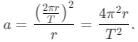JEE Main Physics Mock Test- 1 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Physics Mock Test- 1
An electric lamp is connected to 220 V, 50 Hz supply. Then the peak value of voltage is
In a step-up transformer the voltage in the primary is 220 V and the current is 5A. The secondary voltage is found to be 22000V. The current in the secondary (neglect losses) is
A body moves along a circular path of radius 10 m and the coefficient of friction is 0.5. What should be the angular velocity of the body, if it is not to slip on the surface?
A semi circle arc of radius 'a' is charged uniformly and the charge per unit length is λ. The electric field at its centre is
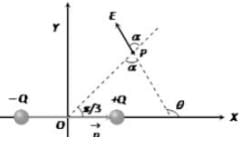
An electric dipole is placed along the X-axis at the origin O. A point P is at a distance of 20 cm from this origin such that OP makes an angle π/3 with the X axis. If electric field at P makes an angle θ with X-axis, the value of θ is
A gun fires the bullets each of mass 10 g with a velocity of 50 m/s. If 1000 bullets are fired per second, then thrust on the shoulder will be
A metre stick AB hinged (without friction) at the end A as shown in the figure is kept horizontal by means of a string tied to the end B, the other end of the string being tied to a hook. The string is carefully cut (or burnt), and the scale executes angular oscillations about an axis passing through the end A. What is the speed of the end B when the metre stick assumes vertical position immediately after the string is burnt? (Acceleration due to gravity = 10 m/s2)

The symbolic representation of four logic gates are given below:
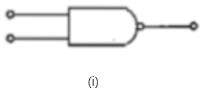
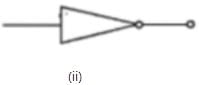
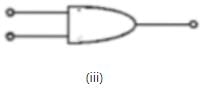
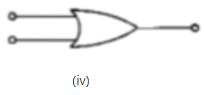
The logic symbols for OR, NOT and NAND gates are respectively:
If a long hollow copper pipe carries a current then magnetic field produced will be
In a capillary tube, water rises upto 3 mm. The height of water that will rise in another capillary tube having one-third radius of the first is
A chain reaction in fission of uranium is possible because
Two bodies of mass 10 kg and 5 kg moving in concentric orbits of radii R and r such that their periods are the same. Then the ratio between their centripetal acceleration is
When there is an electric current through a conducting wire along its length then an electric field must exist
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A):All radio-active elements are finally converted into lead.
Reason(R):All the elements above lead are unstable
The moment of inertia of a uniform disc about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane is 1kg - m2. It is rotating with an angular velocity 100 radians/second. Another identical disc is gently placed on it so that their centres coincide. Now these two discs together continue to rotate about the same axis. Then the loss in kinetic energy in kilo joules is
If T is the reverberation time of an auditorium of volume V, then
Consider the following statements.
(i) All isotopes of an element have the same number of neutrons.
(ii) Only one isotope of an element can be stable and non-radioactive.
(iii) All elements have isotopes.
(iv) All isotopes of Carbon can form chemical compounds with Oxygen-16.
The correct option regarding an isotope is?
The orbital velocity of an artificial satellite in a circular orbit just above the earth’s surface is v0. The orbital velocity of satellite orbiting at an altitude of double the radius of earth is V0/√n Then the value of n is :
A 300 W carrier is modulated to a depth 75%. The total power in the modulated wave is:-
A conducting rod of 1 m length and 1 kg mass is suspended by two vertical wires through its ends. An external magnetic field of 2T is applied normal to the rod. Now, the current to be passed through the rod so as to make the tension in the wires zero is : (Take g = 10 m/s2) :-
At what speed a ball must be projected vertically upward so that distance travelled by it in 5th second is equal to distance travelled in sixth second (in m/s):-
In thermodynamic process pressure of a fixed mass of gas is changed in such a manner that the gas releases 30 joule of heat and 18 joule of work was done on the gas. If the initial internal energy of the gas was 60 joule, then, the final internal energy (in J) will be: