C in conjugate beam?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. What will be the modulus of slope at point A?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. What will be the modulus of slope at point D?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. What will be the modulus of deflection of point A?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
Q. What will be the modulus of deflection of point D?
B is a hinge support and C is roller support. A and D are free ends. A load of 60 KN acts in downward direction at point D. Sign conventions are as usual.
AB = CD = 1m and BC = 3m
All force options are in kN.
All moment options are in KNM.
All deformation options are in M.
E and I are given.
There won’t be any hinge in the conjugate beam.
State whether the above statement is true or false.














