All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of July Week 4 for NEET Exam
The centre of mass of a body is locateda)outside the systemb)inside or outside the systemc)inside the systemd)at the centre of systemCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The centre of mass of a body can lie within or outside the body.
Example
(i) Centre of mass of a uniform rod lies at its geometrical centre which lies within the rod
(ii) Centre of mass of a uniform ring lies at its geometrical centre which lies outside the ring.
Example
(i) Centre of mass of a uniform rod lies at its geometrical centre which lies within the rod
(ii) Centre of mass of a uniform ring lies at its geometrical centre which lies outside the ring.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Two blocks of the masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of negligible mass and placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. An impulse gives a velocity of 14 m/s to the heavier block. The velocity of centre of mass is
- A:
10 m/s
- B:
5 m/s
- C:
15 m/s
- D:
20 m/s
The answer is a.
Two blocks of the masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of negligible mass and placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. An impulse gives a velocity of 14 m/s to the heavier block. The velocity of centre of mass is
10 m/s
5 m/s
15 m/s
20 m/s

|
EduRev JEE answered |
Velocity of heavier block (v2) = 14m/s
Velocity of lighter block (v1) = 0m/s
Velocity of centre of mass,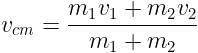
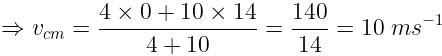
Velocity of lighter block (v1) = 0m/s
Velocity of centre of mass,
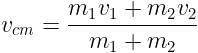
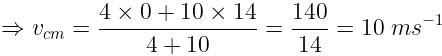
A mass m is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the x-axis, away from the origin. Its angular momentum with respect to the origin
- a)Is zero
- b)Remains constant
- c)Goes on increasing
- d)Goes on decreasing
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A mass m is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the x-axis, away from the origin. Its angular momentum with respect to the origin
a)
Is zero
b)
Remains constant
c)
Goes on increasing
d)
Goes on decreasing
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Angular momentum (L) is defined as the distance of the object from a rotation axis multiplied by the linear momentum
L = mv×y
L = mv×y
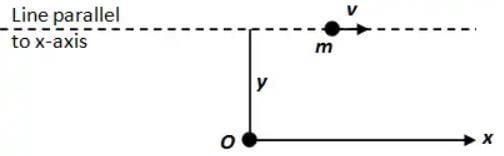
As the particle moves, m; v; and y, all remain unchanged at any point of time
⇒ L = constant
⇒ L = constant
There are two objects of masses 1 kg and 2 kg located at (1, 2) and (-1, 3) respectively. The coordinates of the centre of mass are- a)( 2, -1 )
- b)( 8/3 ,-1/3 )
- c)( -1/3 , 8/3 )
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are two objects of masses 1 kg and 2 kg located at (1, 2) and (-1, 3) respectively. The coordinates of the centre of mass are
a)
( 2, -1 )
b)
( 8/3 ,-1/3 )
c)
( -1/3 , 8/3 )
d)
none of these
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Body A has mass of 1kg and location (1,2)
Body B has mass of 2kg and location (-1,3)
Body B has mass of 2kg and location (-1,3)
mcxc = m1x1 + m2x2
(1+2) xc = (1 * 1) + (2 * -1)
xc = -1/3
(1+2) xc = (1 * 1) + (2 * -1)
xc = -1/3
Similarly,
mcyc = m1y1 + m2y2
(1 + 2) yc = (1 * 2) + (2 * 3)
yc= 8/3
mcyc = m1y1 + m2y2
(1 + 2) yc = (1 * 2) + (2 * 3)
yc= 8/3
Hence, the coordinates of the center of mass are (-1/3, 8/3).
The motion of a potter’s wheel is an example of
- a)rolling motion
- b)rotatory motion
- c)translatory motion
- d)precessional motion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The motion of a potter’s wheel is an example of
a)
rolling motion
b)
rotatory motion
c)
translatory motion
d)
precessional motion
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Potter’s wheel is an example of rotary motion. Rotary motion is that kind of motion in which body of the mass moves along a circular path about an axis which remains fixed.
The centre of mass of a system of particles does not depend on
- a)masses of the particles
- b)forces on the particles
- c)relative distances between the particles
- d)position of the particles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The centre of mass of a system of particles does not depend on
a)
masses of the particles
b)
forces on the particles
c)
relative distances between the particles
d)
position of the particles
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The resultant of all forces, on any system of particles, is zero. Therefore, their centre of mass does not depend upon the forces acting on the particles.
If a shell at rest explodes then the centre of mass of the fragments
- a)remains at rest
- b)Moves along a parabolic path
- c)Moves along a straight line
- d)moves along an elliptical path
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a shell at rest explodes then the centre of mass of the fragments
a)
remains at rest
b)
Moves along a parabolic path
c)
Moves along a straight line
d)
moves along an elliptical path
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
As a shell explosion is not governed by any external force, we get that no external force acts upon the shell, and hence it remains at rest.
