JEE Main Chemistry Mock Test- 3 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Chemistry Mock Test- 3
The compound 'A' when treated with methanol and few drops of H₂SO₄ give wintergreen smell. The compound 'A' is
1-Phenylethanol can be prepared by the reaction of benzaldehyde with
The spectrum produced due to transition of an electron from M to L shell is
The correct order of increasing energy of atomic orbitals is
Elimination of bromine from 2- bromobutane results in the formation of
The name of according to IUPAC nomenclature system is
The bond order in NO is 2.5 while that in NO+ is 3. Which of the following statements is true for these two species?
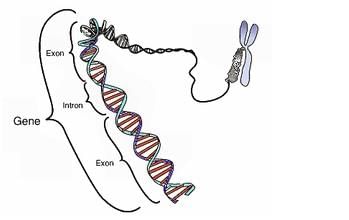
The segment of DNA which acts as the instructional manual for the synthesis of the protein is
What are the products formed in the reaction of xenon hexafluoride with silicon dioxide
The hardness of transition elements is due to their
Sodium nitroprusside reacts with sulphide ion to give a purple colour due to the formation of :
To a solution containing equimolar mixture of sodium acetate and acetic acid, some more amount of sodium acetate solution is added. The pH of mixture solution
The reason for geometrical isomerism by 2-butene is
If chloroform is left open in air in presence of sunlight
The bond dissociation energy of B–F in BF3 is 646 kJ mol-1 whereas that of C–F in CF4 is 515 kJ mol–1. The correct reason for higher B–F bond dissociation energy as compared to that of C–F is
At 35°C, the vapor pressure of CS2 is 512 mm Hg and that of acetone is 344 mm Hg. A solution of CS2 in acetone has a total vapor pressure of 600 mm Hg. The false statement amongst the following is (2020)
(a) Raoult’s law is not obeyed by this system.
(b) A mixture of 100 mL CS2 and 100 mL acetone has a volume < 200 mL.
(c) CS2 and acetone are less attracted to each other than to themselves.
(d) Heat must be absorbed in order to produce the solution at 35°C.
A vessel at 1000 K contains CO2 with a pressure of 0.5 atm. Some of the CO2 is converted into CO on the addition of graphite. If the total pressure at equilibrium is 0.8 atm, the value of K is
If x = Group number of Europium (atomic number 63)
y = Period number of Americium (atomic number 95)
z = Most stable oxidation state shown by Gadolinium (atomic number 64)
then find the value of x + y + z?
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide follows first order kinetics.
2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(ℓ) + O2(g)
If the volume of O2 gas liberated at STP in first 20 minutes of the start of decomposition is 25.00 ml, what should be the total volume of O2 gas (in ml) collected in time, t >> t1/2.
(t1/2 for the decomposition of H2O2 is 10 min)
How many H-atom can be exchanged by D-atom when the following compound is kept in 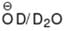 solution for long time?
solution for long time?
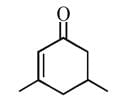
Find out the number of following orders which are INCORRECT against the mentioned properties :
(i) Ortho hydrogen > Para hydrogen (Stability at low temperature)
(ii) Ethanol > Glycerol (Viscosity)
(iii) D2 < He (Boiling Point)
(iv) HF > H2O (Melting point)
(v) H3BO3 > BF3 (Melting point)
(vi) NH3 < SbH3 (Boiling point)
(vii) H2O2 > H2O (Strength of hydrogen bond)
(viii) H2O < D2O (Freezing point)
(ix) 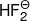 < HF (Strength of hydrogen bond)
< HF (Strength of hydrogen bond)
(x) D2O < H2O (Bond energy)