All Exams >
Back-End Programming >
Learn to Program with C++: Beginner to Expert >
All Questions
All questions of Operator overloading for Back-End Programming Exam
How can we restrict dynamic allocation of objects of a class using new?- a)By overloading new operator
- b)By making an empty private new operator.
- c)By making an empty private new and new[] operators
- d)By overloading new operator and new[] operators
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How can we restrict dynamic allocation of objects of a class using new?
a)
By overloading new operator
b)
By making an empty private new operator.
c)
By making an empty private new and new[] operators
d)
By overloading new operator and new[] operators
|
|
Pranavi Datta answered |
If we declare new and [] new operators, then the objects cannot be created anywhere (within the class and outside the class) See the following example. We can not allocate an object of type Test using new.


How does C++ compiler differs between overloaded postfix and prefix operators?- a)C++ doesn't allow both operators to be overlaoded in a class
- b)A postfix ++ has a dummy parameter
- c)A prefix ++ has a dummy parameter
- d)By making prefix ++ as a global function and postfix as a member function.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How does C++ compiler differs between overloaded postfix and prefix operators?
a)
C++ doesn't allow both operators to be overlaoded in a class
b)
A postfix ++ has a dummy parameter
c)
A prefix ++ has a dummy parameter
d)
By making prefix ++ as a global function and postfix as a member function.
|
|
Nishtha Basak answered |


Which of the following operator functions cannot be global, i.e., must be a member function.- a)new
- b)delete
- c)Converstion Operator
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following operator functions cannot be global, i.e., must be a member function.
a)
new
b)
delete
c)
Converstion Operator
d)
All of the above
|
|
Sanjana Rane answered |
new and delete can be global, see following example.
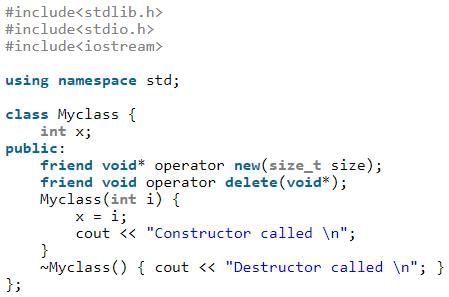



Which of the following operators are overloaded by default by the compiler in every user defined classes even if user has not written?
(1) Comparison Operator ( == )
(2) Assignment Operator ( = )- a)Both 1 and 2
- b)Only 1
- c)Only 2
- d)None of the two
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following operators are overloaded by default by the compiler in every user defined classes even if user has not written?
(1) Comparison Operator ( == )
(2) Assignment Operator ( = )
(1) Comparison Operator ( == )
(2) Assignment Operator ( = )
a)
Both 1 and 2
b)
Only 1
c)
Only 2
d)
None of the two
|
|
Kritika Das answered |
Assign operator is by default available in all user defined classes even if user has not implemented. The default assignement does shallow copy. But comparison operator "==" is not overloaded.




Which of the following operators cannot be overloaded- a). (Member Access or Dot operator)
- b)?: (Ternary or Conditional Operator )
- c):: (Scope Resolution Operator)
- d).* (Pointer-to-member Operator )
- e)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following operators cannot be overloaded
a)
. (Member Access or Dot operator)
b)
?: (Ternary or Conditional Operator )
c)
:: (Scope Resolution Operator)
d)
.* (Pointer-to-member Operator )
e)
All of the above
|
|
Priyanka Rane answered |
See What are the operators that cannot be overloaded in C++?
Predict the output

- a)Compiler Error
- b)10
20 - c)20
20 - d)10
10
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Predict the output


a)
Compiler Error
b)
10
20
20
c)
20
20
20
d)
10
10
10
|
|
Rishika Sharma answered |
Note that the class B has as conversion operator overloaded, so an object of B can be converted to that of A. Also, class A has a constructor which can be called with single integer argument, so an int can be converted to A.
Output of following program?
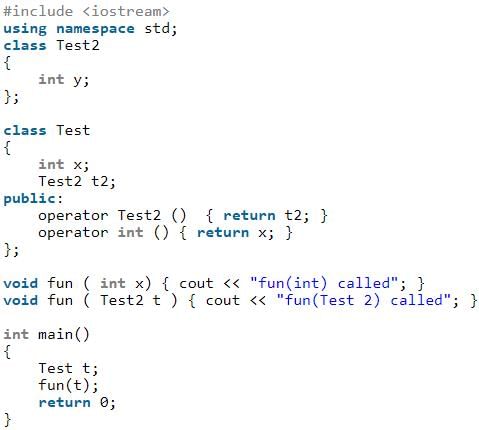
- a)fun(int) called
- b)fun(Test 2) called
- c)Compiler Error: Ambiguous call to fun()
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Output of following program?