If a man of mass M jumps to the ground from height h and his centre of mass moves a distance x in the time taken by him to hit the ground, the average force acting on him is (assuming his retardation to be constant during his impact with the ground)- a)
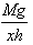
- b)
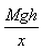
- c)
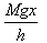
- d)
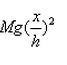
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a man of mass M jumps to the ground from height h and his centre of mass moves a distance x in the time taken by him to hit the ground, the average force acting on him is (assuming his retardation to be constant during his impact with the ground)
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
As the center of mass moves through a distance x, the average force F acting on the man is calculated from :
Work done = Change in potential energy
⇒ Fx = Mgh
⇒ F =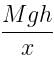
Work done = Change in potential energy
⇒ Fx = Mgh
⇒ F =
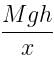
When external forces acting on a body are zero, then its centre of mass- a)remains stationary
- b)moves with uniform velocity
- c)either remains stationary or moves with uniform velocity
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When external forces acting on a body are zero, then its centre of mass
a)
remains stationary
b)
moves with uniform velocity
c)
either remains stationary or moves with uniform velocity
d)
none of these
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
When force acting upon the body results zero, the resulting acceleration due to net force applied is also zero, and hence by the law of inertia the motion of the body either at rest or constant velocity wont change.
There are some passengers inside a stationary railway compartment. The centre of masses of the compartment itself(without the passengers) is C1, while the centre of mass of the compartment plus passengers’ system is C2. if the passengers moves about inside the compartment
- a)both C1 and C2 will move with respect to the ground
- b)neither C1 nor C2 will move with respect to the ground
- c)C1 will move but C2 will be stationary with respect to the ground
- d)C2 will move but C1 will be stationary with respect to the ground
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are some passengers inside a stationary railway compartment. The centre of masses of the compartment itself(without the passengers) is C1, while the centre of mass of the compartment plus passengers’ system is C2. if the passengers moves about inside the compartment
a)
both C1 and C2 will move with respect to the ground
b)
neither C1 nor C2 will move with respect to the ground
c)
C1 will move but C2 will be stationary with respect to the ground
d)
C2 will move but C1 will be stationary with respect to the ground
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
When net Fexternal=0, then the centre of mass of the system remains at rest.
Thus if the passenger move inside the compartment which donot require any external force, so the centre of mass of the "passenger + compartment" system must remain at rest and hence C2 will be fixed w.r.t ground.
Also due to the movement of the passenger, the position of centre of mass of the passengers only will change, thus C1 will have to move in such a way that C2 may remain fixed w.r.t ground.
A rigid body is one
- a)the sum of distances of all particles from the axis remains constant
- b)in which the distance between all pairs of particles remains fixed
- c)whose centre of mass follows a parabolic path
- d)that deforms and comes back to its original shape after getting deformed
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A rigid body is one
a)
the sum of distances of all particles from the axis remains constant
b)
in which the distance between all pairs of particles remains fixed
c)
whose centre of mass follows a parabolic path
d)
that deforms and comes back to its original shape after getting deformed
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
A body is said to be a rigid body if the body remains in its original shape even under the influence of external force. We can also say that if distance between two points of the body does not change with time regardless of external forces exerted on it, then the body is said to be a rigid body.
If three balls of same radius are placed touching each other on a horizontal surface such that they will form an equilateral triangle, when their centers are joined. What will be the position of the centre of mass of the system?- a)At the point of intersection of the medians.
- b)At the line joining the centers of any two balls.
- c)At the centre of one of the ball.
- d)At the horizontal surface.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If three balls of same radius are placed touching each other on a horizontal surface such that they will form an equilateral triangle, when their centers are joined. What will be the position of the centre of mass of the system?
a)
At the point of intersection of the medians.
b)
At the line joining the centers of any two balls.
c)
At the centre of one of the ball.
d)
At the horizontal surface.
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The COM will be at the intersection point of the medians as that is the most symmetric point of this symmetric system.
When a shell was following a parabolic path in the air, it explodes somewhere in its flight. The centre of mass of fragments will continue to move in- a)any direction
- b)horizontal direction
- c)same parabolic path
- d)vertical direction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When a shell was following a parabolic path in the air, it explodes somewhere in its flight. The centre of mass of fragments will continue to move in
a)
any direction
b)
horizontal direction
c)
same parabolic path
d)
vertical direction
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The internal forces have no effect on the trajectory of the center of mass, and the forces due to explosion are the internal forces. So the center of mass will follow the same parabolic path even after the explosion.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:An isolated particle of mass m is moving in a horizontal plane (x,y) along the x axis at a certain height above the ground. It suddenly explodes into two fragments of masses m/4 and 3m/4. An instant later, the smaller fragments is at y = +15 cm. The larger fragment at this instant is at
- A:
y = +5 cm
- B:
y = +20 cm
- C:
y = -20 cm
- D:
y = -5 cm
The answer is d.
An isolated particle of mass m is moving in a horizontal plane (x,y) along the x axis at a certain height above the ground. It suddenly explodes into two fragments of masses m/4 and 3m/4. An instant later, the smaller fragments is at y = +15 cm. The larger fragment at this instant is at
y = +5 cm
y = +20 cm
y = -20 cm
y = -5 cm

|
Ambition Institute answered |
As the particle is exploded only due to its internal energy.
⇒ net external force during this process is 0 i.e. center mass will not change.
⇒ net external force during this process is 0 i.e. center mass will not change.
Let the particle while the explosion was above the origin of the coordinate system i.e. just before explosion xcm =0 and ycm =0
After the explosion, the Centre of mass will be at xcm =0 and ycm =0
Since smaller fragment has fallen on the y-axis.
Let positon of larger fragment be y.
Let positon of larger fragment be y.
m * ycm = (m/4 * 15) + (3m/4 * y)
⇒ (m/4 * 15) + (3m/4 * y) = 0
⇒ y = - 5 cm
⇒ (m/4 * 15) + (3m/4 * y) = 0
⇒ y = - 5 cm
If the net force acting on the system of particles is zero, then which of the following may vary
- a)moment of inertia
- b)Kinetic energy of the system
- c)velocity of centre of mass
- d)position of centre of mass
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the net force acting on the system of particles is zero, then which of the following may vary
a)
moment of inertia
b)
Kinetic energy of the system
c)
velocity of centre of mass
d)
position of centre of mass
|
|
Suresh Kumar answered |
Correct answer is B . because when a=0 then v=constant hence K.E. will be constant and position of com will vary
A child sits stationary at one end of long trolley moving uniformly with speed v on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in the forward direction with speed u. The centre of mass of the system (child + trolley) will move with speed- a)v
- b)zero
- c)u + v
- d)v/u
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A child sits stationary at one end of long trolley moving uniformly with speed v on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in the forward direction with speed u. The centre of mass of the system (child + trolley) will move with speed
a)
v
b)
zero
c)
u + v
d)
v/u
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The child is running arbitrarily on a trolley moving with velocity v. However, the running of the child will produce no effect on the velocity of the centre of mass of the trolley. This is because the force due to the boy’s motion is purely internal. Internal forces produce no effect on the motion of the bodies on which they act. Since no external force is involved in the boy–trolley system, the boy’s motion will produce no change in the velocity of the centre of mass of the trolley.
Three identical spheres each of radius R are placed such that their centres lie on a straight line. What is the location of their centre of mass from the centre of the first sphere?
- a)R
- b)2R
- c)3R
- d)4R
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Three identical spheres each of radius R are placed such that their centres lie on a straight line. What is the location of their centre of mass from the centre of the first sphere?
a)
R
b)
2R
c)
3R
d)
4R
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Distance between first and last sphere = R + 2R + R = 4R
- Since the spheres are identical and lie in a straight line, the centre of mass will lie exactly in the middle.
- Hence the centre of mass lies at a distance of 2R from the centre of the first sphere.
In which of the following molecules the central atomdoes not retain any lone pair of electrons?- a)NO2
- b)NH3
- c)BF3
- d)H2O
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following molecules the central atomdoes not retain any lone pair of electrons?
a)
NO2
b)
NH3
c)
BF3
d)
H2O
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
In all other molecules, N and O retain lone pair
of electrons.
of electrons.
The sum of moments of masses of all the particles in a system about the centre of mass is always:- a)maximum
- b)infinite
- c)zero
- d)minimum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The sum of moments of masses of all the particles in a system about the centre of mass is always:
a)
maximum
b)
infinite
c)
zero
d)
minimum
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero, or the point where if a force is applied it moves in the direction of the force without rotating. The distribution of mass is balanced around the center of mass and the average of the weighted position coordinates of the distributed mass defines its coordinates. Calculations in mechanics are often simplified when formulated with respect to the center of mass.
Every point in a rotating rigid body has the same __________at any instant of time.
- a)linear velocity
- b)angular velocity
- c)displacement
- d)linear momentum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Every point in a rotating rigid body has the same __________at any instant of time.
a)
linear velocity
b)
angular velocity
c)
displacement
d)
linear momentum
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Every point in any rigid rotating object is rotating at the same angular velocity. However, there are a few cases where people have used the term "angular velocity" when they really meant tangential velocity, so you do have to be careful.
The general motion of a rigid body consists of
- a)translational motion only
- b)rotational motion only
- c)both, translational and rotational motion
- d)does not include translational and rotational motions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The general motion of a rigid body consists of
a)
translational motion only
b)
rotational motion only
c)
both, translational and rotational motion
d)
does not include translational and rotational motions
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
The general motion of a rigid body consists of both, translational and rotational motion. This is much obvious as it is seen all around us.
