All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of April Week 4 for NEET Exam
Asexual spores in Ascomycetes are called as _______- a)Ascospores
- b)Conidia
- c)Sporangiospores
- d)Aeciospores
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Asexual spores in Ascomycetes are called as _______
a)
Ascospores
b)
Conidia
c)
Sporangiospores
d)
Aeciospores
|
|
Jaspreet answered |
Conidia is a sexual spores in ascomycetes which are produced exogenously on conidiophores :)
Coenocytic means _______- a)sharing of common cytoplasm
- b)removal of plasma membrane
- c)sharing of common nucleus
- d)sharing of common hyphael wall
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Coenocytic means _______
a)
sharing of common cytoplasm
b)
removal of plasma membrane
c)
sharing of common nucleus
d)
sharing of common hyphael wall
|
|
Srestha Bose answered |
Coenocytic means sharing of common cytoplasm. This term is commonly used to describe a type of cell or organism that does not have distinct cell boundaries or compartments. Instead, coenocytic cells contain multiple nuclei within a single, continuous cytoplasmic mass.
Explanation:
Coenocytic cells are typically found in fungi, algae, and some types of plants. In these organisms, individual cells may fuse together during development to form a single, multinucleate cell. This single cell may then develop into a larger structure or organism, such as a fungus or alga.
Some key characteristics of coenocytic cells include:
- Lack of cell walls: Coenocytic cells do not have distinct cell walls separating them from neighboring cells. Instead, they are connected by a network of cytoplasmic strands.
- Multiple nuclei: Because coenocytic cells contain multiple nuclei within a single cytoplasmic mass, they are often referred to as multinucleate.
- Large size: Without the constraints of cell walls, coenocytic cells can grow to very large sizes. Some fungi, for example, can form structures that are many meters in length.
Overall, the term "coenocytic" refers to a unique type of cell organization that is characterized by the sharing of cytoplasmic material between multiple nuclei.
Explanation:
Coenocytic cells are typically found in fungi, algae, and some types of plants. In these organisms, individual cells may fuse together during development to form a single, multinucleate cell. This single cell may then develop into a larger structure or organism, such as a fungus or alga.
Some key characteristics of coenocytic cells include:
- Lack of cell walls: Coenocytic cells do not have distinct cell walls separating them from neighboring cells. Instead, they are connected by a network of cytoplasmic strands.
- Multiple nuclei: Because coenocytic cells contain multiple nuclei within a single cytoplasmic mass, they are often referred to as multinucleate.
- Large size: Without the constraints of cell walls, coenocytic cells can grow to very large sizes. Some fungi, for example, can form structures that are many meters in length.
Overall, the term "coenocytic" refers to a unique type of cell organization that is characterized by the sharing of cytoplasmic material between multiple nuclei.
Rhizopus belongs to _________- a)Phycomycetes
- b)Ascomycetes
- c)Basidiomycetes
- d)Deuteromycetes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rhizopus belongs to _________
a)
Phycomycetes
b)
Ascomycetes
c)
Basidiomycetes
d)
Deuteromycetes
|
|
Jaspreet answered |
Rhizopus belongs to Phycomycetes :)
Non-motile spores in Phycomycetes are called as _____- a)Phycospores
- b)Zoospores
- c)Aplanospores
- d)Zygospores
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Non-motile spores in Phycomycetes are called as _____
a)
Phycospores
b)
Zoospores
c)
Aplanospores
d)
Zygospores

|
Prahlad Pai answered |
Non motile spore in phycomycetes is aplanospores
Which of the following observations was not correct during Rutherford’s scattering experiment?- a)Most of the α-particles passed through the gold foil undeflected
- b)A small fraction of the α-particles was deflected by small angles
- c)A large number of the α-particles were bounced back
- d)A very few α-particles (~1 in 12,000) were bounced back
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following observations was not correct during Rutherford’s scattering experiment?
a)
Most of the α-particles passed through the gold foil undeflected
b)
A small fraction of the α-particles was deflected by small angles
c)
A large number of the α-particles were bounced back
d)
A very few α-particles (~1 in 12,000) were bounced back
|
|
Dhruba Choudhury answered |
The question appears to be incomplete as it does not provide any options for the answer choices. Could you please provide the options or complete the question?
A ship A sailing due east with a velocity of 10 km/h happens to appear sailing due north with a velocity of 5 km/h, to a person, sitting in a moving ship B. Determine the velocity (absolute) of ship B.
.
- a)
5√5 km/h, tan−1(1/2) S of E
- b)5√5 km/h, tan−1(1/2) E of S
- c)4√5 km/h, tan−1(1/2) S of E
- d)4√5 km/h, tan−1(1/2) E of S
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ship A sailing due east with a velocity of 10 km/h happens to appear sailing due north with a velocity of 5 km/h, to a person, sitting in a moving ship B. Determine the velocity (absolute) of ship B.
.
a)
5√5 km/h, tan−1(1/2) S of E
b)
5√5 km/h, tan−1(1/2) E of S
c)
4√5 km/h, tan−1(1/2) S of E
d)
4√5 km/h, tan−1(1/2) E of S
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Here we are given velocity of 'A', 
Velocity of 'A', w.r.t. 'B',

