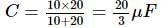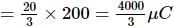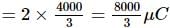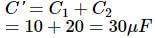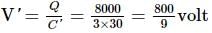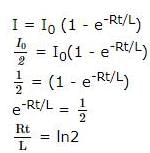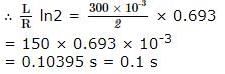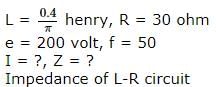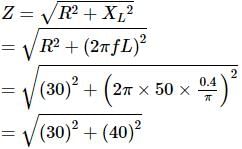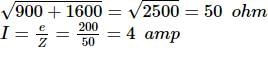AIIMS Full Mock Test 1 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - AIIMS Full Mock Test 1
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Electrical resistivity of typical insulator (≃ 1014Ω-m) is about 1022 times that of metal (≃ 10-8Ω-m) while in case of heat it is only about 103 (as KAg ≃ 400 W/mk while Kglass ≃ 1 W/mk)
Reason(R): In electrical conduction only free electrons take part while in thermal conduction both lattice and free electrons contribute.
Assertion(A): Electrical resistivity of typical insulator (≃ 1014Ω-m) is about 1022 times that of metal (≃ 10-8Ω-m) while in case of heat it is only about 103 (as KAg ≃ 400 W/mk while Kglass ≃ 1 W/mk)
Reason(R): In electrical conduction only free electrons take part while in thermal conduction both lattice and free electrons contribute.
Voltage in the secondary coil of a transformer does not depend upon.
The closest distance of approach of an α - particle travelling with a velocity 'V' to a certain nucleus is 'x'. The distance of closest approach of α - particle travelling with a velocity 3V to the same nucleus is
A 10 μF capacitor and a 20 μF capacitor are connected in series across 200 V supply line. The charged capacitors are then disconnected from the line and reconnected with their positive plates together and negative plates together and no external voltage is applied. What is the potential difference across each capacitor?
If the de Broglie wavelengths for a proton and for a α-particle are equal, then the ratio of their velocities will be
Two solid rubber balls A and B having masses 200 and 400 gm respectively are moving in opposite directions with velocity A equal to 0.3 m/s. After collision the two balls come to rest, then the velocity of B is
If intensity of incident light is increased in PEE then which of the following is true
An electron and a proton have the same de-Broglie wavelength. Then the kinetic energy of the electron is
You are given several identical resistances each of value R = 10 Ω and each capable of carrying maximum current of 1 ampere. It is required to make a suitable combination of these resistances to produce a resistance of 5Ω which can carry a current of 4 amperes. The minimum number of resistances of the type R that will be required for this job
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons from a metal versus frequency of the incident radiation gives a straight line, whose slope
A 100 mH coil carries a current of 10 A. The magnetic energy stored in the coil is
A coil of inductances 300mH and resistance 2 Ω is connected to a source of voltage 2V. The current reaches half of its steady state value in
A straight wire of length l and electric dipole moment p is bent to from a semicircle. The new electric dipole moment would be
A cylinder of radius r and length a is placed in a uniform in a uniform electric field E parallel to the axis of the cylinder. The total electric flux over the curved surface of cylinder is
In an L-R circuit, the value of L is (0.4/π) henry and the value of R is 30 ohm. If in the circuit, an alternating emf of 200 volt at 50 cycles per second is connected, the impedance of the circuit and current will be
A car travelling at a speed of 30 km/hr is brought to a halt in 8 m by applying brakes. If the same car is travelling at 60 km/hr, it can be brought to a halt with the same braking force in
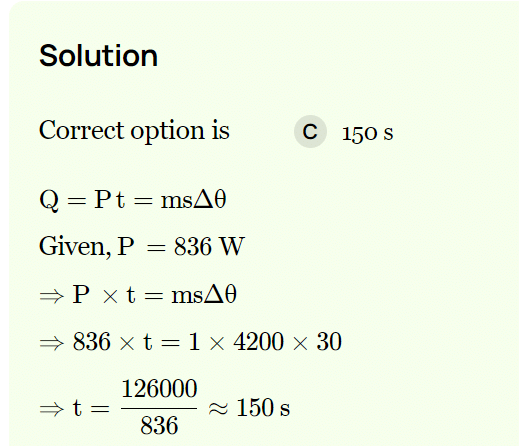
Time taken by a 846 W heater to heat one litre of water from 10ºC to 40ºC is
Two similar bar magnets P and Q each of magnetic moment M are taken. If P is cut along its axial line and Q is cut along its equatorial line, all the four pieces obtained have each of
A bar magnet, of magnetic moment M, is placed in a magnetic field of induction B. The torque exerted on it is
Two wires of the same material and length, but diameters in the ratio 1 : 2 are stretched by the same force. The elastic potential energy stored per unit volume for the two wires when stretched, will be in the ratio of
The ratio of the weight of a man in a stationary lift and when it is moving downward with uniform acceleration 'a' is 3:2. The value of 'a' is (g-Acceleration due to gravity of the earth)
Half life of a radioactive substance which disintegrates by 75% in 60 minutes will be
If a spring is extended to length l, then according to Hooke's law
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): We use a thick wire in the secondary of a step down transformer to reduce the production of heat.
Reason(R): When the plane of the armature is parallel to the line of force of magnetic field, the magnitude of the induced emf is maximum.
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Efficiency of an engine with sink temperature of zero Kelvin is 100%.
Reason(R): Keeping the sink at ice point with the source at 100oC will bring 100% efficiency.
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Energy output in a fusion reaction is very much less than energy released in the fission process.
Reason(R): Fusion is a weaker energy-source than fission.