What is common between the following moleculesSO3, CO2-3, No-3- a)All have linear shape
- b)All have trigonal planar shape
- c)All have tetrahedral shape
- d)All have trigonal pyramidal shape
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is common between the following molecules
SO3, CO2-3, No-3
a)
All have linear shape
b)
All have trigonal planar shape
c)
All have tetrahedral shape
d)
All have trigonal pyramidal shape
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
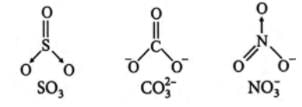
All the moleculeshave trigonal planar structure.
In a bonded molecule, the order of repulsion between the bonded and non-bonded electrons is- a)lone pair - lone pair > bond pair - bond pair > lone pair - bond pair
- b)bond pair-bond pair > lone pair - lone pair > lone pair - bond pair
- c)lone pair - lone pair > lone pair - bond pair > bond pair - bond pair
- d)bond pair- bond pair > lone pair - bond pair > lone pair - lone pair
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a bonded molecule, the order of repulsion between the bonded and non-bonded electrons is
a)
lone pair - lone pair > bond pair - bond pair > lone pair - bond pair
b)
bond pair-bond pair > lone pair - lone pair > lone pair - bond pair
c)
lone pair - lone pair > lone pair - bond pair > bond pair - bond pair
d)
bond pair- bond pair > lone pair - bond pair > lone pair - lone pair
|
|
Keerthana Saha answered |
The order of repulsion between the bonded and non-bonded electrons in a bonded molecule is as follows:
1) Lone pair - Lone pair repulsion: This is the strongest repulsion because both electrons are in close proximity to each other and are not involved in bonding. This repulsion affects the molecular geometry and determines the shape of the molecule.
2) Lone pair - Bonded pair repulsion: This repulsion is weaker than lone pair - lone pair repulsion but still significant. It occurs between a lone pair of electrons and a pair of electrons involved in a bond.
3) Bonded pair - Bonded pair repulsion: This is the weakest repulsion because the bonded electrons are already involved in a covalent bond and have a certain level of sharing. However, there is still some repulsion between the electron pairs due to their negative charge.
Overall, the order of repulsion from strongest to weakest is: Lone pair - Lone pair > Lone pair - Bonded pair > Bonded pair - Bonded pair.
1) Lone pair - Lone pair repulsion: This is the strongest repulsion because both electrons are in close proximity to each other and are not involved in bonding. This repulsion affects the molecular geometry and determines the shape of the molecule.
2) Lone pair - Bonded pair repulsion: This repulsion is weaker than lone pair - lone pair repulsion but still significant. It occurs between a lone pair of electrons and a pair of electrons involved in a bond.
3) Bonded pair - Bonded pair repulsion: This is the weakest repulsion because the bonded electrons are already involved in a covalent bond and have a certain level of sharing. However, there is still some repulsion between the electron pairs due to their negative charge.
Overall, the order of repulsion from strongest to weakest is: Lone pair - Lone pair > Lone pair - Bonded pair > Bonded pair - Bonded pair.
The most stable shape of ClF3 is shown by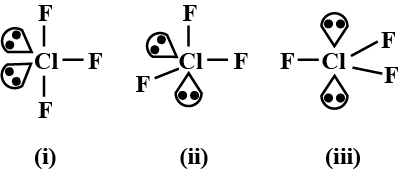
- a)(i) only
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(ii) only
- d)(iii) only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The most stable shape of ClF3 is shown by
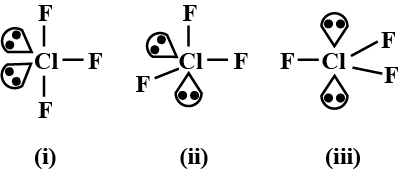
a)
(i) only
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(ii) only
d)
(iii) only
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In (i), the Ip are atequatorial position so there are less Ip - bp repulsions as compared to other positions.
Hence, T-shape is moststable.
Masses 1 kg, 1.5 kg, 2 kg, and “M” kg are situated at (2,1,1), (1,2,1), (2,-2,1) and (-1,4,3). What is the value of “M” if their centre of mass is at (1,1,3/2)?- a)1 kg
- b)1.5 kg
- c)2 kg
- d)2.5 kg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Masses 1 kg, 1.5 kg, 2 kg, and “M” kg are situated at (2,1,1), (1,2,1), (2,-2,1) and (-1,4,3). What is the value of “M” if their centre of mass is at (1,1,3/2)?
a)
1 kg
b)
1.5 kg
c)
2 kg
d)
2.5 kg
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
Sum of masses = 1 + 1.5 + 2 + M = 4.5 + M
x-coordinate;
(1*2 + 1.5*1 + 2*2 – M)/(4.5 + M) = 1
4.5 + M = 7.5 – M
2M = 3
M = 1.5 kg.
x-coordinate;
(1*2 + 1.5*1 + 2*2 – M)/(4.5 + M) = 1
4.5 + M = 7.5 – M
2M = 3
M = 1.5 kg.