Velocity of 'A', w.r.t. 'B',

Now,

 Hence velocity of B,
Hence velocity of B, 



 Hence velocity of B,
Hence velocity of B, 

i.e. S of E
S of E
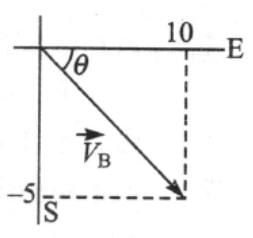
 S of E
S of E
Which among the following are incorrect about Phycomycetes?- a)Phycomycetes are aseptate fungi and are coenocytic
- b)Phycomycetes are also called as algal fungi
- c)Zygospores are formed due to isogamous fertilization and zoospores are formed due to anisogamous fertilization
- d)Phycomycetes are also called as conjugation fungi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following are incorrect about Phycomycetes?
a)
Phycomycetes are aseptate fungi and are coenocytic
b)
Phycomycetes are also called as algal fungi
c)
Zygospores are formed due to isogamous fertilization and zoospores are formed due to anisogamous fertilization
d)
Phycomycetes are also called as conjugation fungi
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Zygospores are formed either due to isogamous or anisogamous fertilization. Zoospores and aplanospores are motile and non-motile spores produced due to asexual mode respectively. Phycomycetes are aseptate fungi and are coenocytic. Phycomycetes are also called as algal fungi or conjugation fungi.
A ball is rolled off the edge of a horizontal table at a speed of 4 m/second. It hits the ground after 0.4 second. Which statement given below is true.- a)It hits the ground at a horizontal distance 1.6 m from the edge of the table.
- b)The speed with which it hits the ground is 4.0 m/second.
- c)Height of the table is 0.8 m.
- d)It hits the ground at an angle of 60o to the horizontal.
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A ball is rolled off the edge of a horizontal table at a speed of 4 m/second. It hits the ground after 0.4 second. Which statement given below is true.
a)
It hits the ground at a horizontal distance 1.6 m from the edge of the table.
b)
The speed with which it hits the ground is 4.0 m/second.
c)
Height of the table is 0.8 m.
d)
It hits the ground at an angle of 60o to the horizontal.
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
Vertical component of velocity of ball at point P

Horizontal component of velocity = initial velocity 


So the speed with which it hits the ground,

and


⇒ θ = 45º
It means the ball hits the ground at an angle of 45∘ to the horizontal.
Height of the table
Height of the table

Horizontal distance travelled by the ball from the edge of table, h = ut = 4 × 0.4 = 1.6 m
Assertion: The maximum horizontal range of projectile is proportional to square of velocity.
Reason: The maximum horizontal range of projectile is equal to maximum height attained by projectile.- a)If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If the assertion and reason both are false.
- e)If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: The maximum horizontal range of projectile is proportional to square of velocity.
Reason: The maximum horizontal range of projectile is equal to maximum height attained by projectile.
Reason: The maximum horizontal range of projectile is equal to maximum height attained by projectile.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If the assertion and reason both are false.
e)
If assertion is false but reason is true.
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |


when θ = 45º, Rmax ∝ u2


when θ = 90º, Hmax ∝ u2
It is clear that,

In fungi, asexual reproduction takes place by- a) Fission, conidia and ascospores
- b)Conidia, hypnospores and zoospores
- c)Conidia, sporangiospores and zoospores
- d)Sporangiospores, conidia and basidiospores
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In fungi, asexual reproduction takes place by
a)
Fission, conidia and ascospores
b)
Conidia, hypnospores and zoospores
c)
Conidia, sporangiospores and zoospores
d)
Sporangiospores, conidia and basidiospores