a)
fun(int) called
b)
fun(Test 2) called
c)
Compiler Error: Ambiguous call to fun()
|
|
Anshu Chopra answered |
The class Test has two conversion operators overloaded, int and Test2. And there are two fun() for int and Test2.
Predict the output?
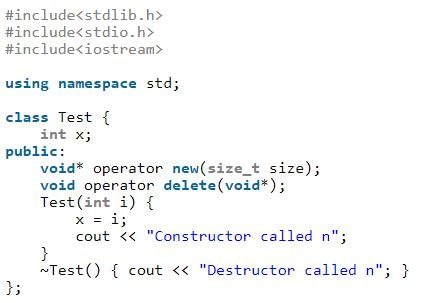
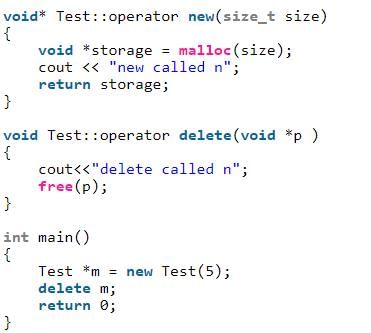
- a)new called
Constructor called
delete called
Destructor called - b)new called
Constructor called
Destructor called
delete called - c)Constructor called
new called
Destructor called
delete called - d)Constructor called
new called
delete called
Destructor called
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Predict the output?




a)
new called
Constructor called
delete called
Destructor called
Constructor called
delete called
Destructor called
b)
new called
Constructor called
Destructor called
delete called
Constructor called
Destructor called
delete called
c)
Constructor called
new called
Destructor called
delete called
new called
Destructor called
delete called
d)
Constructor called
new called
delete called
Destructor called
new called
delete called
Destructor called
|
|
Garima Yadav answered |
Consider the following statement
Test *ptr = new Test;
There are actually two things that happen in the above statement--memory allocation and object construction; the new keyword is responsible for both. One step in the process is to call operator new in order to allocate memory; the other step is to actually invoke the constructor. Operator new only allows us to change the memory allocation method, but does not do anything with the constructor calling method. Keyword new is responsible for calling the constructor, not operator new.
Test *ptr = new Test;
There are actually two things that happen in the above statement--memory allocation and object construction; the new keyword is responsible for both. One step in the process is to call operator new in order to allocate memory; the other step is to actually invoke the constructor. Operator new only allows us to change the memory allocation method, but does not do anything with the constructor calling method. Keyword new is responsible for calling the constructor, not operator new.
While overloading binary operators using member function, it requires ___ argument/s.- a)Zero
- b)One
- c)Two
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
While overloading binary operators using member function, it requires ___ argument/s.
a)
Zero
b)
One
c)
Two
d)
Three
|
|
Sanskriti Menon answered |
Overloading Binary Operators using Member Function
To overload a binary operator using a member function, the operator function must be a member function of the class. When overloading binary operators, it requires one argument.
Explanation:
1. Operator Overloading:
- Operator overloading is a feature in C++ that allows the same operator to be used with different meanings for different data types.
- It provides a way to extend the functionality of operators in the language.
- In C++, binary operators can be overloaded using member functions or friend functions.
2. Overloading Binary Operators using Member Function:
- When overloading binary operators using member functions, the operator function must be a member function of the class.
- The left operand of the operator is implicitly passed as the calling object, and the right operand is the argument to the operator function.
- The binary operators that can be overloaded using member functions include addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), modulus (%), etc.
3. Number of Arguments Required:
- When overloading binary operators using member functions, it requires one argument.
- The single argument represents the right operand of the operator function.
- For example, when overloading the addition operator (+), the member function will have the following signature:
Here, "className" is the name of the class in which the operator function is defined.
4. Example:
- Let's consider a class called "Fraction" that represents a fraction with numerator and denominator.
- We can overload the addition operator (+) using a member function to add two fractions.
- The member function will take one argument, which is the fraction to be added.
- The overloaded operator function can be defined as follows:
This function will be able to add the calling object with another fraction object and return the result.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - One.
To overload a binary operator using a member function, the operator function must be a member function of the class. When overloading binary operators, it requires one argument.
Explanation:
1. Operator Overloading:
- Operator overloading is a feature in C++ that allows the same operator to be used with different meanings for different data types.
- It provides a way to extend the functionality of operators in the language.
- In C++, binary operators can be overloaded using member functions or friend functions.
2. Overloading Binary Operators using Member Function:
- When overloading binary operators using member functions, the operator function must be a member function of the class.
- The left operand of the operator is implicitly passed as the calling object, and the right operand is the argument to the operator function.
- The binary operators that can be overloaded using member functions include addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), modulus (%), etc.
3. Number of Arguments Required:
- When overloading binary operators using member functions, it requires one argument.
- The single argument represents the right operand of the operator function.
- For example, when overloading the addition operator (+), the member function will have the following signature:
className operator+(const className& obj)
Here, "className" is the name of the class in which the operator function is defined.
4. Example:
- Let's consider a class called "Fraction" that represents a fraction with numerator and denominator.
- We can overload the addition operator (+) using a member function to add two fractions.
- The member function will take one argument, which is the fraction to be added.
- The overloaded operator function can be defined as follows:
Fraction operator+(const Fraction& other)
This function will be able to add the calling object with another fraction object and return the result.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - One.
Chapter doubts & questions for Operator overloading - Learn to Program with C++: Beginner to Expert 2025 is part of Back-End Programming exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Back-End Programming exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Back-End Programming 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Operator overloading - Learn to Program with C++: Beginner to Expert in English & Hindi are available as part of Back-End Programming exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Back-End Programming Exam by signing up for free.
Learn to Program with C++: Beginner to Expert
74 videos|7 docs|23 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