For an object with the centre of mass at the origin, the x-coordinates of particles of the object _____.
- a)maybe all positive.
- b)maybe all negative.
- c)maybe all non-negative.
- d)cannot be predicted.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For an object with the centre of mass at the origin, the x-coordinates of particles of the object _____.
a)
maybe all positive.
b)
maybe all negative.
c)
maybe all non-negative.
d)
cannot be predicted.
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
- For an object to have the x-coordinate of its centre of mass, there should be particles on both the negative and positive coordinates of the plane for the sum to be zero.
- However, for 1-dimensional particles that all lie on the y-axis symmetric about the x-axis, the x-coordinate is zero – which is neither positive nor negative, i.e., non-negative.
Assertion (A): Frogs are poikilothermic animals.
Reason (R): They maintain a constant body temperature irrespective of the environment.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)Both A and R are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Reason (R): They maintain a constant body temperature irrespective of the environment.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
Both A and R are false
|
|
Nitya Bose answered |
Assertion (A): Frogs are poikilothermic animals.
Frogs, belonging to the class Amphibia, are indeed considered poikilothermic, which means they do not have a constant body temperature. Their body temperature varies with the temperature of their environment. This adaptation allows them to thrive in various habitats, but it also makes them susceptible to environmental changes.
Reason (R): They maintain a constant body temperature irrespective of the environment.
This statement is false. Frogs do not maintain a constant body temperature. Instead, their body temperature fluctuates according to external temperatures, which is characteristic of poikilothermic organisms. They rely on behavioral adaptations, such as basking in the sun or seeking shade, to regulate their body temperature.
Conclusion: Explanation of the Correct Option
The correct answer is option C: "A is true but R is false." Here’s why:
- Frogs as Poikilothermic Animals:
- They are classified as poikilothermic because their body temperature is influenced by environmental conditions.
- Inaccuracy of the Reason:
- The assertion that frogs maintain a constant body temperature is incorrect, as it contradicts the nature of poikilothermic animals.
In summary, while the assertion about frogs being poikilothermic is true, the reason that they maintain a constant body temperature is false. Therefore, the answer is option C.
Frogs, belonging to the class Amphibia, are indeed considered poikilothermic, which means they do not have a constant body temperature. Their body temperature varies with the temperature of their environment. This adaptation allows them to thrive in various habitats, but it also makes them susceptible to environmental changes.
Reason (R): They maintain a constant body temperature irrespective of the environment.
This statement is false. Frogs do not maintain a constant body temperature. Instead, their body temperature fluctuates according to external temperatures, which is characteristic of poikilothermic organisms. They rely on behavioral adaptations, such as basking in the sun or seeking shade, to regulate their body temperature.
Conclusion: Explanation of the Correct Option
The correct answer is option C: "A is true but R is false." Here’s why:
- Frogs as Poikilothermic Animals:
- They are classified as poikilothermic because their body temperature is influenced by environmental conditions.
- Inaccuracy of the Reason:
- The assertion that frogs maintain a constant body temperature is incorrect, as it contradicts the nature of poikilothermic animals.
In summary, while the assertion about frogs being poikilothermic is true, the reason that they maintain a constant body temperature is false. Therefore, the answer is option C.
Identify correct statements about frog’s reproductive system:
a) Fertilisation is external.
b) A female lays 250–300 ova at a time.
c) Tadpole stage is present in life cycle.
d) Oviducts in females open into cloaca.- a)a, c, d correct
- b)a, b correct
- c)a, c correct
- d)a, c, d correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a) Fertilisation is external.
b) A female lays 250–300 ova at a time.
c) Tadpole stage is present in life cycle.
d) Oviducts in females open into cloaca.
a)
a, c, d correct
b)
a, b correct
c)
a, c correct
d)
a, c, d correct

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Female lays 2500–3000 ova, not 250–300. Fertilisation is external, tadpole stage occurs, and oviducts open into cloaca.
Select the correct route for the passage of sperms in male frogs:- a)Testes → Vasa efferentia → Kidney → Seminal Vesicle → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca
- b)Testes → Vasa efferentia → Bidder's canal → Ureter → Cloaca
- c)Testes → Vasa efferentia → Kidney → Bidder's canal → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca
- d)Testes → Bidder's canal → Kidney → Vasa efferentia → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Testes → Vasa efferentia → Kidney → Seminal Vesicle → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca
b)
Testes → Vasa efferentia → Bidder's canal → Ureter → Cloaca
c)
Testes → Vasa efferentia → Kidney → Bidder's canal → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca
d)
Testes → Bidder's canal → Kidney → Vasa efferentia → Urinogenital duct → Cloaca

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Sperms are produced in the testes, carried by vasa efferentia into the kidney, then enter Bidder’s canal, pass through the urinogenital duct, and finally exit through the cloaca.
According to VSEPR theory- a)The shape of the molecule depends upon the bonded electron pairs
- b)Pair of electrons attract each other in valence shells
- c)The pairs of electrons tend to occupy such positions that minimise repulsions
- d)The pairs of electrons tend to occupy such positions that mimimise distances from each other
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to VSEPR theory
a)
The shape of the molecule depends upon the bonded electron pairs
b)
Pair of electrons attract each other in valence shells
c)
The pairs of electrons tend to occupy such positions that minimise repulsions
d)
The pairs of electrons tend to occupy such positions that mimimise distances from each other
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The pairs of electrons tend to occupy such positions that place them farthest from each other and minimise repulsions.
The BCI3 is a planar molecule whereas NCI3 is pyramidal, because- a)B-Cl bond is more polar than N-Cl bond
- b)N-Cl bond is more covalent than B-Cl bond
- c)Nitrogen atom is smaller than boron atoms
- d)BCI3 has no lone pair but NCI3 has a lone pairofelectrons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The BCI3 is a planar molecule whereas NCI3 is pyramidal, because
a)
B-Cl bond is more polar than N-Cl bond
b)
N-Cl bond is more covalent than B-Cl bond
c)
Nitrogen atom is smaller than boron atoms
d)
BCI3 has no lone pair but NCI3 has a lone pairofelectrons
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
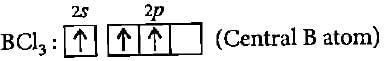
No lone pair ofelectrons is available in BCI3
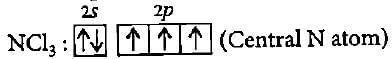
One lone pair of electrons is available on N atom, occupies a corner in the tetrahedral arrangement. Therefore, NCI3 appears pyramidal in shape.
Few examples of the compounds formed by chemical bonding are given below. Mark the incorrect example.- a)A molecule with central atom devoid of octet - BF3
- b)A molecule with linear shape - CO2
- c)A non-polar covalent compound between two different atoms - CH4
- d)A molecule which is V-shaped with a bond angle 104.50 - NH3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Few examples of the compounds formed by chemical bonding are given below. Mark the incorrect example.
a)
A molecule with central atom devoid of octet - BF3
b)
A molecule with linear shape - CO2
c)
A non-polar covalent compound between two different atoms - CH4
d)
A molecule which is V-shaped with a bond angle 104.50 - NH3
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The correct example is H2O. NH3 is pyramidal and bond angle is 104.50.
The shape of water molecule which should be tetrahedral has a bent or distorted tetrahedral shape with a bond angle 104.5°. What could be the reason for this?- a)Ip-lp repulsion is more than Ip-bp repulsion
- b)Ip-bp repulsion is more than Ip-lp repulsion
- c)Ip-lp repulsionis equal to Ip-bp repulsion
- d)Presence of lone pair does not affect the bond angle
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The shape of water molecule which should be tetrahedral has a bent or distorted tetrahedral shape with a bond angle 104.5°. What could be the reason for this?
a)
Ip-lp repulsion is more than Ip-bp repulsion
b)
Ip-bp repulsion is more than Ip-lp repulsion
c)
Ip-lp repulsionis equal to Ip-bp repulsion
d)
Presence of lone pair does not affect the bond angle
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Due to presence of lone pairs, the repulsion is more which changes the bond angle to 104.5°.

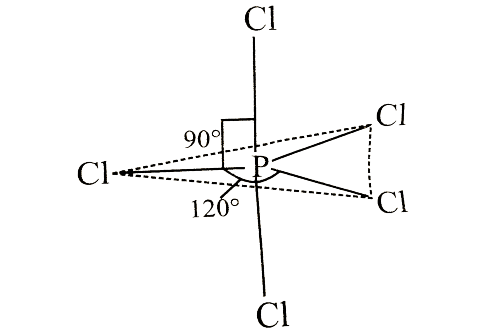
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the structure of PCI5?- a)Three P—Cl bonds lie in one plane and two P—Cl bonds lie above and below the equatorial plane
- b)Five P—Cl bonds lie in the same plane
- c)The bond angle in all P—Cl bonds is 90°
- d)The bond length of all P—Cl bonds is same
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the structure of PCI5?
a)
Three P—Cl bonds lie in one plane and two P—Cl bonds lie above and below the equatorial plane
b)
Five P—Cl bonds lie in the same plane
c)
The bond angle in all P—Cl bonds is 90°
d)
The bond length of all P—Cl bonds is same
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In PCI5, three axial and two equatorial bonds are present.