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Asexual reproduction is by spores called conidia or sporangiospores or zoospores, and sexual reproduction is by oospores, ascospores and basidiospores
Pankaj and Sudhir are playing with two different balls of masses m and 2m, respectively. If Pankaj throws his ball vertically up and Sudhir at an angle θ, both of them stay in our view for the same period. The height attained by the two balls are in the ratio:- a)2 : 1
- b)1 : 1
- c)1 : cos θ
- d)1 : sec θ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pankaj and Sudhir are playing with two different balls of masses m and 2m, respectively. If Pankaj throws his ball vertically up and Sudhir at an angle θ, both of them stay in our view for the same period. The height attained by the two balls are in the ratio:
a)
2 : 1
b)
1 : 1
c)
1 : cos θ
d)
1 : sec θ
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
Time of flight for the ball thrown by pankaj, 
Time of flight for the ball thrown by sudhir, According to problem,
According to problem,


Height of the ball thrown by pankaj,
Height of the thrown by sudhir,



Time of flight for the ball thrown by sudhir,
 According to problem,
According to problem,

Height of the ball thrown by pankaj,

Height of the thrown by sudhir,




Identify the group of fungi that is not correctly matched with all the characters given below:- a)Phycomycetes: Mycelium – aseptate and coenocytic / Asexual reproduction by motile zoospores or by nonmotile aplanospores / spores – endogenously produced in the sporangium
- b)Ascomycetes: Mycelium – unbranched and septate / Asexual spores are conidia / Conidia produced endogenously on conidiophores.
- c)Basidiomycetes: Mycelium–branched and septate / Asexual spores are generally not found.
- d)Deuteromycetes: Only the asexual or vegetative phase of these fungi are known.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the group of fungi that is not correctly matched with all the characters given below:
a)
Phycomycetes: Mycelium – aseptate and coenocytic / Asexual reproduction by motile zoospores or by nonmotile aplanospores / spores – endogenously produced in the sporangium
b)
Ascomycetes: Mycelium – unbranched and septate / Asexual spores are conidia / Conidia produced endogenously on conidiophores.
c)
Basidiomycetes: Mycelium–branched and septate / Asexual spores are generally not found.
d)
Deuteromycetes: Only the asexual or vegetative phase of these fungi are known.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Commonly known as sac-fungi, the ascomycetes are mostly multicellular, e.g., Penicillium, or rarelyunicellular, e.g., yeast (Saccharomyces). They are saprophytic, decomposers, parasitic or coprophilous (growing on dung). is branched and septate. The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores
Which of the following statements is false for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed?- a) The acceleration vector points to the centre of the circle.
- b) The acceleration vector is tangent to the circle.
- c)The velocity vector is tangent to the circle.
- d)The velocity and acceleration vectors are perpendiculai to each other.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is false for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed?
a)
The acceleration vector points to the centre of the circle.
b)
The acceleration vector is tangent to the circle.
c)
The velocity vector is tangent to the circle.
d)
The velocity and acceleration vectors are perpendiculai to each other.
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
In circular motion we know the velocity vector is tangent to the circle. If a particle moves in a circle with constant angular speed it perform uniform circular motion. In uniform circular motion the tangential acceleration of the particle is zero. The particle moves under radial acceleration only which points to the centre of the circle. Hence the velocity and acceleration vectors are perpendicular to each other.
Where are members of phycomycetes primarily found?- a)In dry desert regions
- b)In high-altitude mountain areas
- c)In aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist places
- d)In arid deserts and sandy soils
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Where are members of phycomycetes primarily found?
a)
In dry desert regions
b)
In high-altitude mountain areas
c)
In aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist places
d)
In arid deserts and sandy soils

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Members of phycomycetes are found in aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist and damp places or as obligate parasites on plants.
What are the three main steps involved in the sexual cycle in sequence?- a)Karyoogamy→ Plasmogamy→ Meiosis
- b)Plasmogamy→ Meiosis → Karyogamy
- c)Plasmogamy→ Karyogamy → Meiosis
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the three main steps involved in the sexual cycle in sequence?
a)
Karyoogamy→ Plasmogamy→ Meiosis
b)
Plasmogamy→ Meiosis → Karyogamy
c)
Plasmogamy→ Karyogamy → Meiosis
d)
None of these
|
|
Advait Das answered |
Understanding the Sexual Cycle
The sexual cycle involves a series of events that lead to reproduction, particularly in fungi and certain plants. The correct sequence is Plasmogamy, Karyogamy, and Meiosis.
1. Plasmogamy
- This is the first step where the cytoplasm of two compatible mating types fuse together.
- Plasmogamy results in the formation of a dikaryotic cell, meaning it has two distinct nuclei from each parent.
2. Karyogamy
- Following plasmogamy, karyogamy occurs, which is the fusion of the two nuclei to form a diploid nucleus.
- This step is crucial as it combines genetic material from both parents, leading to genetic variation in the offspring.
3. Meiosis
- The final step is meiosis, where the diploid nucleus undergoes division to produce haploid spores.
- These spores can then germinate and develop into new organisms, completing the sexual cycle.
Conclusion
In summary, the sexual cycle progresses in a specific order:
- Plasmogamy initiates the process by fusing the cytoplasm.
- Karyogamy follows, leading to the fusion of nuclei.
- Meiosis concludes the cycle by producing haploid spores.
This sequence (Plasmogamy → Karyogamy → Meiosis) is essential for genetic diversity and the continuation of species. Understanding these steps is critical for topics related to reproduction and genetics, especially in the context of NEET preparation.
The sexual cycle involves a series of events that lead to reproduction, particularly in fungi and certain plants. The correct sequence is Plasmogamy, Karyogamy, and Meiosis.
1. Plasmogamy
- This is the first step where the cytoplasm of two compatible mating types fuse together.
- Plasmogamy results in the formation of a dikaryotic cell, meaning it has two distinct nuclei from each parent.
2. Karyogamy
- Following plasmogamy, karyogamy occurs, which is the fusion of the two nuclei to form a diploid nucleus.
- This step is crucial as it combines genetic material from both parents, leading to genetic variation in the offspring.
3. Meiosis
- The final step is meiosis, where the diploid nucleus undergoes division to produce haploid spores.
- These spores can then germinate and develop into new organisms, completing the sexual cycle.
Conclusion
In summary, the sexual cycle progresses in a specific order:
- Plasmogamy initiates the process by fusing the cytoplasm.
- Karyogamy follows, leading to the fusion of nuclei.
- Meiosis concludes the cycle by producing haploid spores.
This sequence (Plasmogamy → Karyogamy → Meiosis) is essential for genetic diversity and the continuation of species. Understanding these steps is critical for topics related to reproduction and genetics, especially in the context of NEET preparation.
Assertion(A): Deuteromycetes are called imperfect fungi.
Reason(R): These fungi have autotrophic mode of nutrition .- a)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion(A): Deuteromycetes are called imperfect fungi.
Reason(R): These fungi have autotrophic mode of nutrition .
Reason(R): These fungi have autotrophic mode of nutrition .
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Deuteromycetes are indeed called "imperfect fungi" because only the asexual or vegetative phases of these fungi are known. When the sexual forms of these fungi were discovered they were moved into classes they rightly belong to. It is also possible that the asexual and vegetative stage have been given one name (and placed under deuteromycetes) and the sexual stage another (and placed under another class)
- However, the reason given in the statement that these fungi have an autotrophic mode of nutrition is incorrect. Deuteromycetes are actually heterotrophic, not autotrophic.
- Therefore, the correct answer is: C: (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- However, the reason given in the statement that these fungi have an autotrophic mode of nutrition is incorrect. Deuteromycetes are actually heterotrophic, not autotrophic.
- Therefore, the correct answer is: C: (A) is true, but (R) is false.
A boy projects a stone vertically perpendicular to the trolley car with a speed v. If the trolley car moves with u constant velocity m, the time of flight of the stone is:- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)None of These
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy projects a stone vertically perpendicular to the trolley car with a speed v. If the trolley car moves with u constant velocity m, the time of flight of the stone is:
a)

b)

c)

d)
None of These
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
v = v0 sin θ
u = v0 cos θ
u = v0 cos θ
Time of flight depends on vertical component of velocity.


Which of the following conclusions regarding the structure of atom is based on Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment?- a)The positive charge is concentrated in a very small volume of the atom
- b)The positive charge is scattered with the electrons throughout the atom
- c)The volume occupied by the nucleus is half of the volume of atom
- d)Most of the space in the atom is occupied by the neutrons
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following conclusions regarding the structure of atom is based on Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment?
a)
The positive charge is concentrated in a very small volume of the atom
b)
The positive charge is scattered with the electrons throughout the atom
c)
The volume occupied by the nucleus is half of the volume of atom
d)
Most of the space in the atom is occupied by the neutrons
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
As a very few α-particles were deflected by sharp angles, it was concluded that the positive charge is concentrated in a very small volume of the atom.
Lichens are __________- a)symbiotic existence of blue-green algae and fungi
- b)symbiotic existence of rhizobium bacteria in the roots of leguminous plants
- c)co-existence of coral reef with zooxanthellae
- d)existence of mycorrhiza along with leguminous plants
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Lichens are __________
a)
symbiotic existence of blue-green algae and fungi
b)
symbiotic existence of rhizobium bacteria in the roots of leguminous plants
c)
co-existence of coral reef with zooxanthellae
d)
existence of mycorrhiza along with leguminous plants
|
|
Muhammed Anzal! answered |
No the Correct answer is A. Algal component is called Phycobiont and fungal component is called Mycobiont
An aeroplane is flying horizontally with a velocity of 600 km/h at a height of 1960 m. When it is vertically at a point A on the ground, a bomb is released from it. The bomb strikes the ground at point B. The distance AB is:- a)1200 m
- b)0.33 km
- c)3.33 km
- d)33 km
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An aeroplane is flying horizontally with a velocity of 600 km/h at a height of 1960 m. When it is vertically at a point A on the ground, a bomb is released from it. The bomb strikes the ground at point B. The distance AB is:
a)
1200 m
b)
0.33 km
c)
3.33 km
d)
33 km
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Horizontal displacement of the bomb AB = Horizontal velocity × time available


A particle is dropped from a height and another particle is thrown in horizontal direction with speed of 5 m/sec from the same height. The correct statement is:- a) Both particles will reach at ground simultaneously.
- b)Both particles will reach at ground with same speed.
- c)Particle will reach at ground first with respect to particle.
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle is dropped from a height and another particle is thrown in horizontal direction with speed of 5 m/sec from the same height. The correct statement is:
a)
Both particles will reach at ground simultaneously.
b)
Both particles will reach at ground with same speed.
c)
Particle will reach at ground first with respect to particle.
d)
None of these
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
For both cases,


Because vertical downward component of velocity will be zero for both the particles.
An element with mass number 81 contains 31.7% more neutrons as compared to protons. Find the symbol of the atom- a)

- b)
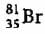
- c)
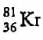
- d)
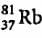
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An element with mass number 81 contains 31.7% more neutrons as compared to protons. Find the symbol of the atom
a)

b)
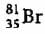
c)
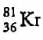
d)
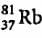
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Mass number of the element = 81
i.e., p + n = 81
Let the number of protons be x.
Number of neutrons
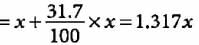
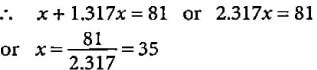
Symbol of the element
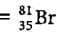
i.e., p + n = 81
Let the number of protons be x.
Number of neutrons
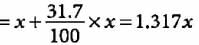
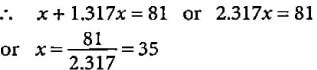
Symbol of the element
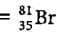
Assertion: In projectile motion, the angle between the instantaneous velocity and acceleration at the highest point is 180∘.
Reason: At the highest point, velocity of projectile will be in horizontal direction only.- a)If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If the assertion and reason both are false.
- e)If assertion is false but reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: In projectile motion, the angle between the instantaneous velocity and acceleration at the highest point is 180∘.
Reason: At the highest point, velocity of projectile will be in horizontal direction only.
Reason: At the highest point, velocity of projectile will be in horizontal direction only.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If the assertion and reason both are false.
e)
If assertion is false but reason is true.
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
At the highest point, vertical component of velocity becomes zero so there will be only horizontal velocity and it is perpendicular to the acceleration due to gravity.
A projectile fired with initial velocity u at some angle θ has a range R. If the initial velocity be doubled at the same angle of projection, then the range will be:- a)2R
- b)R/2
- c)R
- d)4R
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A projectile fired with initial velocity u at some angle θ has a range R. If the initial velocity be doubled at the same angle of projection, then the range will be:
a)
2R
b)
R/2
c)
R
d)
4R
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
 If initial velocity be doubled then range will become four times.
If initial velocity be doubled then range will become four times.A ‘dikaryon’ stage is seen in the members of:- a). Ascomycetes and Phycomycetes
- b)Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes
- c)Basidiomycetes and Phycomycetes
- d)Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A ‘dikaryon’ stage is seen in the members of:
a)
. Ascomycetes and Phycomycetes
b)
Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes
c)
Basidiomycetes and Phycomycetes
d)
Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When a fungus reproduces sexually, two haploid hyphae of compatible mating types come together and fuse. In some fungi the fusion of two haploid cells immediately results in diploid cells (2n). However, in other fungi (ascomycetes and basidiomycetes), an intervening dikaryotic stage (n + n, i.e., two nuclei per cell) occurs; such a condition is called a dikaryon and the phase is called dikaryophase of fungus
Identify the incorrect statement about the diagram of the fungi given below -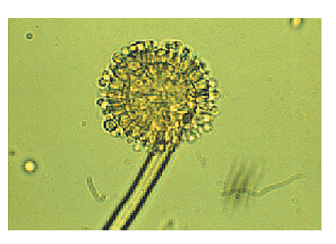
- a)The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores
- b)Sexual spores are called ascospores
- c)Fruiting bodies are called ascocarps.
- d)Fruiting bodies called ascospores.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the incorrect statement about the diagram of the fungi given below -

