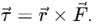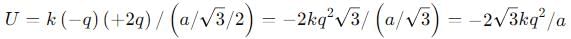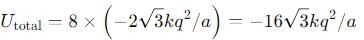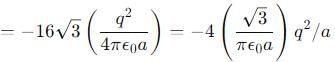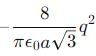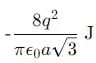JEE Main Physics Mock Test- 2 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Physics Mock Test- 2
Photons of energy 1eV and 2.5 eV successively illuminate a metal whose work function is 0. 5 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the electrons emitted will be
When a charged oil drop moves upwards in an electric field, the electric force acting on the drop is
The material which practically does not show elastic after effect is
The average power dissipation in a pure capacitor in AC circuit is
The root mean square velocity of the molecules in a sample of helium is 5/7th that of the moelcules in a sample of hydrogen. If the temperature of hydrogen sample is 0oC, then the temperature of the helium sample is about
A boat crosses a river from port A to port B, which are just on the opposite side. The speed of the water is vW and that of boat is vB relative to water. Assume vB = 2vW. What is the time taken by the boat, if it has to cross the river directly on the AB line?
The capacity of a parallel plate condenser is 10 μF without dielectric. After that, a dielectric of constant 2 is used to fill half thickness between the plates of another capacitor of same capacitance. The net capacitance after joining both of them in series in μF is
The electric potential at a point (x, y) in the xy-plane is given by: V = -kxy. The electric field intensity at a distance r from the origin varies as
A student has measured the length of a wire equal to 0.04580 m. This value of length has the number of significant figures equal to
If the earth is at one-fourth of its present distance from the sun, then duration of the year will be
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): In a meter bridge, if its wire is replaced by another wire having same length, made of same material but having twice the cross-sectional area, the accuracy decreases.
Reason(R): If its wire is replaced by another wire of same material, having same cross-sectional area but of twice the length, accuracy increases.
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Torque is an axial vector and directed along the axis of rotation.
Reason(R): Torque is equal to cross product of force to the position vector.
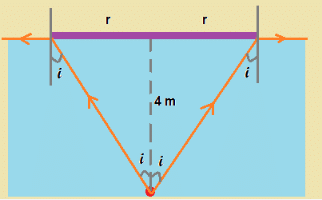
A disc is placed on a surface of pond which has refractive index 5/3. A source of light is placed 4 m below the surface of liquid. The minimum radius of disc needed so that light is not coming out is
In order to double the frequency of the fundamental note emitted by a stretched string, the length is reduced to 3/4 th of the original length and the tension is changed. The factor by which the tension is to be changed is
Three sound waves of equal amplitudes have frequencies v − 1 , v , v + 1. They superpose to give beats. The number of beats produced per second will be-
70 calories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 2 moles of an ideal gas at constant pressure from 30oC to 35oC. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the same sample of the gas through the same range at constant volume is nearly (Gas constant = 1.99 cal/K-mole)
Water is flowing on the blades of a turbine at a rate of 100 kg-s-1 from a certain spring. If the height of the spring be 100 m, then power transferred to the turbine will be
If the two slits in Young's experiment have width ratio 1:4, the ratio of intensity at maxima and minima in the interference pattern in
Eight negative charges each of value q coulomb are placed at the corners of a cube of side 'a' metre, at the centre of which a positive charge of +2q coulomb is placed.
Q.
The central charge 2q makes 8 similar pairs with the charges at corners. Their potential energy is :
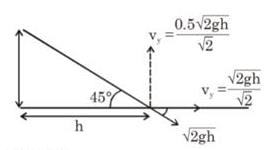
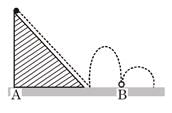
A small elastic ball of mass m is placed at the apex of a 45° inclined plane as shown in the figure below. The ball is allowed to slip without friction down the plane (along the dotted line), hit the ground (as shown) and bounce along it. If the height of the inclined plane is h and the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the ground is 0.5, then the distance AB, as marked on the figure, will be N × h, where N is
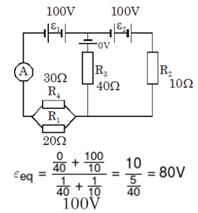
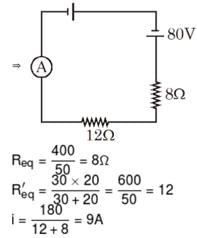
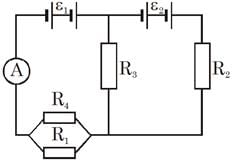
In the circuit in figure we have ε1 = ε2 = 100V, R1 = 20Ω, R2 = 10 Ω, R3 = 40 Ω and R4 = 30 Ω. Find the reading of the ammeter (in A). Disregard the resistance of the battery and the ammeter.
A calorimeter consists of 400 g of water at 24°C. A 500 g piece of copper at 100°C is thrown into the water and the equilibrium temperature is found to be 36.5°C. What is the molar heat capacity of copper in cal/mol k, given that 1 mol of copper has a mass of 63.5g? Neglect the heat capacity of the container.
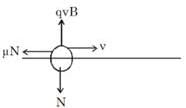
In gravity free space, a bead of charge 1µC and mass 3 mg is threaded on a rough rod of friction coefficient µ = 0.3. A magnetic field of magnitude 0.2 T exists perpendicular to the rod. The bead is projected along the rod with a speed of 4m/s. How much distance (in m) will the bead cover before coming to rest ?
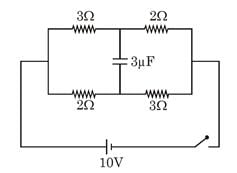
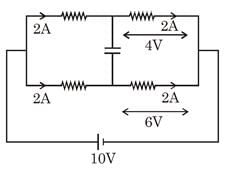
Initially the capacitor is uncharged. What is the steady state charge on it (in µC) after the switch is closed?