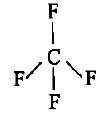
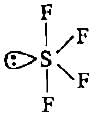
CF4, SF4 and XeF4 contain the following electronicstructure on their central atoms. Which one iscorrect option?- a)1, 2 and 3 lone pairs of electrons respectively
- b)0,1 and 2 lone pairs of electrons respectively
- c)1,1 and 1 lone pairs of electrons respectively
- d)No lone pairs ofelectrons on any molecule
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
CF4, SF4 and XeF4 contain the following electronicstructure on their central atoms. Which one iscorrect option?
a)
1, 2 and 3 lone pairs of electrons respectively
b)
0,1 and 2 lone pairs of electrons respectively
c)
1,1 and 1 lone pairs of electrons respectively
d)
No lone pairs ofelectrons on any molecule
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
CF4−sp3 , tetrahedral but no unpaired electron.
SF4−sp3d, trigonal bipyramidal with one unpaired electron.
XeF4−sp3d2, square planar, two lone pairs of electrons.
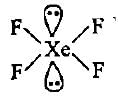
Which of the following does not show octahedral geometry?- a)SF`
- b)IF5
- c)SiF62-
Correct answer is option ''. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not show octahedral geometry?
a)
SF`
b)
IF5
c)
SiF62-
|
|
Aashna Rane answered |
Explanation:
An octahedral geometry refers to a molecular shape in which there are six atoms or groups of atoms arranged symmetrically around a central atom. The central atom is surrounded by six electron pairs, which are located at the corners of an octahedron.
In the given options, we need to identify the molecule that does not possess an octahedral geometry.
a) SF6:
In SF6, the central sulfur atom is bonded to six fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom contributes one electron to form a covalent bond with sulfur. The sulfur atom also has one lone pair of electrons. The molecule has an octahedral geometry with the sulfur atom at the center and the six fluorine atoms and lone pair of electrons occupying the corners of the octahedron.
b) IF5:
In IF5, the central iodine atom is bonded to five fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom contributes one electron to form a covalent bond with iodine. The iodine atom also has two lone pairs of electrons. The molecule has a square pyramidal geometry with the iodine atom at the center and the five fluorine atoms and two lone pairs of electrons occupying the corners of the square pyramid.
c) SiF62-
In SiF62-, the central silicon atom is bonded to six fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom contributes one electron to form a covalent bond with silicon. The silicon atom also has no lone pairs of electrons. The molecule has an octahedral geometry with the silicon atom at the center and the six fluorine atoms occupying the corners of the octahedron.
Based on the above explanations, it can be concluded that the molecule does not show octahedral geometry is IF5 (option b).
An octahedral geometry refers to a molecular shape in which there are six atoms or groups of atoms arranged symmetrically around a central atom. The central atom is surrounded by six electron pairs, which are located at the corners of an octahedron.
In the given options, we need to identify the molecule that does not possess an octahedral geometry.
a) SF6:
In SF6, the central sulfur atom is bonded to six fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom contributes one electron to form a covalent bond with sulfur. The sulfur atom also has one lone pair of electrons. The molecule has an octahedral geometry with the sulfur atom at the center and the six fluorine atoms and lone pair of electrons occupying the corners of the octahedron.
b) IF5:
In IF5, the central iodine atom is bonded to five fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom contributes one electron to form a covalent bond with iodine. The iodine atom also has two lone pairs of electrons. The molecule has a square pyramidal geometry with the iodine atom at the center and the five fluorine atoms and two lone pairs of electrons occupying the corners of the square pyramid.
c) SiF62-
In SiF62-, the central silicon atom is bonded to six fluorine atoms. Each fluorine atom contributes one electron to form a covalent bond with silicon. The silicon atom also has no lone pairs of electrons. The molecule has an octahedral geometry with the silicon atom at the center and the six fluorine atoms occupying the corners of the octahedron.
Based on the above explanations, it can be concluded that the molecule does not show octahedral geometry is IF5 (option b).
The centre of masses of two particles with masses 2 kg and 1 kg located at (1,0,1) and (2,2,0) is located at:- a)4/3, 2/3, 2/3
- b)2/3, 4/3, 2/3
- c)2/3, 2/3, 4/3
- d)1/3, 2/3, 2/3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The centre of masses of two particles with masses 2 kg and 1 kg located at (1,0,1) and (2,2,0) is located at:
a)
4/3, 2/3, 2/3
b)
2/3, 4/3, 2/3
c)
2/3, 2/3, 4/3
d)
1/3, 2/3, 2/3
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
Sum of masses = 2 + 1 = 3
x-coordinate;
(2*1 + 1*2)/3 = 4/3
y-coordinate;
(2*0 + 1*2)/3 = 2/3
z-coordinate;
(2*1 + 1*0)/3 = 2/3.
x-coordinate;
(2*1 + 1*2)/3 = 4/3
y-coordinate;
(2*0 + 1*2)/3 = 2/3
z-coordinate;
(2*1 + 1*0)/3 = 2/3.