a)
The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores
b)
Sexual spores are called ascospores
c)
Fruiting bodies are called ascocarps.
d)
Fruiting bodies called ascospores.

|
Bs Academy answered |
Figure mentioned in the question is aspergillus which belong to class ascomycetes.
The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores. Conidia on germination produce mycelium. Sexual spores are called ascospores which are produced endogenously in sac like asci (singular ascus). These asci are arranged in different types of fruiting bodies called ascocarps. Some examples are Aspergillus, Claviceps and Neurospora.
What is the term for the long, slender thread-like structures that make up the body of fungi?- a)Spores
- b)Hyphae
- c)Mycorrhizae
- d)Stolons
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the term for the long, slender thread-like structures that make up the body of fungi?
a)
Spores
b)
Hyphae
c)
Mycorrhizae
d)
Stolons

|
Infinity Academy answered |
fungi are filamentous. Their bodies consist of long, slender thread-like structures called hyphae. The network of hyphae is known as mycelium. Some hyphae are continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm – these are called coenocytic hyphae. Others have septae or cross walls in their hyphae. The cell walls of fungi are composed of chitin and polysaccharides.
How many neutrons are there in 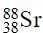 ?
?- a)38
- b)50
- c)126
- d)88
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many neutrons are there in 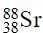 ?
?
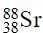 ?
?a)
38
b)
50
c)
126
d)
88
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In 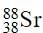
Atomic number = No. of protons = No. of electrons = 38
Atomic mass = 88
Number of neutrons = 88 - 38 = 50
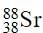
Atomic number = No. of protons = No. of electrons = 38
Atomic mass = 88
Number of neutrons = 88 - 38 = 50
Which of the following is not true regarding the reproduction and life cycle of basidiomycetes?- a)Basidiomycetes reproduce asexually through the formation of basidiospores.
- b)The sex organs are absent in basidiomycetes.
- c)Plasmogamy is brought about by the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells.
- d)Basidia are arranged in fruiting bodies called basidiocarps.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not true regarding the reproduction and life cycle of basidiomycetes?
a)
Basidiomycetes reproduce asexually through the formation of basidiospores.
b)
The sex organs are absent in basidiomycetes.
c)
Plasmogamy is brought about by the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells.
d)
Basidia are arranged in fruiting bodies called basidiocarps.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
a) Basidiomycetes reproduce asexually through the formation of basidiospores.
This statement is not true because basidiomycetes primarily reproduce sexually through the formation of basidiospores, which are produced on basidia after plasmogamy and karyogamy. Asexual reproduction is not the primary mode of reproduction in basidiomycetes, though some may produce conidia or other forms of asexual spores in certain circumstances.
The other statements are true:
- b) The sex organs are absent in basidiomycetes. This is true because basidiomycetes do not have distinct male and female sex organs. Sexual reproduction occurs through the fusion of specialized sexual cells.
- c) Plasmogamy is brought about by the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells. This is true. Plasmogamy involves the fusion of two somatic cells, leading to the formation of a dikaryotic mycelium in basidiomycetes.
- d) Basidia are arranged in fruiting bodies called basidiocarps. This is true. Basidia, which produce basidiospores, are typically found in fruiting bodies known as basidiocarps.
Topic in NCERT: Fungal Reproduction
Line in NCERT: "The sex organs are absent, but plasmogamy is brought about by fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells of different strains or genotypes."
Which of the following species is isoelectronic with CO?- a)HF
- b)N2
- c)
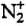
- d)
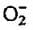
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following species is isoelectronic with CO?
a)
HF
b)
N2
c)
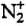
d)
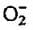
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Isoelectronic species means species having same number of electrons.
In CO; no. of electrons = 6 + 8 = 14
In N2; no. of electrons = 7 + 7 = 14
In CO; no. of electrons = 6 + 8 = 14
In N2; no. of electrons = 7 + 7 = 14
A stone is just released from the window of a train moving along a horizontal straight track. The stone will hit the ground following.- a)Straight path
- b)Circular path
- c)Parabolic path
- d)Hyperbolic path
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A stone is just released from the window of a train moving along a horizontal straight track. The stone will hit the ground following.
a)
Straight path
b)
Circular path
c)
Parabolic path
d)
Hyperbolic path
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Due to constant velocity along horizontal and vertical downward force of gravity stone will hit the ground following parabolic path.
The radius vector describing the position of the particle A relative to origin.
 Which of the following statements are true about the motion.
Which of the following statements are true about the motion.- a)The particle is experiencing uniform acceleration motion.
- b)The particle starts at y axis and touched x axis in 1sec.
- c)The initial velocity is towards negative Y axis
- d)The velocity at t=1 is towards positive x axis
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The radius vector describing the position of the particle A relative to origin.

