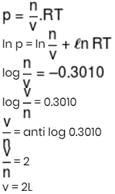JEE Main Chemistry Mock Test- 2 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Chemistry Mock Test- 2
The compound 'A' when treated with methyl alcohol and few drops of H₂SO₄ give wintergreen smell. The compound 'A' is
Which of the following will not give iodoform test?
Splitting of spectral lines under the influence of magnetic field is called
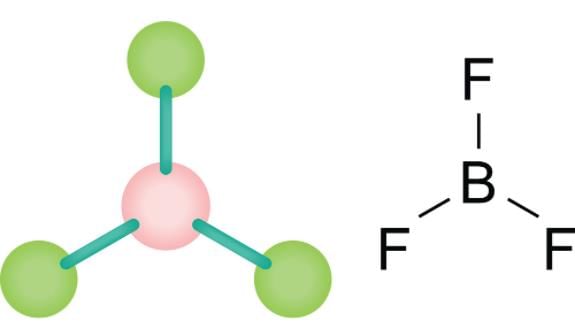
In which of the following molecules do all the atoms lie in one plane?
Pairs of species having identical shapes for molecules is
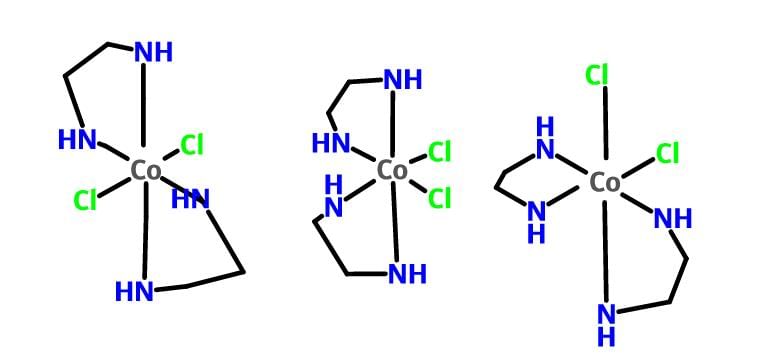
Which one of the following is expected to exhibit optical isomerism
Which of the following noble gas is least polarisable?
When HCl gas is passed through a saturated solution of common salt, pure NaCl is precipitated because
Which of the following pair represents stereoisomerism?
Which of the following pair of elements belongs to same period of the periodic table?
In view of their low ionization energies, the alkali metals are
100 ml of liquid A was mixed with 25 ml of liquid B to form a non-ideal solution. What is the volume of the mixture?
Total number of species in which atleast one atom have same hybridization as in central atom of azide ion.
N2O, C2H2, CO2, C3O2, BeF2, NO2, PF3
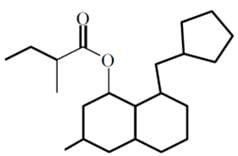
How many chiral centers are in the following compound?
An ideal solution was found to have a vapour pressure of 80 torr when the mole fraction of a non-volatile solute was 0.2. What would be the vapour pressure of the pure solvent at the same temperature?
What is the final temperature (in kelvin) of 0.10 mole monoatomic ideal gas that performs 75 cal of work adiabatically if the initial temperature is 227°C ? (use R = 2 cal/K-mol)
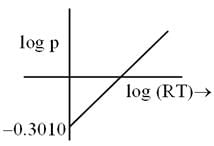
log p v/s log RT curve plotted for 1 mole ideal gas. Calculate molar volume occupied by gas? (in liter)