Which of the following best describes the respiration in frog during hibernation?- a)Only pulmonary respiration
- b)Only cutaneous respiration
- c)Both pulmonary and buccal respiration
- d)Only buccopharyngeal respiration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Only pulmonary respiration
b)
Only cutaneous respiration
c)
Both pulmonary and buccal respiration
d)
Only buccopharyngeal respiration

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
During aestivation and hibernation, gaseous exchange takes place mainly through skin (cutaneous respiration).
For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body?- a)Pen
- b)Dice
- c)Rectangular tile
- d)Bangle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body?
a)
Pen
b)
Dice
c)
Rectangular tile
d)
Bangle
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
- The centre of mass of a bangle lies at its geometric centre which does not lie on or in the object.
- Hence the centre of mass of a bangle lies outside the body.
Which molecule is depicted by the given ball and stick models?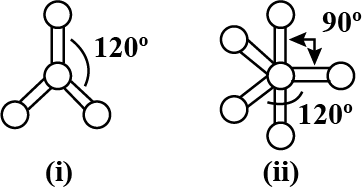
- a)(i) BeCl2, (ii)CH4
- b)(i) BF3, (ii) PCl5
- c)(i) BF4, (ii) CH4
- d)(i) BeCl2, (ii) PCl5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which molecule is depicted by the given ball and stick models?

a)
(i) BeCl2, (ii)CH4
b)
(i) BF3, (ii) PCl5
c)
(i) BF4, (ii) CH4
d)
(i) BeCl2, (ii) PCl5
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
BF3 - Trigonal planar with bond angle 120º.
PCI5 - Trigonal bipyramidal with bond angles 120º and 90º.
PCI5 - Trigonal bipyramidal with bond angles 120º and 90º.
Consider the following statements:
a) Frog’s RBCs are nucleated.
b) Frogs respire only through lungs.
c) Sinus venosus joins the right atrium in frog’s heart.
d) Male frog has vocal sacs.
Choose the correct option:- a)a, b correct
- b)a, c, d correct
- c)b, c correct
- d)a, b, d correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a) Frog’s RBCs are nucleated.
b) Frogs respire only through lungs.
c) Sinus venosus joins the right atrium in frog’s heart.
d) Male frog has vocal sacs.
Choose the correct option:
a)
a, b correct
b)
a, c, d correct
c)
b, c correct
d)
a, b, d correct

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
RBCs are nucleated, sinus venosus connects to right atrium, and male frogs have vocal sacs. Respiration is through skin, buccal cavity, and lungs (not only lungs).
Match the molecules given in column I with their shapes given in column II and mark the appropriate choice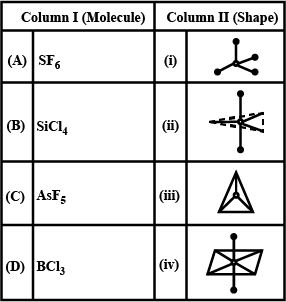
- a)(A)→(iv),(B)→(ii),(C)→(iii),(D)→(i)
- b)(A)→(iv),(B)→(i),(C)→(ii),(D)→(iii)
- c)(A)→(iii),(B)→(i),(C)→(ii),(D)→(iv)
- d)(A)→(ii),(B)→(iii),(C)→(i),(D)→(iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the molecules given in column I with their shapes given in column II and mark the appropriate choice

a)
(A)→(iv),(B)→(ii),(C)→(iii),(D)→(i)
b)
(A)→(iv),(B)→(i),(C)→(ii),(D)→(iii)
c)
(A)→(iii),(B)→(i),(C)→(ii),(D)→(iv)
d)
(A)→(ii),(B)→(iii),(C)→(i),(D)→(iv)
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
(A) SF6 − Octahedral
(B) SiCl4 − Tetrahedral
(C) AsF5 − Trigonal bipyramidal
(D) BCl3− Trigonal planar
Which of the following shapes of SF4 is more stable and why?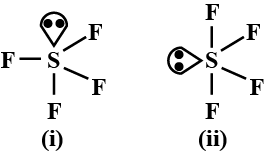
- a)(i), due to 3 Ip-bp repulsions at 90°
- b)(ii), due to 2 Ip-bp repulsions
- c)Both are equally stable due to 2 Ip-bp repulsions
- d)Both are unstable since SF4 has tetrahedral shape
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following shapes of SF4 is more stable and why?
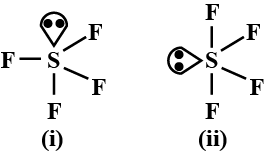
a)
(i), due to 3 Ip-bp repulsions at 90°
b)
(ii), due to 2 Ip-bp repulsions
c)
Both are equally stable due to 2 Ip-bp repulsions
d)
Both are unstable since SF4 has tetrahedral shape
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In structure (ii), Ip-bp repulsions are minimum.
Chapter doubts & questions for July Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of July Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