Which of the following statements are true about the motion.
a)
The particle is experiencing uniform acceleration motion.
b)
The particle starts at y axis and touched x axis in 1sec.
c)
The initial velocity is towards negative Y axis
d)
The velocity at t=1 is towards positive x axis
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
For these, it is clear that all the four options are correct
The radius vector describing the position of the particle A relative to origin.

Find the rectangular components of the average velocity in the time interval between t and t + Δ t.- a)(Δ t + 2t), (Δ t + 2t - 2)
- b)(Δ t - 2t), (Δ t + 2t - 2)
- c)(Δ t - t), (Δ t + 2t + 2)
- d)(Δ t + t), (Δ t + 2t )
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The radius vector describing the position of the particle A relative to origin.

Find the rectangular components of the average velocity in the time interval between t and t + Δ t.
Find the rectangular components of the average velocity in the time interval between t and t + Δ t.
a)
(Δ t + 2t), (Δ t + 2t - 2)
b)
(Δ t - 2t), (Δ t + 2t - 2)
c)
(Δ t - t), (Δ t + 2t + 2)
d)
(Δ t + t), (Δ t + 2t )
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
A particle is projected from point O with velocity u in a direction making an angle α with the horizontal. At any instant its position is at point p at right angles to the initial direction of projection, Its velocity at point p is:

- a)u tan α
- b)u cot α
- c)u sec α
- d)u cosec α
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle is projected from point O with velocity u in a direction making an angle α with the horizontal. At any instant its position is at point p at right angles to the initial direction of projection, Its velocity at point p is:


a)
u tan α
b)
u cot α
c)
u sec α
d)
u cosec α
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Horizontal velocity at point O = u cos α
Horizontal velocity at point P = v sin α
Horizontal velocity at point P = v sin α
In projectile motion horizontal, component of velocity remains constant throughout the motion
∴ v sin α = u cos α
⇒ v = u cot α
∴ v sin α = u cos α
⇒ v = u cot α

A particle is moving on a circular path of radius r with uniform velocity v. The change in velocity when the particle moves from P to Q is (∠POQ=40∘). 
- a)2v cos 40∘
- b)2v sin 40∘
- c)2v cos 20∘
- d)2v sin 20∘
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle is moving on a circular path of radius r with uniform velocity v. The change in velocity when the particle moves from P to Q is (∠POQ=40∘).

a)
2v cos 40∘
b)
2v sin 40∘
c)
2v cos 20∘
d)
2v sin 20∘
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Change in velocity:

Chapter doubts & questions for April Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of April Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily