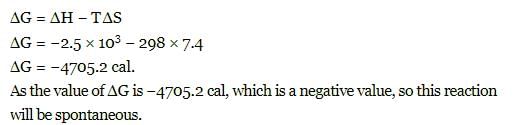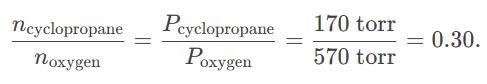SRMJEEE Chemistry Mock Test - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - SRMJEEE Chemistry Mock Test - 2
Which of the following reactions is used for detecting presence of carbonyl group ?
The reaction of chloroform with alcoholic KOH and p-toluidine form
The acidic solution of salt produced a deep blue colour with starch iodide solution. The salt may be
The quantum number values for the designation 3d are
Other factors being constant which bond order is expected to correspond to shortest bond length
A carboxylic acid is converted into its anhydride using
When enthalpy and entropy change for a chemical reaction are -2.5 x103 cals and 7.4 cals deg⁻1 respectively . Predict that reaction at 298 K is
The bond between carbon - 1 and carbon -2 in the compound N ≡ C − CH = CH2 is
The chemical equilibrium of a reversible reaction is not influenced by
The rate of reaction, A + B → products; is given by the equation, r = k [A] [B]. If B is taken in large excess, the order of the reaction would be
Streptomycin, a well known antibiotic, is a derivative of
The IUPAC name of the compound having the molecular formula Cl₃C-CH₂CHO is
Which of the following electronic configuration corresponds to an inert gas?
The heat of combustion of methane at 298K is expressed by CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l), ΔH = − 890.2 k J. The magnitude of ΔE of the reaction at this temperature is
The limiting molar conductivities for NaCl. KBr and KCl are 126, 152 and 150 S-cm2-mol⁻1 respectively. The molar conductivity of NaBr is
Oxygen and cyclopropane at partial pressure of 570 torr and 170 torr respectively are mixed in a gas cylinder. What is the ratio of the number of moles of cyclopropane to the number of moles of oxygen ?
Which of the following compound is used to prevent the deposition of oxides of lead on spark plug, combustion chamber and exhaust pipe?
When HCl gas is passed through a saturated Solutions of NaCl , the solubility of Nacl:
Which of the following molecule having molecular formula C₄H₆O₂ will be optically active?
Which one of the following is a typical example of compound which exists as zwitter ion?
1 g of radioactive element reduces to 125 mg after 24 hours. Half life of isotope is
A substance C₄H₁₀O yields on oxidation a compound C₄H₈O, which gives an oxime and a positive iodoform test. The original substance on treatment with conc. H₂SO₄ gives C₄H₈. The structure of the compound is
Which of the following is an example of natural polymer?
If 0.6387 of plantinichloride of a monoacid base on ignition gave 0.209g of platinum, then molecular weight of the base is
Which acts as both oxidising as well as reducing agent ?