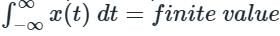Test: Discrete Time Signals & Useful Signals - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Discrete Time Signals & Useful Signals
The function y[n] = sin(x[n]) is periodic
What is the time period of the function x[n] = exp(jwn)?
A time invariant system is a system whose output
Is the function y[n] = x[n-1] – x[n-4] memoryless?
Is the function y[n] = y[n-1] + x[n] stable in nature?
We define y[n] = nx[n] – (n-1)x[n]. Now, z[n] = z[n-1] + y[n], is z[n] stable?
We define y[n] = nx[n] – (n-1)x[n]. Now, z[n] = z[n-1] + y[n]. Is z[n] a causal system?
What is the value of d[0], such that d[n] is the unit impulse function?
What is the value of u[1], where u[n] is the unit step function?
Evaluate the following function in terms of t: {sum from -1 to infinity:d[n]}/{Integral from 0 to t: u(t)}
Evaluate the following function in terms of t: {integral from 0 to t}{Integral from -inf to inf}d(t)
The fundamental period of exp(jwt) is
Find the magnitude of exp(jwt). Find the boundness of sin(t) and cos(t).
Find the value of {sum from -inf to inf} exp(jwn)*d[n].
Compute d[n]d[n-1] + d[n-1]d[n-2] for n = 0, 1, 2.
Defining u(t), r(t) and s(t) in their standard ways, are their derivatives defined at t = 0?
Which is the correct Euler expression?
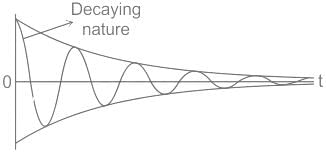
A linear time invariant (LTI) system is said to be stable if ________.
Exponential signal is an example of _________ signal.
If x(t) is a continuous signal and 'A' is a constant, then x(At) = ?